|
Digital Differential Analyzer (graphics Algorithm)
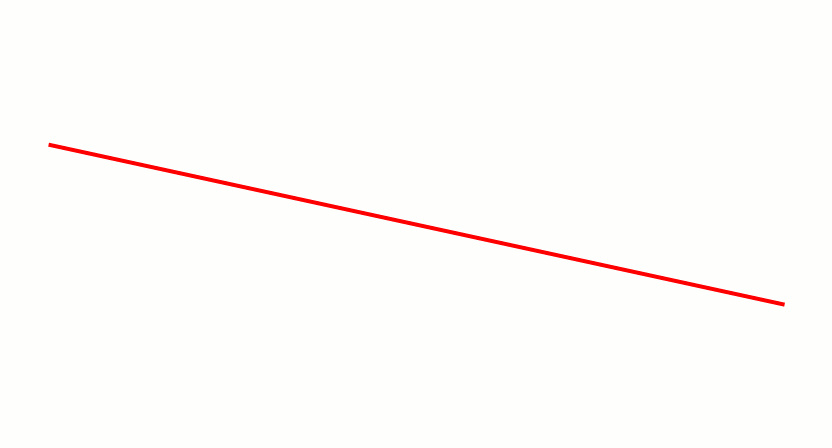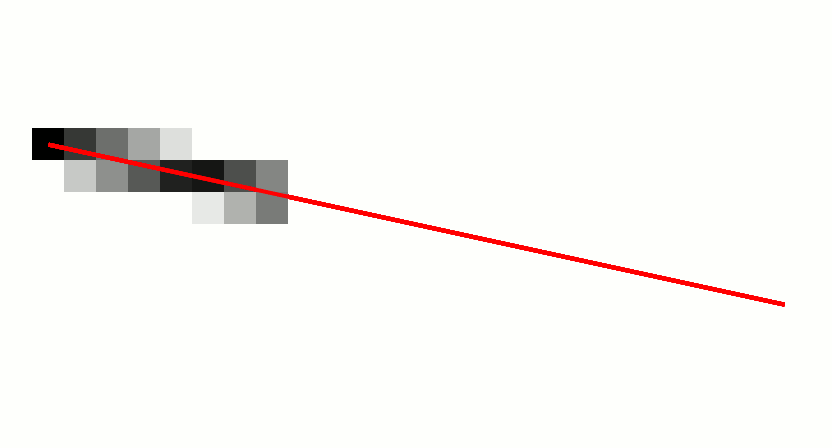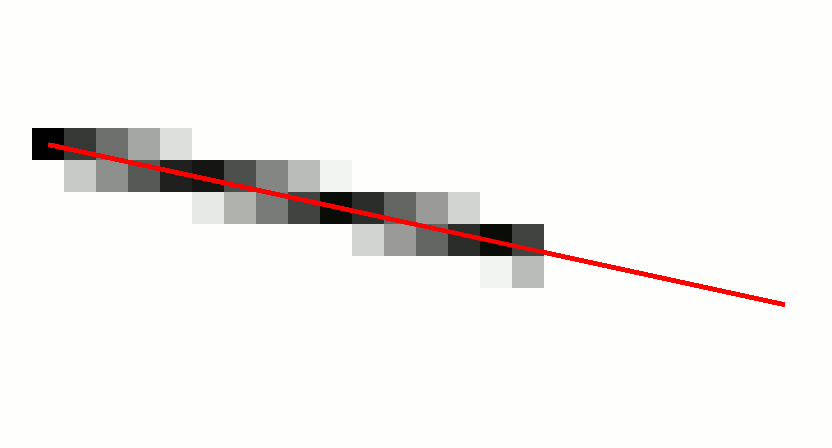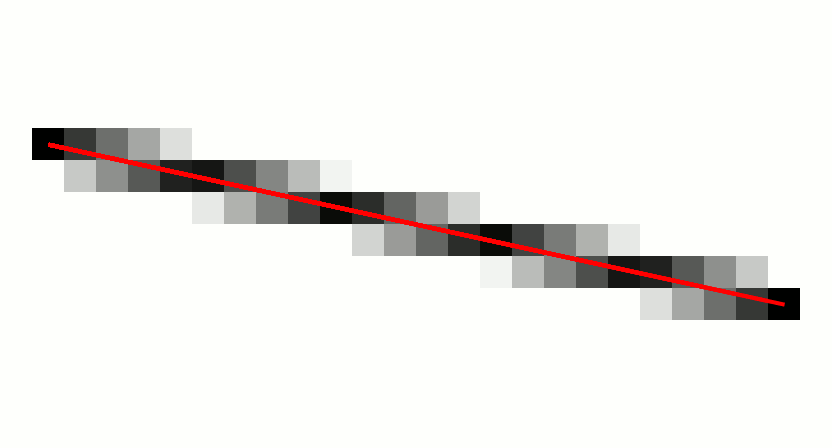
In computer graphics, a digital differential analyzer (DDA) is hardware or software used for interpolation of variables over an interval between start and end point. DDAs are used for rasterization of lines, triangles and polygons. They can be extended to non linear functions, such as perspective correct texture mapping, quadratic curves, and traversing voxels. In its simplest implementation for linear cases such as lines, the DDA algorithm interpolates values in interval by computing for each xi the equations xi = xi−1 + 1, yi = yi−1 + m, where m is the slope of the line. This slope can be expressed in DDA as follows: :m = \frac In fact any two consecutive points lying on this line segment should satisfy the equation. Performance The DDA method can be implemented using floating-point or integer arithmetic. The native floating-point implementation requires one addition and one rounding operation per interpolated value (e.g. coordinate x, y, depth, color component e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great deal of specialized hardware and software has been developed, with the displays of most devices being driven by graphics hardware, computer graphics hardware. It is a vast and recently developed area of computer science. The phrase was coined in 1960 by computer graphics researchers Verne Hudson and William Fetter of Boeing. It is often abbreviated as CG, or typically in the context of film as Computer-generated imagery, computer generated imagery (CGI). The non-artistic aspects of computer graphics are the subject of Computer graphics (computer science), computer science research. Some topics in computer graphics include user interface design, Sprite (computer graphics), sprite graphics, raster graphics, Rendering (computer graph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a ''significand'' (a Sign (mathematics), signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some Radix, base) multiplied by an integer power of that base. Numbers of this form are called floating-point numbers. For example, the number 2469/200 is a floating-point number in base ten with five digits: 2469/200 = 12.345 = \! \underbrace_\text \! \times \! \underbrace_\text\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\overbrace^ However, 7716/625 = 12.3456 is not a floating-point number in base ten with five digits—it needs six digits. The nearest floating-point number with only five digits is 12.346. And 1/3 = 0.3333… is not a floating-point number in base ten with any finite number of digits. In practice, most floating-point systems use Binary number, base two, though base ten (decimal floating point) is also common. Floating-point arithmetic operations, such as addition and division, approximate the correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Graphics Algorithms
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', which enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. The term computer system may refer to a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system, software, and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation; or to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of industrial and consumer products use computers as control systems, including simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls, and factory devices like industrial robots. Computers are at the core of general-purpose devices such as personal computers and mobile devices such as smartphones. Computers power the Internet, which links billions of computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiaolin Wu's Line Algorithm
Xiaolin Wu's line algorithm is an algorithm for line spatial anti-aliasing, antialiasing. Antialiasing technique Xiaolin Wu's line algorithm was presented in the article "An Efficient Antialiasing Technique" in the July 1991 issue of ''Computer Graphics (newsletter), Computer Graphics'', as well as in the article "Fast Antialiasing" in the June 1992 issue of ''Dr. Dobb's Journal''. Bresenham's line algorithm, Bresenham's algorithm draws lines extremely quickly, but it does not perform anti-aliasing. In addition, it cannot handle any cases where the line endpoints do not lie exactly on integer points of the pixel grid. A naive approach to anti-aliasing the line would take an extremely long time. Wu's algorithm is comparatively fast, but is still slower than Bresenham's algorithm. The algorithm consists of drawing pairs of pixels straddling the line, each coloured according to its distance from the line. Pixels at the line ends are handled separately. Lines less than one pixel lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incremental Error Algorithm
This is a glossary of terms relating to computer graphics. For more general computer hardware terms, see glossary of computer hardware terms. 0–9 A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P Q R S T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bresenham's Line Algorithm
Bresenham's line algorithm is a line drawing algorithm that determines the points of an ''n''-dimensional raster that should be selected in order to form a close approximation to a straight line between two points. It is commonly used to draw line primitives in a bitmap image (e.g. on a computer screen), as it uses only integer addition, subtraction, and bit shifting, all of which are very cheap operations in historically common computer architectures. It is an incremental error algorithm, and one of the earliest algorithms developed in the field of computer graphics. An extension to the original algorithm called the '' midpoint circle algorithm'' may be used for drawing circles. While algorithms such as Wu's algorithm are also frequently used in modern computer graphics because they can support antialiasing, Bresenham's line algorithm is still important because of its speed and simplicity. The algorithm is used in hardware such as plotters and in the graphics chips of mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed-point Arithmetic
In computing, fixed-point is a method of representing fractional (non-integer) numbers by storing a fixed number of digits of their fractional part. Dollar amounts, for example, are often stored with exactly two fractional digits, representing the cents (1/100 of dollar). More generally, the term may refer to representing fractional values as integer multiples of some fixed small unit, e.g. a fractional amount of hours as an integer multiple of ten-minute intervals. Fixed-point number representation is often contrasted to the more complicated and computationally demanding floating-point representation. In the fixed-point representation, the fraction is often expressed in the same number base as the integer part, but using negative powers of the base ''b''. The most common variants are decimal (base 10) and binary (base 2). The latter is commonly known also as binary scaling. Thus, if ''n'' fraction digits are stored, the value will always be an integer multiple of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating-point Unit
A floating-point unit (FPU), numeric processing unit (NPU), colloquially math coprocessor, is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating-point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square root. Modern designs generally include a fused multiply-add instruction, which was found to be very common in real-world code. Some FPUs can also perform various transcendental functions such as exponential or trigonometric calculations, but the accuracy can be low, so some systems prefer to compute these functions in software. Floating-point operations were originally handled in software in early computers. Over time, manufacturers began to provide standardized floating-point libraries as part of their software collections. Some machines, those dedicated to scientific processing, would include specialized hardware to perform some of these tasks with much greater speed. The introduction of microcode in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative integers. The set (mathematics), set of all integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the set of natural numbers, the set of integers \mathbb is Countable set, countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fraction, fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , 5/4, and Square root of 2, are not. The integers form the smallest Group (mathematics), group and the smallest ring (mathematics), ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slope
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a Line (mathematics), line is a number that describes the direction (geometry), direction of the line on a plane (geometry), plane. Often denoted by the letter ''m'', slope is calculated as the ratio of the vertical change to the horizontal change ("rise over run") between two distinct points on the line, giving the same number for any choice of points. The line may be physical – as set by a Surveying, road surveyor, pictorial as in a diagram of a road or roof, or Pure mathematics, abstract. An application of the mathematical concept is found in the grade (slope), grade or gradient in geography and civil engineering. The ''steepness'', incline, or grade of a line is the absolute value of its slope: greater absolute value indicates a steeper line. The line trend is defined as follows: *An "increasing" or "ascending" line goes from left to right and has positive slope: m>0. *A "decreasing" or "descending" line goes from left to right ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpolation
In the mathematics, mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points. In engineering and science, one often has a number of data points, obtained by sampling (statistics), sampling or experimentation, which represent the values of a function for a limited number of values of the Dependent and independent variables, independent variable. It is often required to interpolate; that is, estimate the value of that function for an intermediate value of the independent variable. A closely related problem is the function approximation, approximation of a complicated function by a simple function. Suppose the formula for some given function is known, but too complicated to evaluate efficiently. A few data points from the original function can be interpolated to produce a simpler function which is still fairly close to the original. The resulting gai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line (geometry)
In geometry, a straight line, usually abbreviated line, is an infinitely long object with no width, depth, or curvature, an idealization of such physical objects as a straightedge, a taut string, or a ray (optics), ray of light. Lines are space (mathematics), spaces of dimension one, which may be Embedding, embedded in spaces of dimension two, three, or higher. The word ''line'' may also refer, in everyday life, to a line segment, which is a part of a line delimited by two Point (geometry), points (its ''endpoints''). Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements'' defines a straight line as a "breadthless length" that "lies evenly with respect to the points on itself", and introduced several postulates as basic unprovable properties on which the rest of geometry was established. ''Euclidean line'' and ''Euclidean geometry'' are terms introduced to avoid confusion with generalizations introduced since the end of the 19th century, such as Non-Euclidean geometry, non-Euclidean, Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |