|
Digital Component Video
Digital component video is defined by the ITU-R BT.601 (formerly CCIR 601) standard and uses the Y'CbCr colorspace. The specific encoding of ITU-R BT.656 was used to transmit uncompressed analog standard-definition television component signals in a multiplexed digital format. Like analog component video,The common name for 'component analog video (CAV)' it gets its name from the fact that the video signal has been split into two or more components, that are then carried on multiple conductors between devices. Digital component video is used in both computer and home-theatre applications, such as . It was the internal signalling ''(as opposed to, e.g. RGB)'' in MiniDV, DV, and Digital Betacam Component video can carry signals such as 480i, 480p, 576i, 576p, 720p, 1080i and 1080p, although many TVs do not support 1080p through component video. See also * Serial digital interface Serial digital interface (SDI) is a family of digital video Interface (computing), in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITU-R
The ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) is one of the three sectors (divisions or units) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and is responsible for radio communications. Its role is to manage the international radio-frequency spectrum and satellite orbit resources and to develop standards for radiocommunication systems with the objective of ensuring the effective use of the spectrum. ITU is required, according to its constitution, to allocate spectrum and register frequency allocation, orbital positions and other parameters of satellites, "in order to avoid harmful interference between radio stations of different countries". The international spectrum management system is therefore based on regulatory procedures for frequency coordination, notification and registration. ITU-R has a permanent secretariat, the Radiocommunication Bureau, based at the ITU HQ in Geneva, Switzerland. The elected Director of the Bureau is Mario Maniewicz; he was first elected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
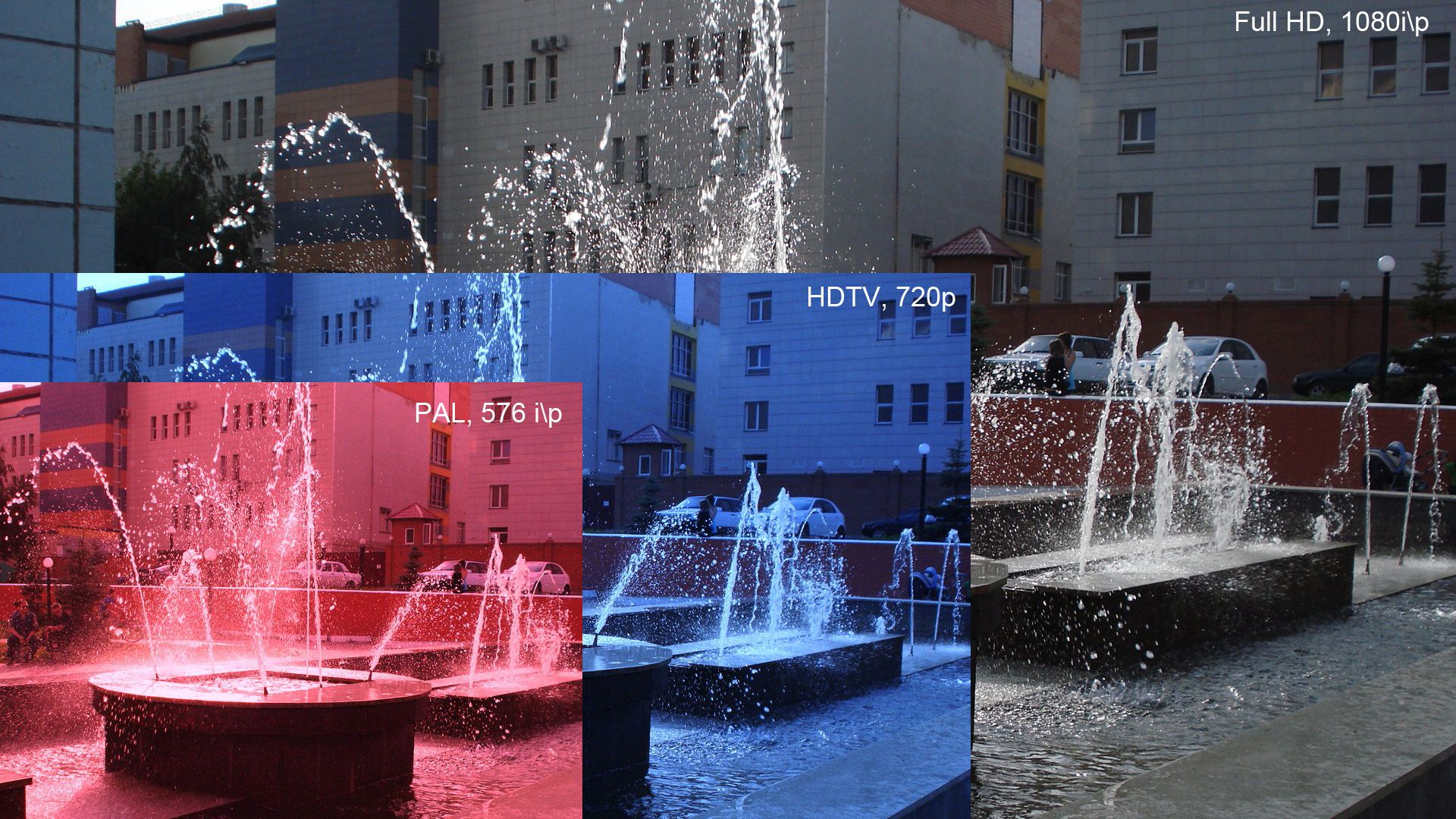
576p
576p is the shorthand name for a video display resolution. The ''p'' stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced, the ''576'' for a vertical resolution of 576 pixels (the frame rate can be given explicitly after the letter). Usually it corresponds to a digital video mode with a 4:3 anamorphic resolution of 720x576 and a frame rate of 25 frames per second (576p25), and thus using the same bandwidth and carrying the same amount of pixel data as 576i, but other resolutions and frame rates are possible. ITU-R Recommendation BT.1358 allows the following resolutions, coded as R'G'B' or YCBCR, with timings compatible with BT.656: * 1024 x 576p ( 16:9 square pixel format) * 960 x 576p * 936 x 576p (based on 960 x 576p, blanking the first and last 12 pixels of each line) * 768 x 576p ( 4:3 square pixel format) * 720 x 576p (4:3 anamorphic) * 704 x 576p (based on 720 x 576p, blanking the first and last 8 pixels of each line) * 544 x 576p * 480 x 576p 576p is considered standar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Technology
The technology of television has evolved since its early days using a mechanical system invented by Paul Gottlieb Nipkow in 1884. Every television system works on the scanning principle first implemented in the rotating disk scanner of Nipkow. This turns a two-dimensional image into a time series of signals that represent the brightness and color of each resolvable element of the picture. By repeating a two-dimensional image quickly enough, the impression of motion can be transmitted as well. For the receiving apparatus to reconstruct the image, synchronization information is included in the signal to allow proper placement of each line within the image and to identify when a complete image has been transmitted and a new image is to follow. While mechanically scanned systems were experimentally used, television as a mass medium was made practical by the development of electronic camera tubes and displays. By the turn of the 21st century, it was technically feasible to replace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Display Connectors
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits. Businesses *Digital bank, a form of financial institution *Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) or Digital, a computer company *Digital Research (DR or DRI), a software company Computing and technology Hardware *Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals **Digital camera, which captures and stores digital images *** Digital versus film photography **Digital computer, a computer that handles information represented by discrete values **Digital recording, information recorded using a digital signal Socioeconomic phenomena *Digital culture, the anthropological dimension of the digital social changes *Digital divide, a form of economic and social inequality in access to or use of information and communication technologies *Digital economy, an economy based on computing and telecommunications resources *Digital rights, legal rights of access to computers or the Internet Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhanced-definition Television
Enhanced-definition television, or extended-definition television (EDTV) is a Consumer Electronics Association (CEA) marketing shorthand term for certain digital television (DTV) formats and devices. Specifically, this term defines an extension of the standard-definition television (SDTV) format that enables a clearer picture during high-motion scenes compared to previous iterations of SDTV, but not producing images as detailed as high-definition television (HDTV). The term refers to devices capable of displaying 480-line or 576-line signals in progressive scan, commonly referred to as 480p ( NTSC-HQ) and 576p ( PAL/SECAM) respectively, as opposed to interlaced scanning, commonly referred to as 480i (NTSC) or 576i (PAL, SECAM). High-motion is optional for EDTV. In Australia, the 576p resolution standard was used by the Special Broadcasting Service (SBS TV) and Seven Network, being technically considered high-definition. In Japan, the term is associated with improvements to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMPTE 344M
SMPTE 344M is a standard published by SMPTE which expands upon SMPTE 259M allowing for serial digital interface bit-rates of 540 Mbit/s,SMPTE 344M allowing EDTV resolutions of 480p and 576p. This standard is part of a family of standards that define a serial digital interface Serial digital interface (SDI) is a family of digital video Interface (computing), interfaces first standardized by SMPTE (The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers) in 1989. For example, ITU-R BT.656 and SMPTE 259M define digital .... References Film and video technology SMPTE standards {{Measurement-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Digital Interface
Serial digital interface (SDI) is a family of digital video Interface (computing), interfaces first standardized by SMPTE (The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers) in 1989. For example, ITU-R BT.656 and SMPTE 259M define digital video interfaces used for Broadcasting, broadcast-grade video. A related standard, known as high-definition serial digital interface (HD-SDI), is standardized in SMPTE 292M; this provides a nominal data rate of 1.485 Gbit/s. Additional SDI standards have been introduced to support increasing video resolutions (High definition video, HD, Ultra high definition, UHD and beyond), High frame rate, frame rates, 3D video, stereoscopic (3D) video, and color depth. Dual link HD-SDI consists of a pair of SMPTE 292M links, standardized by SMPTE 372M in 1998; this provides a nominal 2.970 Gbit/s interface used in applications (such as digital cinema or HDTV 1080P) that require greater fidelity and resolution than standard HDTV can provide. 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1080p
1080p (1920 × 1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non- interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes referred to as 2K resolution (meaning having a horizontal resolution of approximately 2,000 pixels), other sources differentiate between 1080p and (true) 2K resolution. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1080i
In high-definition television (HDTV) and video display technology, 1080i is a video display format with 1080 lines of vertical resolution and Interlaced video, interlaced scanning method. This format was once a standard in HDTV. It was particularly used for broadcast television because it can deliver high-resolution images without needing excessive bandwidth. This format is used in the SMPTE 292M standard. Definition The number "1080" in 1080i refers to the number of horizontal lines that make up the vertical resolution of the display. Each of these lines contributes to the overall detail and clarity of the image. The letter "i" stands for Interlaced video, interlaced. This is a technique where the image is not displayed all at once. Instead, the frame is split into two fields. One field contains the odd-numbered lines, and the other field contains the even-numbered lines. These fields are displayed in rapid succession, giving the appearance of a full image to the human eye. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
720p
720p (720 lines progressive) is a progressive HD signal format with 720 horizontal lines/1280 columns and an aspect ratio (AR) of 16:9, normally known as widescreen HD (1.78:1). All major HD broadcasting standards (such as SMPTE 292M) include a 720p format, which has a resolution of 1280×720. The number ''720'' stands for the 720 horizontal scan lines of image display resolution (also known as 720 pixels of vertical resolution). The ''p'' stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. When broadcast at 60 frames per second, 720p features the highest temporal resolution possible under the ATSC and DVB standards. The term assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, thus implying a resolution of 1280×720 px (0.9 megapixels). 720i (720 lines interlaced) is an erroneous term found in numerous sources and publications. Typically, it is a typographical error in which the author is referring to the 720p HDTV format. However, in some cases it is incorrectly presented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
576i
576i is a standard-definition television, standard-definition digital video mode, originally used for Digitization, digitizing 625 lines, 625 line Analog television, analogue television in most countries of the world where the utility frequency for electric power distribution is 50 Hz. Because of its close association with the legacy colour encoding systems, it is often referred to as PAL#PAL region, PAL, PAL/SECAM or SECAM when compared to its 60 Hz (typically, see PAL-M) NTSC-colour-encoded counterpart, 480i. The ''576'' identifies a vertical resolution of 576 lines, and the ''i'' identifies it as an Interlaced video, interlaced resolution. The Refresh rate, field rate, which is 50 Hertz, Hz, is sometimes included when identifying the video mode, i.e. 576i50; another notation, endorsed by both the International Telecommunication Union in Rec. 601, BT.601 and SMPTE in SMPTE 259M, includes the frame rate, as in 576i/25. Operation In analogue television, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YCbCr
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in digital video and digital photography, photography systems. Like YPbPr, YPBPR, it is based on RGB primaries; the two are generally equivalent, but YCBCR is intended for digital video, while YPBPR is designed for use in Analogue electronics, analog systems. Y′ is the Luma (video), luma component, and CB and CR are the B-Y, blue-difference and R-Y, red-difference chrominance, chroma components. Luma Y′ (with Prime (symbol), prime) is distinguished from relative luminance, luminance Y, meaning that light intensity is nonlinearly encoded based on gamma corrected RGB primaries. Y′CbCr color spaces are defined by a mathematical coordinate transformation from an associated RGB primaries and white point. If the underlying RGB color spaces, RGB color space is absolute, the Y′CbCr color space is an absolute color space as well; conversely, if the RGB spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |