|
Arterioles
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries. Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the primary site of vascular resistance. The greatest change in blood pressure and velocity of blood flow occurs at the transition of arterioles to capillaries. This function is extremely important because it prevents the thin, one-layer capillaries from exploding upon pressure. The arterioles achieve this decrease in pressure, as they are the site with the highest resistance (a large contributor to total peripheral resistance) which translates to a large decrease in the pressure. Structure In a healthy vascular system, the endothelium lines all blood-contacting surfaces, including arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, capillaries, and heart chambers. This healthy condition is promoted by the ample production of nitric oxide by the endothelium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteriole
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillary, capillaries. Arterioles have vascular smooth muscle, muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the primary site of vascular resistance. The greatest change in blood pressure and velocity of blood flow occurs at the transition of arterioles to capillaries. This function is extremely important because it prevents the thin, one-layer capillaries from exploding upon pressure. The arterioles achieve this decrease in pressure, as they are the site with the highest resistance (a large contributor to total peripheral resistance) which translates to a large decrease in the pressure. Structure In a healthy vascular system, the endothelium lines all blood-contacting surfaces, including arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, capillaries, and heart chambers. This healthy condition is promoted by the ample production of n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
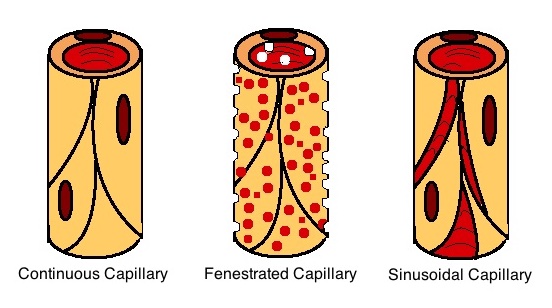
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
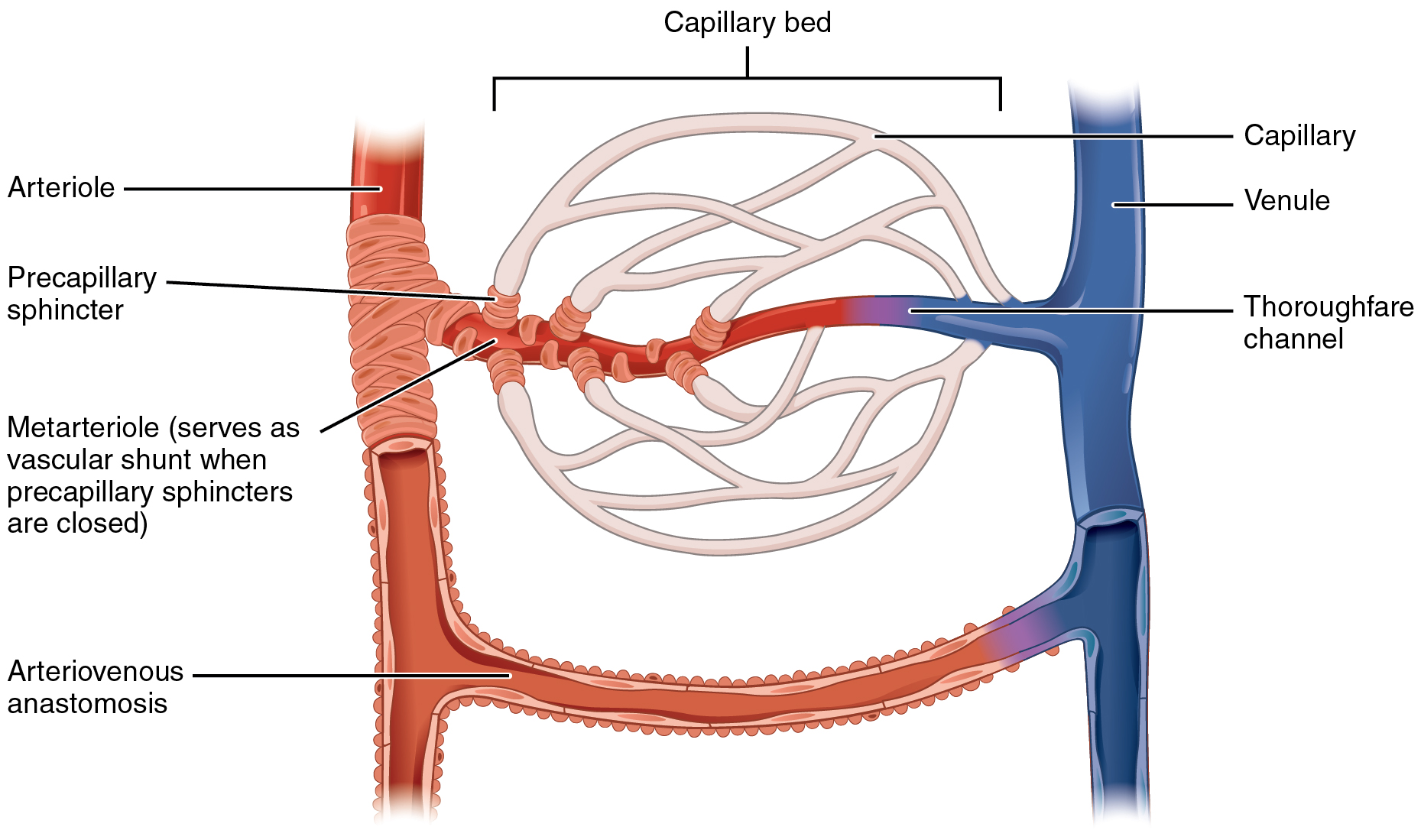
Microcirculation
The microcirculation is the circulation of the blood in the smallest blood vessels, the microvessels of the microvasculature present within organ tissues. The microvessels include terminal arterioles, metarterioles, capillaries, and venules. Arterioles carry oxygenated blood to the capillaries, and blood flows out of the capillaries through venules into veins. In addition to these blood vessels, the microcirculation also includes lymphatic capillaries and collecting ducts. The main functions of the microcirculation are the delivery of oxygen and nutrients and the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). It also serves to regulate blood flow and tissue perfusion, thereby affecting blood pressure and responses to inflammation which can include edema (swelling). Most vessels of the microcirculation are lined by flattened cells of the endothelium and many of them are surrounded by contractile cells called pericytes. The endothelium provides a smooth surface for the flow of blood and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Peripheral Resistance
Vascular resistance is the resistance that must be overcome for blood to flow through the circulatory system. The resistance offered by the systemic circulation is known as the systemic vascular resistance or may sometimes be called by another term total peripheral resistance, while the resistance caused by the pulmonary circulation is known as the pulmonary vascular resistance. Vasoconstriction (i.e., decrease in the diameter of arteries and arterioles) increases resistance, whereas vasodilation (increase in diameter) decreases resistance. Blood flow and cardiac output are related to blood pressure and inversely related to vascular resistance. Measurement The measurement of vascular resistance is challenging in most situations. The standard method is by the use of a Pulmonary artery catheter. This is common in ICU settings but impractical is most other settings. Units for measuring Units for measuring vascular resistance are dyn·s·cm−5, pascal seconds per cubic metre ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in a brachial artery, where it is most commonly measured. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one Cardiac cycle, heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in Millimetre of mercury, millimetres of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in Pascal (unit), kilopascals (kPa). The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is known as pulse pressure, while the average pressure during a cardiac cycle is known as mean arterial pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, Oxygen saturation (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artery
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in the pulmonary circulation that carry blood to the lungs for oxygenation, and the umbilical arteries in the fetal circulation that carry deoxygenated blood to the placenta. It consists of a multi-layered artery wall wrapped into a tube-shaped channel. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry deoxygenated blood back towards the heart; or in the pulmonary and fetal circulations carry oxygenated blood to the lungs and fetus respectively. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic scale, macroscopic level, and histology, microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscope. The arterial system of the human body is divided into systemic circulation, systemic arteries, carrying blood from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Resistance
Vascular resistance is the resistance that must be overcome for blood to flow through the circulatory system. The resistance offered by the systemic circulation is known as the systemic vascular resistance or may sometimes be called by another term total peripheral resistance, while the resistance caused by the pulmonary circulation is known as the pulmonary vascular resistance. Vasoconstriction (i.e., decrease in the diameter of arteries and arterioles) increases resistance, whereas vasodilation (increase in diameter) decreases resistance. Blood flow and cardiac output are related to blood pressure and inversely related to vascular resistance. Measurement The measurement of vascular resistance is challenging in most situations. The standard method is by the use of a Pulmonary artery catheter. This is common in ICU settings but impractical is most other settings. Units for measuring Units for measuring vascular resistance are dyn·s·cm−5, pascal seconds per cubic metre (Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arterial
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in the pulmonary circulation that carry blood to the lungs for oxygenation, and the umbilical arteries in the fetal circulation that carry deoxygenated blood to the placenta. It consists of a multi-layered artery wall wrapped into a tube-shaped channel. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry deoxygenated blood back towards the heart; or in the pulmonary and fetal circulations carry oxygenated blood to the lungs and fetus respectively. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscope. The arterial system of the human body is divided into systemic arteries, carrying blood from the heart to the whole body, and pulmonary arteries, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteriolosclerosis
Arteriolosclerosis is a form of cardiovascular disease involving hardening and loss of elasticity of arterioles or small arteries and is most often associated with hypertension and diabetes mellitus. Types include hyaline arteriolosclerosis and hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis, both involved with vessel wall thickening and luminal narrowing that may cause downstream ischemic injury. The following two terms whilst similar, are distinct in both spelling and meaning and may easily be confused with arteriolosclerosis. * Arteriosclerosis is any hardening (and loss of elasticity) of medium or large arteries (from the Greek '' arteria'', meaning ''artery'', and '' sclerosis'', meaning ''hardening'') * Atherosclerosis is a hardening of an artery specifically due to an atheromatous plaque. The term ''atherogenic'' is used for substances or processes that cause atherosclerosis. Hyaline arteriolosclerosis Also arterial hyalinosis and arteriolar hyalinosis refers to thickening of the wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venules
A venule is a very small vein in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the venous system via increasingly larger veins. Post-capillary venules are the smallest of the veins with a diameter of between 10 and 30 micrometres (μm). When the post-capillary venules increase in diameter to 50μm they can incorporate smooth muscle and are known as muscular venules. Veins contain approximately 70% of total blood volume, while about 25% is contained in the venules. Many venules unite to form a vein. Structure Post-capillary venules have a single layer of endothelium surrounded by a basal lamina. Their size is between 10 and 30 micrometers and are too small to contain smooth muscle. They are instead supported by pericytes that wrap around them. When the post-capillary venules increase in diameter to 50μm they can incorporate smooth muscle and are known as muscular venules. They have an inner endothelium composed of squamous endothelial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (biology), body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Some tissues such as cartilage, epithelium, and the lens (anatomy), lens and cornea of the eye are not supplied with blood vessels and are termed ''avascular''. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning ''vessel'', and is mostly used in relation to blood vessels. Etymology * artery – late Middle English; from Latin ''arteria'', from Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
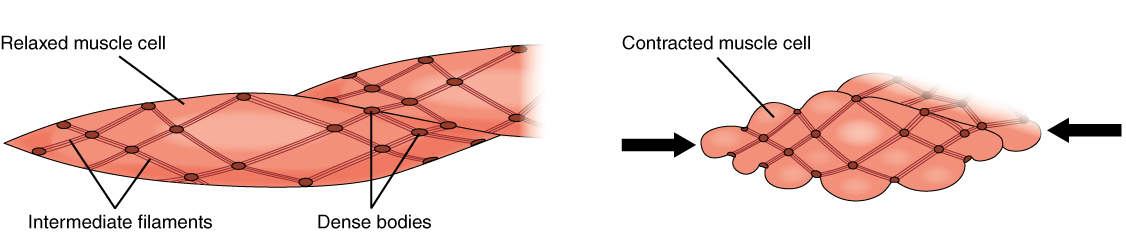
Smooth Muscle Cells
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal muscle, skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non-striated muscle tissue, striated, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It can be divided into two subgroups, ''single-unit'' and ''multi-unit'' smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of #Smooth muscle cells, smooth muscle cells muscle contraction, contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, urinary bladder, bladder and uterus. In the walls of blood vessels, and lymph vessels, (excluding blood and lymph capillaries) it is known as vascular smooth muscle. There is smooth muscle in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive Organ system, systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |