|
Dietericambria
''Dietericambria'' is an extinct genus of Cambrian pentastomids from the Henson Gletscher Formation of Greenland. It is the oldest known pentastomid, being at least 15 million years older than the forms recorded from the Orsten. The genus contains a single species, ''Dietericambria hensoniensis''. Description ''Dietericambria'' was at least 1.2 mm long, with cylindrical segments. (Due to it only being known from fragmentary specimens, any lengths are purely estimates.) It resembles '' Aengapentastomum'', however it has much smaller, unsegmented head limbs. ''Dietericambria'' also has an unusual complex of flanges on the ventral surface of the head. The trunk seems to have had limbs, with their sockets being preserved, however their shape is unknown. Unusually, instead of the lateral position of Orsten pentastomids, these limbs are positioned ventrally, similar to that of tardigrades. While hooks similar to the cephalic hooks of modern pentastomids are known from the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henson Gletscher Formation
The Henson Gletscher Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic formation in Greenland. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cambrian Period (geology), period. It is named after the Henson Glacier (Greenland). It preserves numerous Phosphatocopina, phosphatocopines and bradoriids, alongside priapulid larvae such as ''Inuitiphlaskus'' and pentastomids like ''Dietericambria''. Paleobiota See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Greenland References Cambrian Greenland Cambrian southern paleotropical deposits Long stubs with short prose {{Greenland-geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
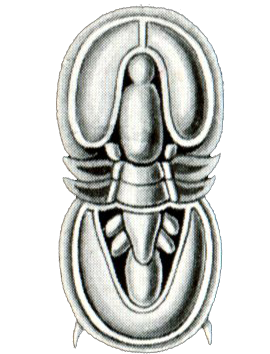
Pentastomid
The Pentastomida are an enigmatic group of parasite, parasitic arthropods commonly known as tongue worms due to the resemblance of the species of the genus ''Linguatula'' to a vertebrate tongue; molecular studies point to them being highly derived crustaceans. About 130 species of pentastomids are known; all are obligate parasites with correspondingly degenerate anatomy. Adult tongue worms vary from about in length and parasitize the respiratory tracts of vertebrates. They have five anterior appendages. One is the mouth; the others are two pairs of hooks, which they use to attach to the host. This arrangement led to their scientific name, meaning "five openings", but although the appendages are similar in some species, only one is a mouth. Taxonomy Historically significant accounts of tongue worm biology and systematics include early work by Josef Aloys Frölich, Alexander von Humboldt, Karl Asmund Rudolphi, Karl Moriz Diesing and Rudolph Leuckart. Other important summaries h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orsten
The Orsten fauna are fossilized organisms preserved in the Orsten lagerstätte of Cambrian (Late Miaolingian to Furongian) rocks, notably at Kinnekulle and on the island of Öland, all in Sweden. The initial site, discovered in 1975 by Klaus Müller and his assistants, exceptionally preserves soft-bodied organisms, and their larvae, who are preserved uncompacted in three dimensions. The fossils are phosphatized and silicified, thus the delicate chitinous cuticle and soft parts are not affected by acids, which act upon the limestone nodules within which the fossils have survived. Acids dissolve the limestone, revealing the microfossils in a recovery process called "acid etching". To recover the fossils, more than one and a half tons of Orsten limestone have been dissolved in acid, originally in a specifically designed laboratory in Bonn, more recently moved to Ulm. The insoluble residue is scanned by electron microscope. The phosphorus used to replace the fossils with calcium p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 486.85 Ma. Most of the continents lay in the southern hemisphere surrounded by the vast Panthalassa Ocean. The assembly of Gondwana during the Ediacaran and early Cambrian led to the development of new convergent plate boundaries and continental-margin arc magmatism along its margins that helped drive up global temperatures. Laurentia lay across the equator, separated from Gondwana by the opening Iapetus Ocean. The Cambrian marked a profound change in life on Earth; prior to the Period, the majority of living organisms were small, unicellular and poorly preserved. Complex, multicellular organisms gradually became more common during the Ediacaran, but it was not until the Cambrian that fossil diversity seems to rapidly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenland are full Danish nationality law, citizens of Denmark and European Union citizenship, of the European Union. Greenland is one of the Special territories of members of the European Economic Area#Overseas countries and territories, Overseas Countries and Territories of the European Union and is part of the Council of Europe. It is the List of islands by area, world's largest island, and lies between the Arctic Ocean, Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Arctic Archipelago, Canadian Arctic Archipelago. It is the location of the northernmost point of land in the world; Kaffeklubben Island off the northern coast is the world's Northernmost point of land, northernmost undisputed point of land—Cape Morris Jesup on the mainland was thought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of Genus, genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GFF (journal)
GFF may refer to: Entertainment * Girlfriends Films, an American pornographic studio * Glasgow Film Festival, in Scotland * Gothenburg Film Festival, in Sweden Sports * Gabonese Football Federation * Gambia Football Federation * Georgian Football Federation * Göteborgs FF, Swedish football club * Gothenburg Football Association * Guinean Football Federation * Guyana Football Federation Other uses * ''GFF'' (journal), a geology journal * General feature format, a file format used for describing genes * Gesellschaft für Freiheitsrechte (Society for Civil Rights), a Berlin-based non-profit organization * Göteborgs FyrverkeriFabrik, a Swedish fireworks company * Griffith Airport, in New South Wales, Australia * Griffith railway station Griffith railway station is located on the Yanco–Griffith line in New South Wales, Australia. It serves the city of Griffith. History Griffith station opened on 3 July 1916 when the Temora-Roto line was extended from Barellan. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aengapentastomum
''Aengapentastomum'' is a Cambrian genus of pentastomid from the Orsten The Orsten fauna are fossilized organisms preserved in the Orsten lagerstätte of Cambrian (Late Miaolingian to Furongian) rocks, notably at Kinnekulle and on the island of Öland, all in Sweden. The initial site, discovered in 1975 by Klaus M� ... of Sweden, containing one species, ''Aengapentastomum andresi''. Description ''Aengapentastomum'' is roughly 730 micrometers long from head to tail. Unlike other Cambrian pentastomids, it lacks vestigial trunk limbs, therefore it is likely closer to the crown-group. It has two pairs of head limbs, both smooth and rounded, with inward-facing podomeres. A swelling of unknown function, likely akin to the "dorsal organs" of modern pentastomid larvae, occurs roughly half-way down the length of the body. The tail has a rounded end, with two structures at its tip. The head is subtriangular, with no head shield, despite a furrow around the appendages and a promine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tardigrades
Tardigrades (), known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged Segmentation (biology), segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them . In 1776, the Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani named them Tardigrada, which means 'slow walkers'. They live in diverse regions of Earth's biospheremountaintops, the deep sea, tropical rainforests, and the Antarctic. Tardigrades are among the most resilient animals known, with individual species able to survive extreme conditions – such as exposure to extreme temperatures, extreme pressures (both high and low), air deprivation, radiation, dehydration, and starvation – that would quickly kill most other forms of life. Tardigrades have survived exposure to outer space. There are about 1,500 known species in the phylum Tardigrada, a part of the superphylum Ecdysozoa. The earliest known fossil is from the Cambrian, some 500 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conodonts
Conodonts, are an extinct group of marine jawless vertebrates belonging to the Class (biology), class Conodonta (from Ancient Greek κῶνος (''kōnos''), meaning "cone", and ὀδούς (''odoús''), meaning "tooth"). They are primarily known from their hard, mineralised tooth-like structures called "conodont elements" that in life were present in the oral cavity and used to process food. Rare soft tissue remains suggest that they had elongate eel-like bodies with large eyes. Conodonts were a long-lasting group with over 300 million years of existence from the Cambrian (over 500 million years ago) to the beginning of the Jurassic (around 200 million years ago). Conodont elements are highly distinctive to particular species and are widely used in biostratigraphy as indicative of particular periods of geological time. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Sain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinocaridida
DinocarididaGreek for ''deinos'' "terrible" and Latin for ''caris'' "crab" – sometimes informally spelt Dinocarida, but the second 'id' is linguistically correct – see is a proposed fossil taxon of basal arthropods, which flourished during the Cambrian period and survived up to Early Devonian. Characterized by a pair of frontal appendages and series of body flaps, the name of Dinocaridids (Greek for ''deinos'' "terrible" and Latin for ''caris'' "crab") refers to the suggested role of some of these members as the largest marine predators of their time. Dinocaridids are occasionally referred to as the 'AOPK group' by some literatures, as the group composed of Radiodonta (''Anomalocaris'' and relatives), Opabiniidae (''Opabinia'' and relatives), and the "gilled lobopodians" ''Pambdelurion'' and Kerygmachelidae. It is most likely paraphyletic, with Kerygmachelidae and ''Pambdelurion'' more basal than the clade compose of Opabiniidae, Radiodonta and other arthropods. Anatomy D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |