|
Dilijan Uyezd
Dilijan () is a spa town and urban municipal community in the Dilijan Municipality of the Tavush Province of Armenia. The town is one of the most important resorts in Armenia, situated within the Dilijan National Park. The forested town is home to numerous Armenians, Armenian artists, composers, and filmmakers and features some traditional Armenian architecture. Sharambeyan Street in the city centre, has been preserved and maintained as the heart of Dilijan's old town, complete with craftsman's workshops, a Art gallery, gallery and a museum. Hiking, mountain biking, and picnicking are popular recreational activities. As of the 2011 census, Dilijan has a population of 17,712. Dilijan is currently the fastest-growing urban settlement in Armenia. As of the 2022 census, Dilijan has a population of 15,914. Etymology In an ancient popular legend, the name of the town is named after a shepherd called Dili. The shepherd Dili was in love with his master's daughter, however her father was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Committee Of Armenia
The Statistical Committee of Armenia (), or ArmStat in short, is the national statistical agency of Armenia. History The statistical institution started its main activities on 7 January 1922 and was previously known as the Statistical Department of Soviet Socialist Republic of Armenia. It was also previously known as: *National Statistical Service of the Republic of Armenia (May 2000- April 2018) *Ministry of Statistics, State Register and Analysis of the Republic of Armenia (April 1998-May 2000), *State Department of Statistics, State Register and Analysis of the Republic of Armenia (1992-1998), *State Statistical Committee of the Soviet Socialist Republic of Armenia (1987-1992). International cooperation Armenia joined the International Monetary Fund's Special Data Dissemination Standard on 7 November 2003, being the third member of the Commonwealth of Independent States to join. From 1 January 2009, Armenia was a member of the United Nations Statistical Commission until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
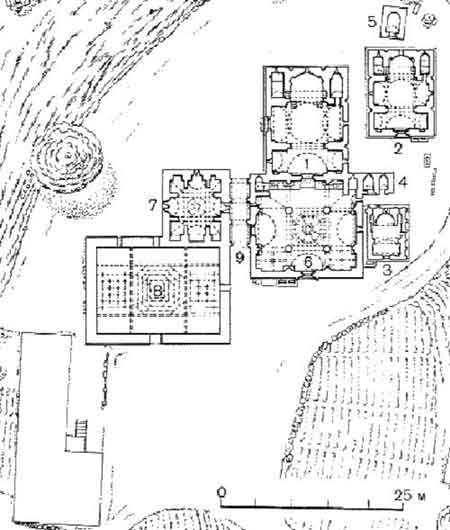
Goshavank
Goshavank (; meaning "Monastery of Gosh"; previously known as Nor Getik) is a 12–13th-century Armenian monastery located in the village of Gosh, Armenia, Gosh in the Tavush Province of Armenia. The monastery which has remained in relatively good condition also houses one of the world's finest examples of a khachkar. History Goshavank was erected in the place of an older monastery once known as ''Nor Getik'', which had been destroyed by an earthquake in 1188. Mkhitar Gosh, a statesman, scientist and author of numerous fables and parables as well as The Lawcode (Datastanagirk') of Mkhitar Gosh, the first criminal code, took part in the rebuilding of the monastery. At Goshavank, Mkhitar Gosh founded a school. One of its alumni, an Armenian scientist by the name of Kirakos Gandzaketsi wrote ''The History of Armenia''. The architect Mkhitar the Carpenter and his disciple Hovhannes also took an active part in the building of the monastery. The complex was later renamed Goshavan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haghartsin Monastery
Haghartsin () is a medieval monastery located near the town of Dilijan in the Tavush Province of Armenia. It was built between the 10th and 13th centuries. It is composed of three churches: St. Gregory's (the oldest one), St. Stephen's, and St. Astvatsatsin (St. Mary's, the largest one), as well as a ''gavit'' and a refectory. Etymology Popular etymology derives the name of Haghartsin from the words 'moved around, played' and 'eagle'. ''Haghartsin'' is also the name of a stream which flows past the monastery and empties into the Aghstev. History Haghartsin is thought to have been founded in the 10th century, although the exact founding date is unknown. It is assumed that kings of the Kiurikian dynasty, a branch of the Bagratuni dynasty, are buried in the partially destroyed sepulchre next to St. Gregory's Church, which contains two graves (formerly three) with partially legible inscriptions. According to another view, the Bagratuni kings Smbat II () and Gagik I () are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsacid Dynasty Of Armenia
The Arsacid dynasty, called the Arshakuni () in Armenian, ruled the Kingdom of Armenia (with some interruptions) from 12 to 428 AD. The dynasty was a branch of the Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Arsacid kings reigned intermittently throughout the chaotic years following the fall of the Artaxiad dynasty until 62, when Tiridates I, brother of Parthian King Vologases I, secured Arsacid rule in Armenia as a client king of Rome. However, he did not succeed in establishing his line on the throne, and various princes of different Arsacid lineages ruled until the accession of Vologases II, who succeeded in establishing his own line on the Armenian throne, which ruled the kingdom until its abolishment by the Sasanian Empire in 428. Two of the most notable events under Arsacid rule in Armenian history were the conversion of Armenia to Christianity by Gregory the Illuminator and Tiridates III in the early 4th century and the creation of the Armenian alphabet by Mesrop Mashtots in . In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerevan is the administrative, cultural, and industrial center of the country, as its primate city. It has been the Historical capitals of Armenia, capital since 1918, the Historical capitals of Armenia, fourteenth in the history of Armenia and the seventh located in or around the Ararat Plain. The city also serves as the seat of the Araratian Pontifical Diocese, which is the largest diocese of the Armenian Apostolic Church and one of the oldest dioceses in the world. The history of Yerevan dates back to the 8th century BC, with the founding of the fortress of Erebuni Fortress, Erebuni in 782 BC by King Argishti I of Urartu, Argishti I of Urartu at the western extreme of the Ararat Plain. Erebuni was "designed as a great administrative and reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baku
Baku (, ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Azerbaijan, largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and in the Caucasus region. Baku is below sea level, which makes it the List of capital cities by elevation, lowest lying national capital in the world and also the largest city in the world below sea level. Baku lies on the southern shore of the Absheron Peninsula, on the Bay of Baku. Baku's urban population was estimated at two million people as of 2009. Baku is the primate city of Azerbaijan—it is the sole metropolis in the country, and about 25% of all inhabitants of the country live in Baku's metropolitan area. Baku is divided into #Administrative divisions, twelve administrative raions and 48 townships. Among these are the townships on the islands of the Baku Archipelago, as well as the industrial settlement of Neft Daşları built on oil rigs away from Baku city in the Caspian Sea. The Old City (Baku), Old City, conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი, ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), ( ka, ტფილისი, tr ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city of Georgia (country), Georgia, located on the banks of the Kura (Caspian Sea), Kura River. With around 1.2 million inhabitants, it contains almost one third of the country's population. Tbilisi was founded in the fifth century Anno Domini, AD by Vakhtang I of Iberia and has since served as the capital of various Georgian kingdoms and republics. Between 1801 and 1917, then part of the Russian Empire, it was the seat of the Caucasus Viceroyalty (1801–1917), Caucasus Viceroyalty, governing both the North Caucasus, northern and the South Caucasus, southern sides of the Caucasus. Because of its location at the crossroads between Europe and Asia, and its proximity to the lucrative Silk Road, throughout history, Tbilisi has been a point of contention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601,911 residents as of 2021, with more than 6.4 million people living in the Saint Petersburg metropolitan area, metropolitan area. Saint Petersburg is the List of European cities by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in Europe, the List of cities and towns around the Baltic Sea, most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's List of northernmost items#Cities and settlements, northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As the former capital of the Russian Empire, and a Ports of the Baltic Sea, historically strategic port, it is governed as a Federal cities of Russia, federal city. The city was founded by Tsar Peter the Great on 27 May 1703 on the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents within the city limits, over 19.1 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in Moscow metropolitan area, its metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's List of largest cities, largest cities, being the List of European cities by population within city limits, most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest List of urban areas in Europe, urban and List of metropolitan areas in Europe, metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow became the capital of the Grand Principality of Moscow, which led the unification of the Russian lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progressing to protohistory (before written history). In this usage, it is preceded by the Stone Age (subdivided into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic) and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the ancient Near East. In the archaeology of the Americas, a five-period system is conventionally used instead; indigenous cultures there did not develop an iron economy in the pre-Columbian era, though some did work copper and bronze. Indigenous metalworking arrived in Australia with European contact. Although meteoric iron has been used for millennia in many regions, the beginning of the Iron Age is defined locally around the world by archaeological convention when the production of Smelting, smelted iron (espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |