|
Organotin
Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin–carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide (), discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory. Structure Organotin compounds are generally classified according to their oxidation states. Tin(IV) compounds are much more common and more useful. Organic derivatives of tin(IV) The tetraorgano derivatives are invariably tetrahedral. Compounds of the type SnRR'R''R have been resolved into individual enantiomers. Organotin halides Organotin chlorides have the formula for values of ''n'' up to 3. Bromides, iodides, and fluorides are also known, but are less imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethyltin Chloride
Trimethyltin chloride is an organotin compound with the formula . It is a white solid that is highly toxic and malodorous. It is susceptible to hydrolysis. Synthesis Trimethyltin chloride can be prepared by the Redistribution (chemistry), redistribution reaction of tetramethyltin with tin tetrachloride. : This redistribution reaction is typically performed with no solvent because high temperatures are required and purification is simplified. A second route to involves treating the corresponding Organotin chemistry#Organotin oxides and hydroxides, hydroxide or oxide (in the following reaction, trimethyltin hydroxide ) with a halogenating agent such as hydrogen chloride or thionyl chloride (): : Uses Trimethyltin chloride is used as a source of the trimethylstannyl group (). For example, it is a precursor to vinyltrimethylstannane () and indene, indenyltrimethylstanane (see Transition metal indenyl complex): : : An example of an Organolithium reagent, organolithium reagent reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tributyltin Chloride
Tributyltin chloride is an organotin compound with the formula ( C4H9)3SnCl. It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. Preparation and reactions The compound is prepared by a redistribution reaction by combining stannic chloride and tetrabutyltin: :3 (C4H9)4Sn + SnCl4 → 4 (C4H9)3SnCl Tributyltin chloride hydrolyzes to the oxide C4H9)3Snsub>2O Tributyltin chloride is used as a precursor to other organotin compounds{{cite journal, title=Palladium-catalyzed Coupling Of Acid Chlorides With Organotin Reagents: Ethyl (E)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-2-butenoate, author=A. F. Renaldo , author2=J. W. Labadie , author3=J. K. Stille , journal=Org. Synth., year=1989, volume=67, page=86, doi=10.15227/orgsyn.067.0086 and reagents, such as tributyltin hydride Tributyltin hydride is an organotin compound with the formula (C4H9)3SnH. It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of hydrogen atoms in organic synthesis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyhexatin
Cyhexatin, also known as tricyclohexyltin hydroxide is an organometallic compound of tin with the chemical formula . Properties Cyhexatin forms colorless crystals or white crystalline powder. It is practically insoluble in water. The powder is wettable by water. Reactions Cyhexatin is stable in aqueous suspensions in neutral and alkaline conditions ( pH above 6), but reacts exothermically with strong acids, acting as a base, to form salts. Reacts with strong oxidizers. Decomposes upon exposure to ultraviolet light to dicyclohexyltin oxide (which is not an analog of ketones because it exists as a polymer) and cyclohexylstannanoic acid . Contact with metals may emit flammable hydrogen gas. Upon heating above it decomposes to bis(tricyclohexyltin) oxide , emitting irritating and toxic fumes and acrid smoke. : Uses Cyhexatin is used in paints. In agriculture, cyhexatin is used as a pesticide against insects, as well as parasitic mites that attack plants, like vegetables (e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well (e.g. amides), but not according to the IUPAC. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters; naturally occurring lactones are mainly 5- and 6-membered ring lactones. Lactones contribute to the aroma of fruits, butter, cheese, vegetables like celery and other foods. Esters can be formed from oxoacids (e.g. esters of acetic acid, carbonic acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
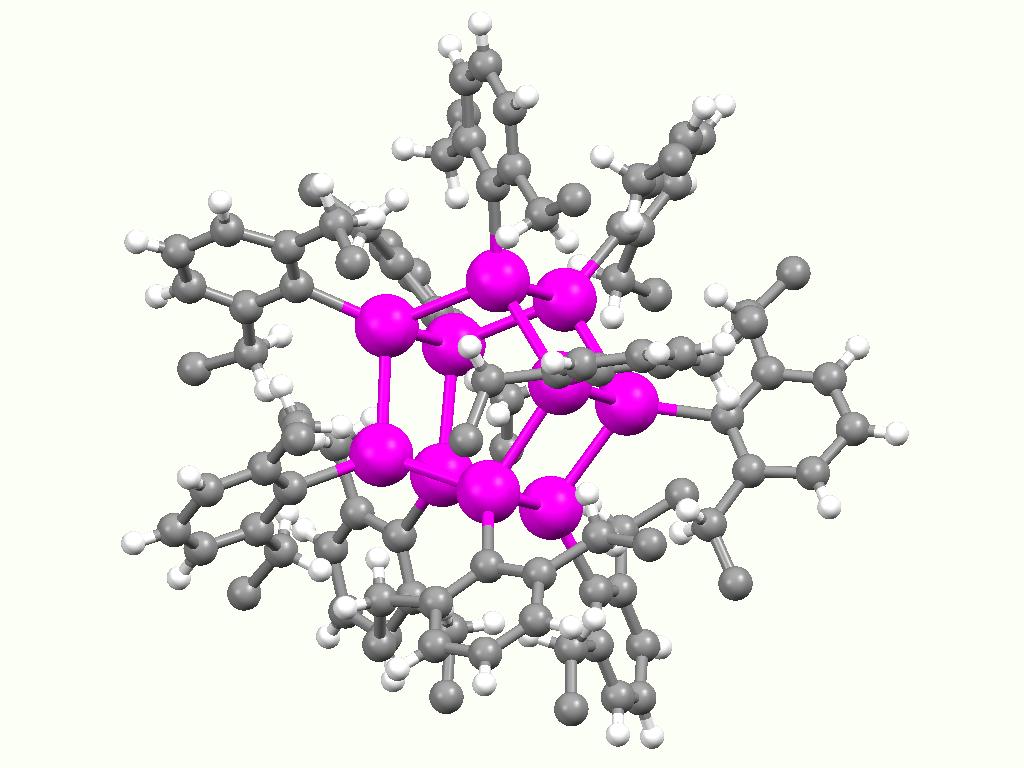
Stannoxane
Stannoxane is a functional group in organotin chemistry with the connectivity (IV indicates the oxidation state of tin). Aside from the oxide group, usually 3 or 4 other substituents are attached to tin. In aqueous or aquatic environments, most organotin compounds contain this group.Davies, Alwyn George. (2004) Organotin Chemistry, 2nd Edition Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. : Synthesis and formation Stannoxanes form upon hydrolysis of organotin halides. For example, hydrolysis of dibutyltin dichloride gives the tetratin compound . The hydrolysis appears to proceed via organotin hydroxides. For example, the commercially important cyhexatin converts at 200 °C into the hexacyclohexyldistannoxane: : The condensation process is proposed to occur via an associative mechanism In mathematics, the associative property is a property of some binary operations that rearranging the parentheses in an expression will not change the result. In propositional logic, associativity is a valid rule o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Compounds
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide ( metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tributyltin Hydride
Tributyltin hydride is an organotin compound with the formula (C4H9)3SnH. It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of hydrogen atoms in organic synthesis. Synthesis and characterization The compound is produced by reduction of tributyltin oxide with polymethylhydrosiloxane: : 2 " eSi(H)Osub>n" + (Bu3Sn)2O → " eSi(OH)Osub>n" + 2 Bu3SnH It can also be synthesized by a reduction of tributyltin chloride with lithium aluminium hydride. The hydride is a distillable liquid that is mildly sensitive to air, decomposing to (Bu3Sn)2O. Its IR spectrum exhibits a strong band at 1814 cm−1 for ''ν''Sn−H. Applications It is a specialized reagent in organic synthesis. Combined with azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) or by irradiation with light, tributyltin hydride converts organic halides (and related groups) to the corresponding hydrocarbon. This process occurs via a radical chain mechanism involving the radical Bu3S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stannane
Stannane or tin hydride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Sn H4. It is a colourless gas and the tin analogue of methane. Stannane can be prepared by the reaction of and . : Stannane decomposes slowly at room temperature to give metallic tin and hydrogen and ignites on contact with air. Variants of stannane can be found as a highly toxic, gaseous, inorganic metal hydrides and group 14 hydrides. See also * Organotin Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin–carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide (), discove ... References {{Hydrides by group Tin(IV) compounds Metal hydrides Reducing agents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Frankland
Sir Edward Frankland, (18 January 18259 August 1899) was an English chemist. He was one of the originators of organometallic chemistry and introduced the concept of combining power or valence. An expert in water quality and analysis, he was a member of the second royal commission on the pollution of rivers, and studied London's water quality for decades. He also studied luminous flames and the effects of atmospheric pressure on dense ignited gas, and was one of the discoverers of helium. Biography Edward Frankland was born in Catterall, Lancashire and baptised at Churchtown, Lancashire on 20 February 1825. As his baptismal record shows, his birth was illegitimate. His natural father was Edward Chaddock Gorst, the father of John Eldon Gorst. His mother, Margaret "Peggy" Frankland, later married William Helm, a Lancaster cabinet-maker. "His illegitimacy cast a shadow over all his life since he was pledged to silence as to the identity of his natural father, although a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,2'-Bipyridine
The comma is a punctuation mark that appears in several variants in different languages. Some typefaces render it as a small line, slightly curved or straight, but inclined from the vertical; others give it the appearance of a miniature filled-in figure placed on the baseline. In many typefaces it is the same shape as an apostrophe or single closing quotation mark . The comma is used in many contexts and languages, mainly to separate parts of a sentence such as clauses, and items in lists mainly when there are three or more items listed. The word ''comma'' comes from the Greek (), which originally meant a cut-off piece, specifically in grammar, a short clause. A comma-shaped mark is used as a diacritic in several writing systems and is considered distinct from the cedilla. In Byzantine and modern copies of Ancient Greek, the " rough" and "smooth breathings" () appear above the letter. In Latvian, Romanian, and Livonian, the comma diacritic appears below the letter, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimer (chemistry)
In chemistry, dimerization is the process of joining two identical or similar Molecular entity, molecular entities by Chemical bond, bonds. The resulting bonds can be either strong or weak. Many symmetrical chemical species are described as dimers, even when the monomer is unknown or highly unstable. The term ''homodimer'' is used when the two subunits are identical (e.g. A–A) and ''heterodimer'' when they are not (e.g. A–B). The reverse of dimerization is often called Dissociation (chemistry), dissociation. When two oppositely-charged ions associate into dimers, they are referred to as ''Bjerrum pairs'', after Danish chemist Niels Bjerrum. Noncovalent dimers Anhydrous carboxylic acids form dimers by hydrogen bonding of the acidic hydrogen and the carbonyl oxygen. For example, acetic acid forms a dimer in the gas phase, where the monomer units are held together by hydrogen bonds. Many OH-containing molecules form dimers, e.g. the water dimer. Dimers that form based on w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallics
''Organometallics'' is a biweekly journal published by the American Chemical Society. Its area of focus is organometallic and organometalloid chemistry. This peer-reviewed journal has an impact factor of 3.837 as reported by the 2021 Journal Citation Reports by Thomson Reuters. Since 2015 Paul Chirik is the editor-in-chief of ''Organometallics''. He is an American chemist and the Edwards S. Sanford Professor of Chemistry at Princeton University, and associate director for external partnerships of the Andlinger Center for Energy and the Environment. He writes about the catalysis of hydrocarbons. Past editors-in-chief are Dietmar Seyferth and John Gladysz. Retrieved on 2014-07-30. This journal is indexed in |