|
Dibutyltin Oxide
Dibutyltin oxide, or dibutyloxotin, is an organotin compound with the chemical formula (C4H9)2SnO. It is a colorless solid that, when pure, is insoluble in organic solvents. It is used as a reagent and a catalyst.Davies, Alwyn G. "Organotin Chemistry", 2nd Edition, 2004, Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. . Structure The structure of diorganotin oxides depends on the size of the organic groups. For smaller substituents, the materials are assumed to be polymeric with five-coordinate Sn centers and 3-coordinate oxide centers. The result is a net of interconnected four-membered Sn2O2 and eight-membered Sn4O4 rings. The presence of pentacoordinate Sn centers is deduced from 119Sn NMR spectroscopy and 119Sn Mössbauer spectroscopy. Uses In organic synthesis, among its many applications, it is particularly useful in directing regioselective O-alkylation, acylation, and sulfonation reactions for diols and polyol. DBTO has been used in the regioselective tosylation (a specific type of sulfonation) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organotin
Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin–carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide (), discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory. Structure Organotin compounds are generally classified according to their oxidation states. Tin(IV) compounds are much more common and more useful. Organic derivatives of tin(IV) The tetraorgano derivatives are invariably tetrahedral. Compounds of the type SnRR'R''R have been resolved into individual enantiomers. Organotin halides Organotin chlorides have the formula for values of ''n'' up to 3. Bromides, iodides, and fluorides are also known, but are less imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocyclic
In organic chemistry, an alicyclic compound contains one or more all-carbon rings which may be either saturated or unsaturated, but do not have aromatic character. Alicyclic compounds may have one or more aliphatic side chains attached. Cycloalkanes The simplest alicyclic compounds are the monocyclic cycloalkanes: cyclopropane, cyclobutane, cyclopentane, cyclohexane, cycloheptane, cyclooctane, and so on. Bicyclic alkanes include decalin, housane, and norbornane. Polycyclic alkanes include cubane, basketane, and tetrahedrane. Spiro compounds have two or more rings that are connected through only one carbon atom. The mode of ring-closing in the formation of many alicyclic compounds can be predicted by Baldwin's rules. Otto Wallach, a German chemist, received the 1910 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on alicyclic compounds. Cycloalkenes Monocyclic cycloalkenes are cyclopropene, cyclobutene, cyclopentene, cyclohexene, cycloheptene, cyclooctene, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-dimensional Nanomaterials
In materials science, the term single-layer materials or 2D materials refers to crystalline solids consisting of a single layer of atoms. These materials are promising for some applications but remain the focus of research. Single-layer materials derived from single elements generally carry the -ene suffix in their names, e.g. graphene. Single-layer materials that are compounds of two or more elements have -ane or -ide suffixes. 2D materials can generally be categorized as either 2D allotropes of various elements or as compounds (consisting of two or more covalently bonding elements). It is predicted that there are hundreds of stable single-layer materials. The atomic structure and calculated basic properties of these and many other potentially synthesisable single-layer materials, can be found in computational databases. 2D materials can be produced using mainly two approaches: top-down exfoliation and bottom-up synthesis. The exfoliation methods include sonication, mechanical, hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organotin Compounds
Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin–carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide (), discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory. Structure Organotin compounds are generally classified according to their oxidation states. Tin(IV) compounds are much more common and more useful. Organic derivatives of tin(IV) The tetraorgano derivatives are invariably tetrahedral. Compounds of the type SnRR'R''R have been resolved into individual enantiomers. Organotin halides Organotin chlorides have the formula for values of ''n'' up to 3. Bromides, iodides, and fluorides are also known, but are less imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
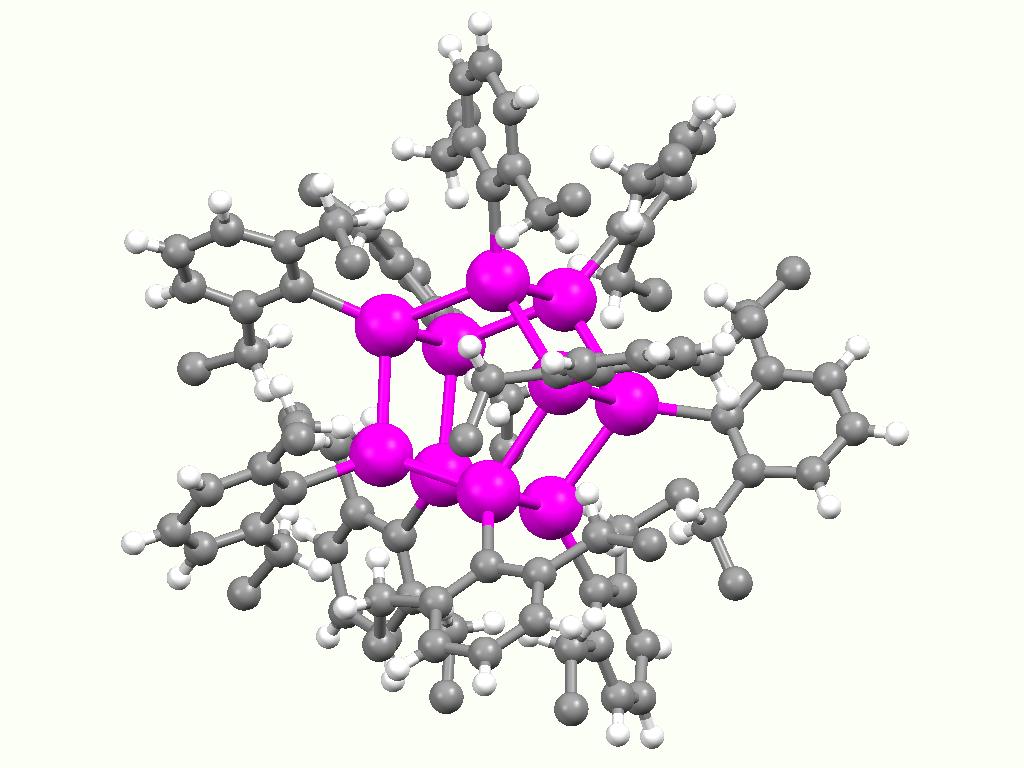
Otera's Catalyst
Otera's catalyst, named after Japanese chemist Junzo Otera, is an organostannane compound which has been used as a transesterification catalyst. This isothioscyanate compound is a member of a family of organostannanes reported by Wada and coworkers, and elaborated upon by Otera and coworkers. Preparation This class of compounds may be prepared generally by the reaction of an organotin halide and oxide: : 2 R2SnO + 2 R2SnX2 → (XR2SnOSnR2X)2 In particular, the thiocyanate compound was prepared by the reaction of dibutyltin oxide with dibutyltin diisothiocyanate. Otherwise, this compound is not commercially available. Applications This thiocyanate compound can be used as a transesterification catalyst. Although it is not well known, it has been used in a number of total syntheses. In this application, the reaction occurs via the displacement of the bridging isothiocyanate ligands with the incoming alcohol to form an alcohol-bridged active catalyst. Tin acts as the Lewis acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term does not refer to the single type of polymer but a group of polymers. Unlike polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethanes can be produced from a wide range of starting materials resulting in various polymers within the same group. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many List of polyurethane applications, different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, and coatings, adhesives, Potting (electronics), electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and polyurethane laminate (PUL). Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016. A polyurethane is typically produced by reacting a polymeric isocyanate with a polyol. Since a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicone
In Organosilicon chemistry, organosilicon and polymer chemistry, a silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer composed of repeating units of siloxane (, where R = Organyl group, organic group). They are typically colorless oils or elastomer, rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, silicone grease, grease, silicone rubber, rubber, silicone resin, resin, and Caulking, caulk. Silicone is often confused with one of its constituent elements, silicon, but they are distinct substances. Silicon is a chemical element, a hard dark-grey semiconductor, semiconducting metalloid, which in its crystalline form is used to make integrated circuits ("electronic chips") and solar cells. Silicones are compounds that contain silicon, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and perhaps other kinds of atoms as well, and have many very different physical and chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transesterification
Transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic functional group R″ of an ester with the organic group R' of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. Strong acids catalyze the reaction by donating a proton to the carbonyl group, thus making it a more potent electrophile. Bases catalyze the reaction by removing a proton from the alcohol, thus making it more nucleophilic. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of enzymes, particularly lipases (one example is the lipase E.C.3.1.1.3). If the alcohol produced by the reaction can be separated from the reactants by distillation this will drive the equilibrium toward the products. This means that esters with larger alkoxy groups can be made from methyl or ethyl esters in high purity by heating the mixture of ester, acid/base, and large alcohol. Mechanism In the transesterification mechanism, the carbonyl carbon of the starting ester reacts to give a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Alcohols
A primary alcohol is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol in which the hydroxy group is bonded to a primary carbon atom. It can also be defined as a molecule containing a “–CH2OH” group. In contrast, a secondary alcohol has a formula “–CHROH” and a tertiary alcohol has a formula “–CR2OH”, where “R” indicates a carbon-containing group. Examples of primary alcohols include ethanol, 1-propanol, and n-Butanol, 1-butanol. Methanol is also generally regarded as a primary alcohol, including by the 1911 edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica. See also * Alcohol (chemistry), Alcohol (especially Nomenclature section for discussion on Secondary and Tertiary alcohols.) * Oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids References Primary alcohols, {{organic-chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |