|
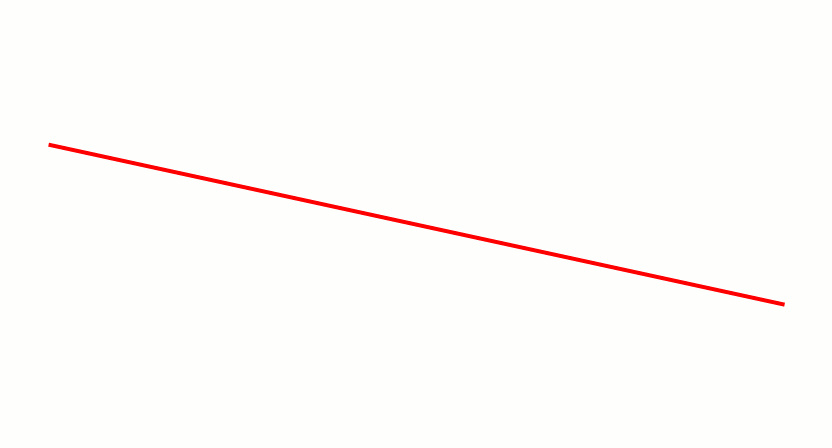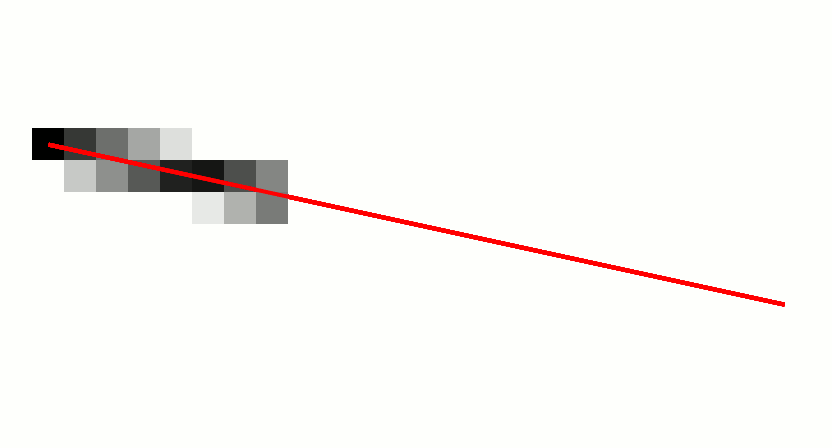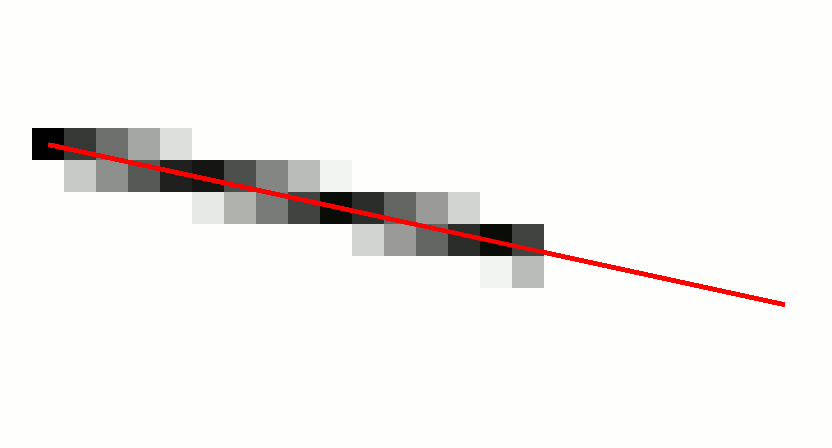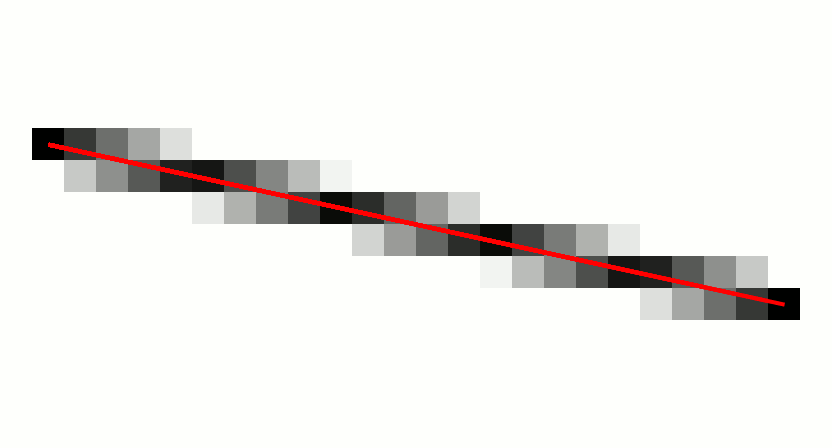
Digital Differential Analyzer (graphics Algorithm)
In computer graphics, a digital differential analyzer (DDA) is hardware or software used for interpolation of variables over an interval between start and end point. DDAs are used for rasterization of lines, triangles and polygons. They can be extended to non linear functions, such as perspective correct texture mapping, quadratic curves, and traversing voxels. In its simplest implementation for linear cases such as lines, the DDA algorithm interpolates values in interval by computing for each xi the equations xi = xi−1 + 1, yi = yi−1 + m, where m is the slope of the line. This slope can be expressed in DDA as follows: :m = \frac In fact any two consecutive points lying on this line segment should satisfy the equation. Performance The DDA method can be implemented using floating-point or integer arithmetic. The native floating-point implementation requires one addition and one rounding operation per interpolated value (e.g. coordinate x, y, depth, color component e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great deal of specialized hardware and software has been developed, with the displays of most devices being driven by graphics hardware, computer graphics hardware. It is a vast and recently developed area of computer science. The phrase was coined in 1960 by computer graphics researchers Verne Hudson and William Fetter of Boeing. It is often abbreviated as CG, or typically in the context of film as Computer-generated imagery, computer generated imagery (CGI). The non-artistic aspects of computer graphics are the subject of Computer graphics (computer science), computer science research. Some topics in computer graphics include user interface design, Sprite (computer graphics), sprite graphics, raster graphics, Rendering (computer graph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a ''significand'' (a Sign (mathematics), signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some Radix, base) multiplied by an integer power of that base. Numbers of this form are called floating-point numbers. For example, the number 2469/200 is a floating-point number in base ten with five digits: 2469/200 = 12.345 = \! \underbrace_\text \! \times \! \underbrace_\text\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\overbrace^ However, 7716/625 = 12.3456 is not a floating-point number in base ten with five digits—it needs six digits. The nearest floating-point number with only five digits is 12.346. And 1/3 = 0.3333… is not a floating-point number in base ten with any finite number of digits. In practice, most floating-point systems use Binary number, base two, though base ten (decimal floating point) is also common. Floating-point arithmetic operations, such as addition and division, approximate the correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Graphics Algorithms
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', which enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. The term computer system may refer to a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system, software, and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation; or to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of industrial and consumer products use computers as control systems, including simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls, and factory devices like industrial robots. Computers are at the core of general-purpose devices such as personal computers and mobile devices such as smartphones. Computers power the Internet, which links billions of computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiaolin Wu's Line Algorithm
Xiaolin Wu's line algorithm is an algorithm for line spatial anti-aliasing, antialiasing. Antialiasing technique Xiaolin Wu's line algorithm was presented in the article "An Efficient Antialiasing Technique" in the July 1991 issue of ''Computer Graphics (newsletter), Computer Graphics'', as well as in the article "Fast Antialiasing" in the June 1992 issue of ''Dr. Dobb's Journal''. Bresenham's line algorithm, Bresenham's algorithm draws lines extremely quickly, but it does not perform anti-aliasing. In addition, it cannot handle any cases where the line endpoints do not lie exactly on integer points of the pixel grid. A naive approach to anti-aliasing the line would take an extremely long time. Wu's algorithm is comparatively fast, but is still slower than Bresenham's algorithm. The algorithm consists of drawing pairs of pixels straddling the line, each coloured according to its distance from the line. Pixels at the line ends are handled separately. Lines less than one pixel lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |