|
Distributing Artery
A muscular artery (or distributing artery) is a medium-sized artery that draws blood from an elastic artery and branches into "resistance vessels" including small arteries and arterioles. Their walls contain larger number of smooth muscles, allowing them to contract and expand depending on peripheral blood demand. This contrasts to the mechanism of elastic arteries, which use their elastic properties to store the energy generated by the heart's contraction for a brief moment (elastic recoil). Examples of muscular arteries include the radial artery, femoral artery and the splenic artery. Muscular arteries, along with elastic arteries, are common sites for atherosclerosis. Structure The tunica intima of muscular arteries features a thin subendothelial layer and a prominent internal elastic lamina, while the media may contain up to 40 layers of large smooth muscle cells interspersed with a variable number of elastic lamellae, depending on the vessel size. Only the larger muscula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artery
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in the pulmonary circulation that carry blood to the lungs for oxygenation, and the umbilical arteries in the fetal circulation that carry deoxygenated blood to the placenta. It consists of a multi-layered artery wall wrapped into a tube-shaped channel. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry deoxygenated blood back towards the heart; or in the pulmonary and fetal circulations carry oxygenated blood to the lungs and fetus respectively. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic scale, macroscopic level, and histology, microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscope. The arterial system of the human body is divided into systemic circulation, systemic arteries, carrying blood from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastic Artery
An elastic artery (conducting artery or conduit artery) is an artery with many collagen and elastin filaments in the tunica media, which gives it the ability to stretch in response to each pulse. This elasticity also gives rise to the Windkessel effect, which helps to maintain a relatively constant pressure in the arteries despite the pulsating nature of the blood flow. Elastic arteries include the largest arteries in the body, those closest to the heart. They give rise to medium-sized vessels known as distributing arteries (or ''muscular arteries''). The pulmonary arteries, the aorta, and its branches together comprise the body's system of elastic arteries. Other examples include the brachiocephalic artery, common carotid arteries, subclavian artery, and common iliac artery. Structure The most prominent feature of elastic arteries is the very thick tunica media in which elastic lamellae alternate with layers of smooth muscle fibers. The adult aorta has about 50 elastic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arterioles
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries. Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the primary site of vascular resistance. The greatest change in blood pressure and velocity of blood flow occurs at the transition of arterioles to capillaries. This function is extremely important because it prevents the thin, one-layer capillaries from exploding upon pressure. The arterioles achieve this decrease in pressure, as they are the site with the highest resistance (a large contributor to total peripheral resistance) which translates to a large decrease in the pressure. Structure In a healthy vascular system, the endothelium lines all blood-contacting surfaces, including arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, capillaries, and heart chambers. This healthy condition is promoted by the ample production of nitric oxide by the endothelium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
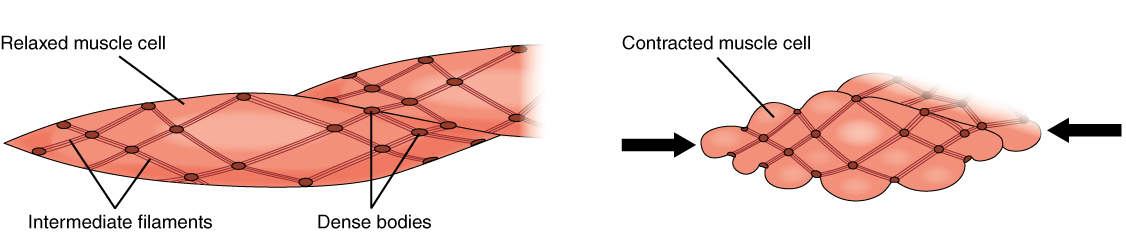
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It can be divided into two subgroups, ''single-unit'' and ''multi-unit'' smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus. In the walls of blood vessels, and lymph vessels, (excluding blood and lymph capillaries) it is known as vascular smooth muscle. There is smooth muscle in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, iris dilator muscle, and iris sphincter muscle are types of smooth muscles. The iris dilator and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm. Structure The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the forearm. There, it serves as a landmark for the division between the anterior compartment of the forearm, anterior and posterior compartment of the forearm, posterior compartments of the forearm, with the posterior compartment beginning just lateral to the artery. The artery winds laterally around the wrist, passing through the anatomical snuff box and between the heads of the first dorsal interossei of the hand, dorsal interosseous muscle. It passes anteriorly between the heads of the adductor pollicis, and becomes the deep palmar arch, which joins with the deep branch of the ulnar artery. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein, the radial vein. Branches The named branches of the radial artery may be divided int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh. The femoral artery proximal to the origin of the deep femoral artery is referred to as the ''common femoral artery'', whereas the femoral artery distal to this origin is referred to as the ''superficial femoral artery''. Structure The femoral artery represents the continuation of the external iliac artery beyond the inguinal ligament underneath which the vessel passes to enter the thigh. The vessel passes under the inguinal ligament just medial of the midpoint of this ligament, midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenic Artery
In human anatomy, the splenic artery or lienal artery, an older term, is the blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the spleen. It branches from the celiac artery, and follows a course superior to the pancreas. It is known for its tortuous path to the spleen. Structure The splenic artery, the largest branch of the celiac trunk, gives off branches to the stomach and pancreas before reaching the spleen. Note that the branches of the splenic artery do not reach all the way to the lower part of the greater curvature of the stomach. Instead, that region is supplied by the right gastroepiploic artery, a branch of the gastroduodenal artery. The two gastroepiploic arteries anastomose with each other at that point. Relations The splenic artery passes between the layers of the lienorenal ligament. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein, the splenic vein, which drains into the hepatic portal vein. Clinical significance Splenic artery aneurysms are rare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by elevated blood levels of cholesterol. These lesions may lead to narrowing of the arterial walls due to buildup of atheromatous plaques. At the onset, there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. In severe cases, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney disorders, depending on which body part(s) the affected arteries are located in the body. The exact cause of atherosclerosis is unknown and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include dyslipidemia, abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory biomarkers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking (both active and passive smoking), obesity, genetic factors, family history, lifes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Intima
The tunica intima (Neo-Latin "inner coat"), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (biology), tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelium, endothelial cells (and macrophages in areas of disturbed blood flow), and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow. The three layers of a blood vessel are an inner layer (the tunica intima), a middle layer (the tunica media), and an outer layer (the tunica externa). In dissection, the inner coat (tunica intima) can be separated from the middle (tunica media) by a little maceration, or it may be stripped off in small pieces; but, because of its friability, it cannot be separated as a complete membrane. It is a fine, transparent, colorless structure which is highly elastic, and, after death, is commonly corrugated into longitudinal wrinkles. Structure The structure of the tunica intima depends on the blood vessel type. Elastic artery, E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Elastic Lamina
The internal elastic lamina or internal elastic lamella is a layer of elastic tissue that forms the outermost part of the tunica intima of blood vessels. It separates tunica intima from tunica media. Histology It is readily visualized with light microscopy in sections of muscular arteries, where it is thick and prominent, and arterioles, where it is slightly less prominent and often incomplete. It is very thin in veins and venules. In elastic arteries such as the aorta, which have very regular elastic laminae between layers of smooth muscle cells in their tunica media, the internal elastic lamina is approximately the same thickness as the other elastic laminae that are normally present. There is small amount of subendothelial connective tissue between basement membrane of endothelial cells and internal elastic lamina. Reduplication of internal elastic lamina can be seen in elderly individuals due to intimal fibroplasia, which is part of the aging process. Associated pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It can be divided into two subgroups, ''single-unit'' and ''multi-unit'' smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus. In the walls of blood vessels, and lymph vessels, (excluding blood and lymph capillaries) it is known as vascular smooth muscle. There is smooth muscle in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, iris dilator muscle, and iris sphincter muscle are types of smooth muscles. The iris dilator and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Adventitia
The tunica externa (Neo-Latin "outer coat"), also known as the tunica adventitia (Neo-Latin "additional coat"), is the outermost tunica (layer) of a blood vessel, surrounding the tunica media. It is mainly composed of collagen and, in arteries, is supported by external elastic lamina. The collagen serves to anchor the blood vessel to nearby organs, giving it stability. The three layers of the blood vessels are: an inner tunica intima, a middle tunica media, and an outer tunica externa. Structure The tunica externa is made from collagen and elastic fibers in a loose connective tissue. This is secreted by fibroblasts. This is normally the thickest tunic in veins and may be thicker than the tunica media in some larger arteries. The outer layers of the tunica externa are not distinct but rather blend with the surrounding connective tissue outside the vessel, helping to hold the vessel in relative position. Function The tunica externa provides basic structural support to blood v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |