|
Dominique Vandamme
General Dominique-Joseph René Vandamme, Count of Unseburg (5 November 1770, Cassel, Nord15 July 1830) was a French military officer, who fought in the Napoleonic Wars. He was a dedicated career soldier with a reputation as an excellent division and corps commander. However he had a nasty disposition that alienated his colleagues, and would publicly criticize Napoleon, who never appointed him marshal. Biography Vandamme enlisted in the army in 1786 and rapidly rose through the ranks. At the outbreak of the French Revolutionary Wars in 1793 he was a Brigadier General. He served in this rank in the campaigns of 1794 in the Low Countries, 1795 on the Rhine and 1796 in Germany. He was court-martialled for looting and suspended. Reinstated, he fought at the First Battle of Stockach on 25 March 1799, but disagreement with General Jean Moreau led to his being sent to occupation duties in Holland. At the Battle of Austerlitz in 1805 he led his division, alongside Gen. St. Hilaire's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassel, Nord
Cassel (; nl, Kassel) is a commune in the Nord départment in northern France. Built on a prominent hill overlooking French Flanders, the town has existed since Roman times. It was developed by the Romans into an important urban centre and was the focus of a network of roads, which are still in use today, that converge on the hill. After the fall of the Roman Empire, Cassel became an important fortified stronghold for the rulers of Flanders which was repeatedly fought over before finally being annexed to France in the 17th century. It was the headquarters of Marshal Ferdinand Foch during part of the First World War. In 1940, during the German invasion of France, Cassel was the scene of a fierce three-day battle between British forces (led in part by Major Ronald Cartland, MP) and German forces which resulted in much of the town being destroyed. The town, which was rebuilt following the war, is a popular destination for visitors to French Flanders. It is renowned for its extensiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Austerlitz
The Battle of Austerlitz (2 December 1805/11 Frimaire An XIV FRC), also known as the Battle of the Three Emperors, was one of the most important and decisive engagements of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle occurred near the town of Austerlitz in the Austrian Empire (modern-day Slavkov u Brna in the Czech Republic). The decisive victory of Napoleon's Grande Armée at Austerlitz brought the War of the Third Coalition to a rapid end, with the Treaty of Pressburg signed by the Austrians later in the month. The battle is often cited as a tactical masterpiece, in the same league as other historic engagements like Cannae or Gaugamela.Farwell p. 64. "Austerlitz is generally regarded as one of Napoleon's tactical masterpieces and has been ranked as the equal of Arbela, Cannae, and Leuthen."Dupuy p. 102 After eliminating an Austrian army during the Ulm Campaign, French forces seized Vienna in November 1805. The Austrians avoided further conflict until the arrival of the Russians bols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Graf Kleist Von Nollendorf
Friedrich Emil Ferdinand Heinrich Graf Kleist von Nollendorf (9 April 1762 – 17 February 1823), born and died in Berlin, was a Prussian field marshal and a member of the old ' family von Kleist. Biography Kleist entered the Prussian Army in 1778 and served in the War of the Bavarian Succession and the French Revolutionary Wars. By 1799, Kleist had been promoted to major and was put in command of a battalion of grenadiers. Kleist served in the Napoleonic Wars and fought at Jena. In 1807 he went on extended leave but by 1808 he was put in command of an infantry brigade and the next year he was made commandant of Berlin. During the War of Liberation he was given a corps with which he fought in the battles of Kulm and Leipzig. In 1814, he was given the title Count of Nollendorf (from the German name of the town Nakléřov, now part of Petrovice in the Czech Republic) for his decisive role in this battle. After Leipzig, Kleist blockaded the fortress of Erfurt, bringing about i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
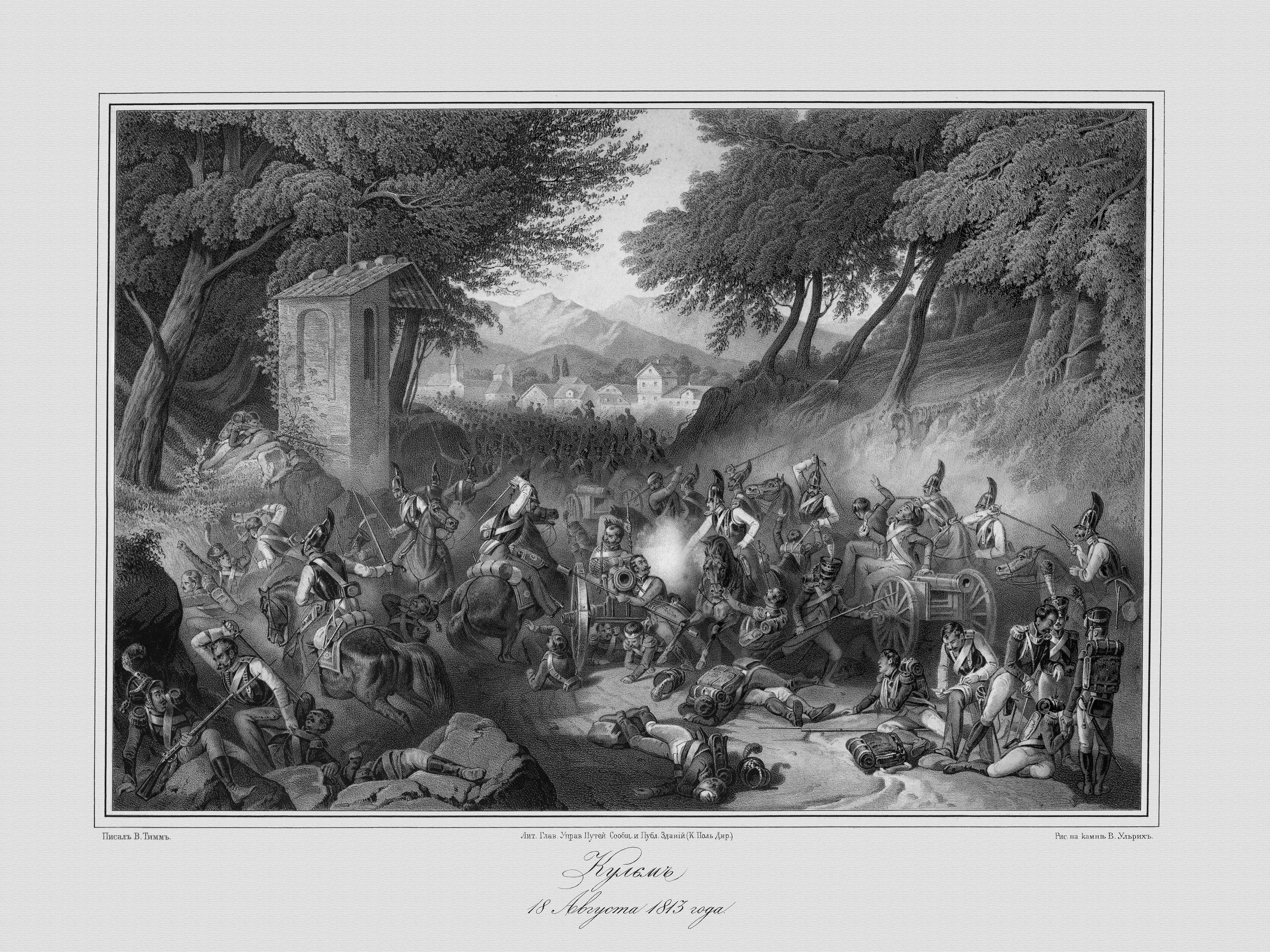
Battle Of Kulm
:''See Battle of Chlumec for the 1126 battle at Kulm The Battle of Kulm was fought near the town Kulm () and the village Přestanov in northern Bohemia. It was fought on 29–30 August 1813, during the War of the Sixth Coalition. A French Corps under General Dominique Vandamme attacked Alexander Ostermann-Tolstoy's Russian Corps on 29 August. The next day, Friedrich von Kleist's Prussian Corps hit Vandamme in the rear while Russian and Austrian reinforcements attacked the French front and left. Vandamme was defeated with the loss of 13,000 men and 82 guns. Background Following the French victory at Dresden, Vandamme pursued the retreating allies. Napoleon sent Marshals Gouvion Saint Cyr and Auguste Marmont to support Vandamme's corps. With Vandamme in advance, Saint Cyr's and Marmont's corps brought up the rear. Vandamme caught up with Alexander Ivanovich Ostermann-Tolstoy's forces near the town of Kulm, eight kilometres northwest of Aussig ( Ústí nad Labem, now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dresden
The Battle of Dresden (26–27 August 1813) was a major engagement of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle took place around the city of Dresden in modern-day Germany. With the recent addition of Austria, the Sixth Coalition felt emboldened in their quest to expel the French from Central Europe. Despite being heavily outnumbered, French forces under Napoleon scored a victory against the Army of Bohemia led by Generalissimo Karl von Schwarzenberg. However, Napoleon's victory did not lead to the collapse of the coalition, and the weather and the uncommitted Russian reserves who formed an effective rear-guard precluded a major pursuit. Three days after the battle, the Allies surrounded and destroyed a French corps advancing into their line of withdrawal at the Battle of Kulm. Prelude On the 16 August, Napoleon had sent Marshal Saint-Cyr's corps to fortify and hold Dresden in order to hinder allied movements and to serve as a possible base for his own manoeuvres. He planned to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanguard
The vanguard (also called the advance guard) is the leading part of an advancing military formation. It has a number of functions, including seeking out the enemy and securing ground in advance of the main force. History The vanguard derives from the traditional division of a medieval army into three '' battles'' or ''wards''; the Van, the Main (or Middle), and the Rear. The term originated from the medieval French ''avant-garde'', i.e. "the advance guard". The vanguard would lead the line of march and would deploy first on the field of battle, either in front of the other wards or to the right if they deployed in line. The makeup of the vanguard of a 15th century Burgundian army is a typical example. This consisted of *A contingent of foreriders, from whom a forward detachment of scouts was drawn; *The main body of the vanguard, accompanied by civil officials and trumpeters to carry messages and summon enemy towns and castles to surrender; and *A body of workmen under th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Looting
Looting is the act of stealing, or the taking of goods by force, typically in the midst of a military, political, or other social crisis, such as war, natural disasters (where law and civil enforcement are temporarily ineffective), or rioting. The proceeds of all these activities can be described as booty, loot, plunder, spoils, or pillage. During modern-day armed conflicts, looting is prohibited by international law, and constitutes a war crime.Rule 52. Pillage is prohibited. ''Customary IHL Database'', (ICRC)/ |
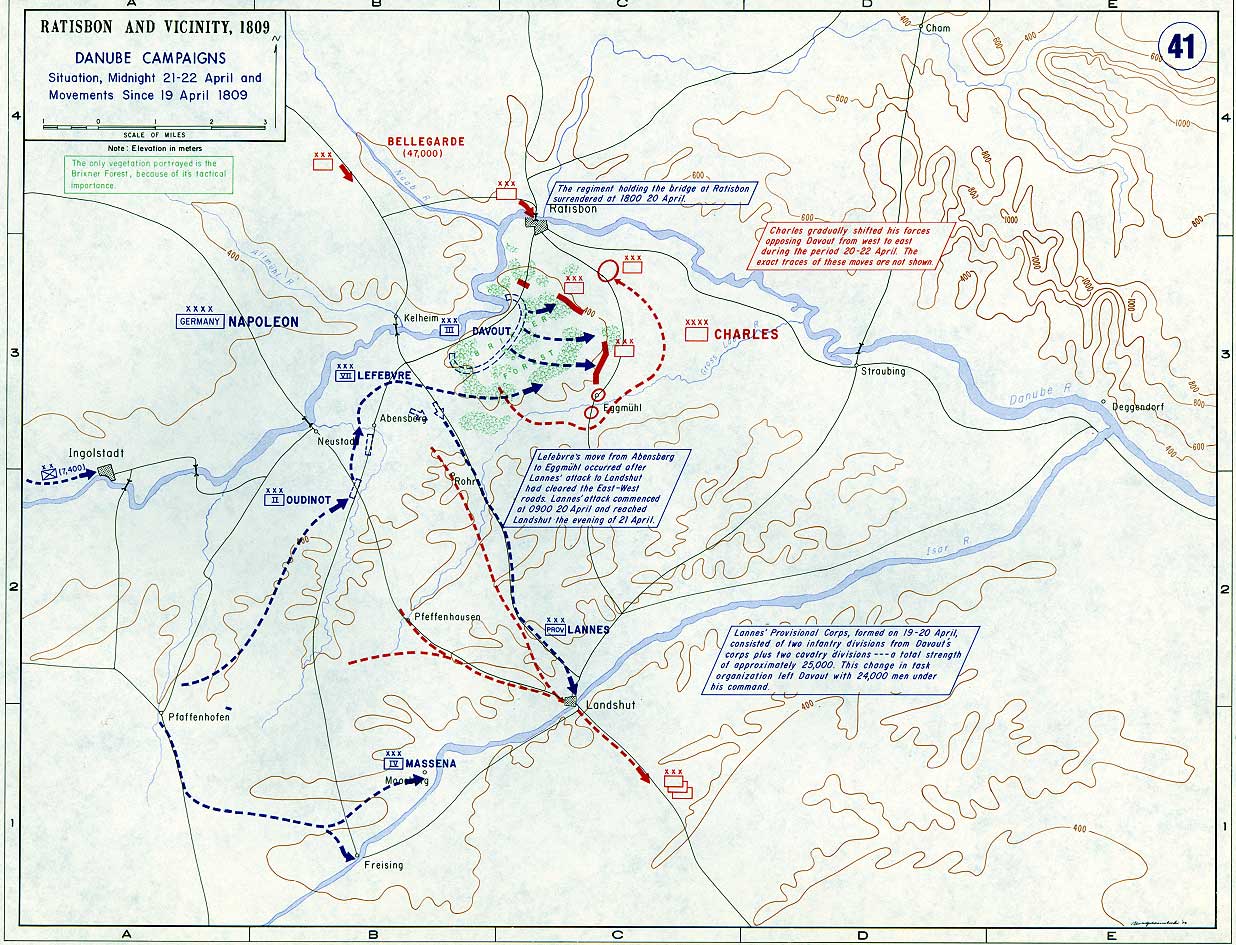
Battle Of Eckmühl
The Battle of Eckmühl, fought on 22 April 1809, was the turning point of the 1809 Campaign, also known as the War of the Fifth Coalition. Napoleon I had been unprepared for the start of hostilities on 10 April 1809, by the Austrians under the Archduke Charles of Austria and for the first time since assuming the French Imperial Crown had been forced to give up the strategic initiative to an opponent. Thanks to the dogged defense waged by the III Corps, commanded by Marshal Davout, and the Bavarian VII Corps, commanded by Marshal Lefebvre, Napoleon was able to defeat the principal Austrian army and wrest the strategic initiative for the remainder of the war. Strategic situation Operating over a fifty-mile front, from Regensburg (Ratisbon to the French) to Pfaffenhofen, marked by stretches of rugged, wooded terrain, neither the French nor the Austrians had developed adequate intelligence about their opponent's strength, dispositions or intentions. Assuming that the bulk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Landshut (1809)
The Battle of Landshut took place on 21 April 1809 between the French, Württembergers (VIII Corps) and Bavarians (VII Corps) under Napoleon which numbered about 77,000 strong, and 36,000 Austrians under the General Johann von Hiller. The Austrians, though outnumbered, fought hard until Napoleon arrived, when the battle subsequently became a clear French victory. Prelude There were in fact two engagements at Landshut. The first occurred on 16 April when Hiller pushed a defending Bavarian division out of the town. Five days later, after the French victory at Abensberg, the left wing of the Austrian army (36,000 men) withdrew on Landshut (this force was once more led by Hiller). Napoleon believed that this was the main Austrian army and ordered Lannes to pursue the enemy. Lannes’s troops caught up with Hiller on the twenty-first. Hiller had decided to defend Landshut to allow his baggage train to withdraw. At Landshut the Isar river was spanned by two bridges with a small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Abensberg
The Battle of Abensberg took place on 20 April 1809 between a Franco-German force under the command of Emperor Napoleon I of France and a reinforced Austrian corps led by Feldmarschall-Leutnant Archduke Louis of Austria. As the day wore on, Feldmarschall-Leutnant Johann von Hiller arrived with reinforcements to take command of the three corps that formed the Austrian left wing. The action ended in a complete Franco-German victory. The battlefield was southeast of Abensberg and included clashes at Offenstetten, Biburg- Siegenburg, Rohr in Niederbayern, and Rottenburg an der Laaber. On the same day, the French garrison of Regensburg capitulated. After Marshal Louis-Nicolas Davout's hard-fought victory at Battle of Teugen-Hausen the previous day, Napoleon determined to break through the Austrian defenses behind the Abens River. The emperor assembled a provisional corps consisting of part of Davout's corps plus cavalry and gave Marshal Jean Lannes command over it. Napoleon d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart. Together with Baden and Hohenzollern, two other historical territories, Württemberg now forms the Federal State of Baden-Württemberg. Württemberg was formerly also spelled Würtemberg and Wirtemberg. History Originally part of the old Duchy of Swabia, its history can be summarized in the following periods: * County of Württemberg (1083–1495) * Duchy of Württemberg (1495–1803) * Electorate of Württemberg (1803–1806) * Kingdom of Württemberg (1806–1918) * Free People's State of Württemberg (1918–1945) After World War II, it was split into Württemberg-Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern due to the different occupation zones of the United States and France. Finally, in 1952, it was integrated into Baden-Württemberg Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Fourth Coalition
The Fourth Coalition fought against Napoleon's French Empire and were defeated in a war spanning 1806–1807. The main coalition partners were Prussia and Russia with Saxony, Sweden, and Great Britain also contributing. Excluding Prussia, some members of the coalition had previously been fighting France as part of the Third Coalition, and there was no intervening period of general peace. On 9 October 1806, Prussia declared war on France and joined a renewed coalition, fearing the rise in French power after the defeat of Austria and establishment of the French-sponsored Confederation of the Rhine in addition to having learned of French plans to cede Prussian-desired Hannover to Britain in exchange for peace. Prussia and Russia mobilized for a fresh campaign with Prussia massing troops in Saxony. Napoleon decisively defeated the Prussians in an expeditious campaign that culminated at the Battle of Jena–Auerstedt on 14 October 1806. French forces under Napoleon occupied P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)