|
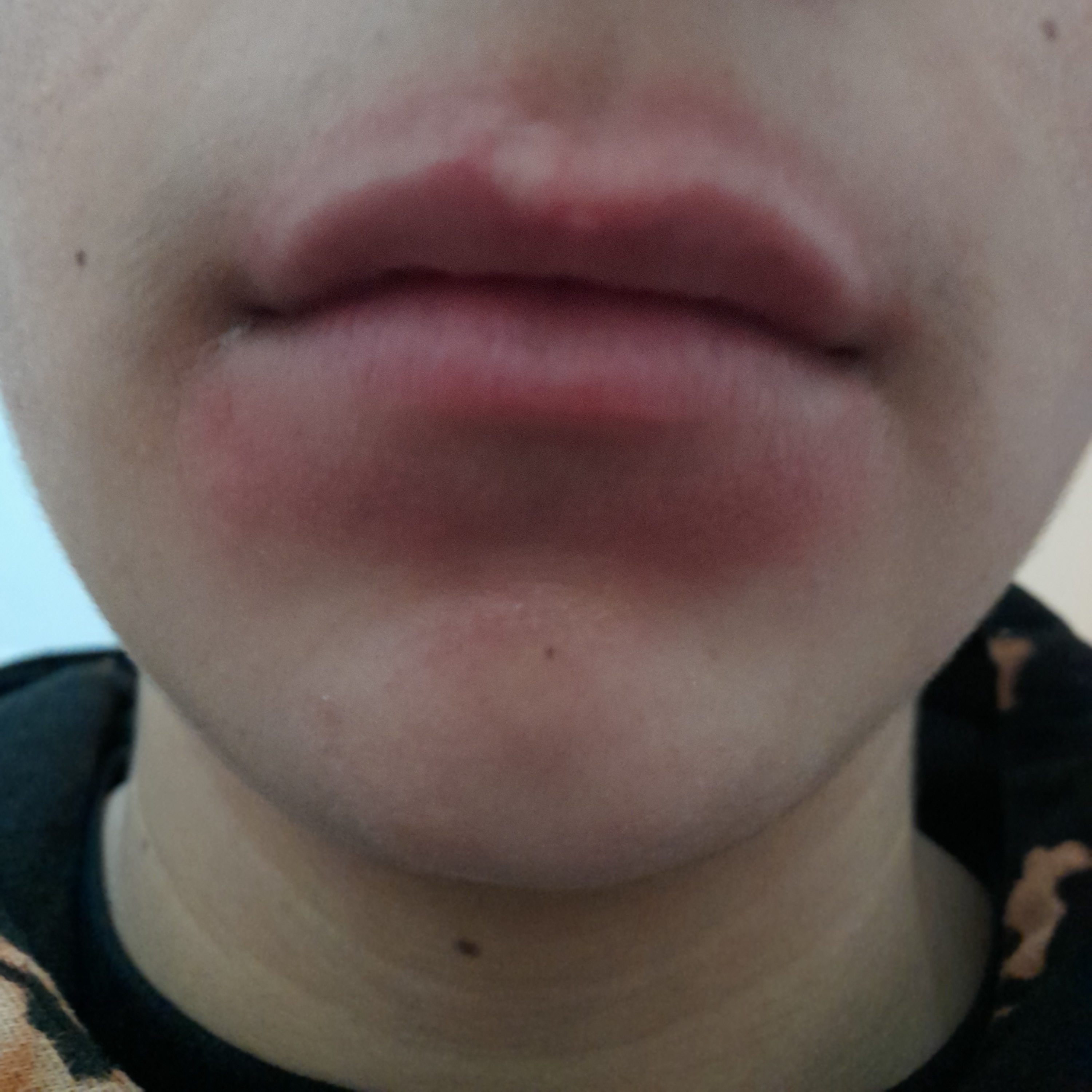
Denavir
Penciclovir is a guanosine analogue antiviral drug used for the treatment of various herpesvirus infections. It is a nucleoside analogue which exhibits low toxicity and good selectivity. Because penciclovir is absorbed poorly when given orally (by mouth) it is more often used as a topical treatment. It is the active ingredient in the cold sore medications Denavir ( NDC 0135-0315-52), Vectavir and Fenivir. Famciclovir is a prodrug of penciclovir with improved oral bioavailability. Penciclovir was approved for medical use in 1996. Medical use In herpes labialis, the duration of healing, pain and detectable virus is reduced by up to one day,Fass.se">Farmaceutiska Specialiteter i Sverige - the Swedish official drug catalog Vectavir. Retrieved on August 12, 2009. Translated from "Tiden för läkning, smärta och påvisbart virus förkortas med upp till ett dygn." compared with the total duration of 2–3 weeks of disease presentation. Mechanism of action Penciclovir is inactive in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine
Guanosine (symbol G or Guo) is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose ( ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9- glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). When guanine is attached by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of a deoxyribose ring it is known as deoxyguanosine. Physical and chemical properties Guanosine is a white, crystalline powder with no odor and mild saline taste. It is very soluble in acetic acid, slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene and chloroform. Functions Guanosine is required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus. In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid, phosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one proton gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion while removal of two protons gives the hydrogen phosphate ion . These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate or orthophosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleoside Analogue
Nucleoside analogues are structural analogues of a nucleoside, which normally contain a nucleobase and a sugar. Nucleotide analogues are analogues of a nucleotide, which normally has one to three phosphates linked to a nucleoside. Both types of compounds can deviate from what they mimick in a number of ways, as changes can be made to any of the constituent parts (nucleobase, sugar, phosphate). They are related to nucleic acid analogues. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogues can be used in therapeutic drugs, including a range of antiviral products used to prevent viral replication in infected cells. The most commonly used is acyclovir. Nucleotide and nucleoside analogues can also be found naturally. Examples include ddhCTP (3ʹ-deoxy-3′,4ʹdidehydro-CTP) produced by the human antiviral protein viperin and sinefungin (a S-Adenosyl methionine analogue) produced by some '' Streptomyces''. Function These agents can be used against hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, herpe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aciclovir
Aciclovir, also known as acyclovir, is an antiviral medication. It is primarily used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, chickenpox, and shingles. Other uses include the prevention of cytomegalovirus infections following transplant, and severe complications of Epstein–Barr virus infection. It can be taken by mouth, applied as a cream, or injected. Common side effects include nausea and diarrhea. Potentially serious side effects include kidney problems and low platelets. Greater care is recommended in those with poor liver or kidney function. It is generally considered safe for use in pregnancy with no harm having been observed. It appears to be safe during breastfeeding. Aciclovir is a nucleoside analogue that mimics guanosine. It works by decreasing the production of the virus's DNA. Aciclovir was patented in 1974, by Burroughs Wellcome, and approved for medical use in 1981. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are toxic metals, toxic chemicals, microbe neurotoxins, radiation particles and even specific neurotransmitters when the system is out of balance. Also some types of drugs, e.g alcohol, and some venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'') are toxic to cells. Cell physiology Treating cells with the cytotoxic compound can result in a variety of prognoses. The cells may undergo necrosis, in which they lose membrane integrity and die rapidly as a result of cell lysis. The cells can stop actively growing and dividing (a decrease in cell viability), or the cells can activate a genetic program of controlled cell death (apoptosis). Cells undergoing necrosis typically exhibit rapid swelling, lose membrane integrity, shut down metabolism, and release their contents into the environment. Cells that undergo rapid necrosis in vitro do not have sufficient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selective Toxicity
Selective may refer to: * Selective school, a school that admits students on the basis of some sort of selection criteria ** Selective school (New South Wales) See also * Selective breeding, the process of breeding for specific traits * Selection (other) Selection may refer to: Science * Selection (biology), also called natural selection, selection in evolution ** Sex selection, in genetics ** Mate selection, in mating ** Sexual selection in humans, in human sexuality ** Human mating strateg ... * Selectivity (other) * * {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. These enzymes catalysis, catalyze the chemical reaction : deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNAn pyrophosphate + DNAn+1. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the Directionality (molecular biology), three prime (3')-end of a DNA strand, one nucleotide at a time. Every time a Cell division, cell divides, DNA polymerases are required to duplicate the cell's DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each daughter cell. In this way, genetic information is passed down from generation to generation. Before replication can take place, an enzy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. As a result, kinase produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group (producing a dephosphorylated substrate and the high energy molecule of ATP). These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis. Kinases are part of the larger family of phosphotransferases. Kinases should not be confused with phosphorylases, which catalyze the addition of inorganic phosphate groups to an acceptor, nor with phosphatases, which remove phosphate groups (dephosphorylation). The phosphorylation state of a molecule, whether it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymidine Kinase
Thymidine kinase is an enzyme, a phosphotransferase (a kinase): 2'-deoxythymidine kinase, ATP-thymidine 5'-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.21. It can be found in most living cells. It is present in two forms in mammalian cells, TK1 and TK2. Certain viruses also have genetic information for expression of viral thymidine kinases. Thymidine kinase catalyzes the reaction: :Thd + ATP → TMP + ADP where Thd is (deoxy)thymidine, ATP is adenosine triphosphate, TMP is (deoxy) thymidine monophosphate and ADP is adenosine diphosphate. Thymidine kinases have a key function in the synthesis of DNA and therefore in cell division, as they are part of the unique reaction chain to introduce thymidine into the DNA. Thymidine is present in the body fluids as a result of degradation of DNA from food and from dead cells. Thymidine kinase is required for the action of many antiviral drugs. It is used to select hybridoma cell lines in production of monoclonal antibodies. In clinical chemistry it is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiviral Drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic (also termed antibacterial), antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to pharmacotherapy, treat infections. They should be distinguished from virucides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural virucides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees. Medical uses Most of the antiviral drugs now available are designed to help deal with HIV, Herpesviridae, herpes viruses, the hepatitis B and Hepatitis C, C viruses, and Influenzavirus A, influenza A and Influenzavirus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpes Labialis
A cold sore is a type of herpes infection caused by the herpes simplex virus that affects primarily the lip. Symptoms typically include a burning pain followed by small blisters or sores. The first attack may also be accompanied by fever, sore throat, and enlarged lymph nodes. The rash usually heals within ten days, but the virus remains dormant in the trigeminal ganglion. The virus may periodically reactivate to create another outbreak of sores in the mouth or lip. The cause is usually herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and occasionally herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). The infection is typically spread between people by direct non-sexual contact. Attacks can be triggered by sunlight, fever, psychological stress, or a menstrual period. Direct contact with the genitals can result in genital herpes. Diagnosis is usually based on symptoms but can be confirmed with specific testing. Prevention includes avoiding kissing or using the personal items of a person who is infec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodrug
A prodrug is a pharmacologically inactive medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be used to improve how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted (ADME). Prodrugs are often designed to improve bioavailability when a drug itself is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. A prodrug may be used to improve how selectively the drug interacts with cells or processes that are not its intended target. This reduces adverse or unintended effects of a drug, especially important in treatments like chemotherapy, which can have severe unintended and undesirable side effects. History Many herbal extracts historically used in medicine contain glycosides (sugar derivatives) of the active agent, which are hydrolyzed in the intestines to release the active and more bioavailable aglycone. For example, sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |