|
Deccani Urdu
Deccani ( ''dakanī'' or ''dakhanī''; also known as Deccani Urdu, Deccani Hindi, and Deccani Hindustani) is an Indo-Aryan language variety based on a form of Hindustani spoken in the Deccan region of south-central India and is the native language variety of the Deccani people. The historical form of Deccani sparked the development of Urdu literature during the late-Mughal period. Deccani arose as a ''lingua franca'' under the Delhi Sultanate and Bahmani Sultanates, as trade and migration from the north introduced Hindustani to the Deccan. It later developed a literary tradition under the patronage of the Deccan Sultanates. Deccani itself came to influence modern standard Urdu and later Hindi. The Deccani language has an Indo-Aryan core vocabulary, though it incorporated loanwords from Persian, which was the official language of the Deccan Sultanates. Additionally, Deccani differs from northern Hindustani sociolects due to archaisms retained from the medieval era, as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitab-i-Navras
''Kitab-i Nauras'' (), also transliterated as Kitab-e-Nauras, is a 16th-century treatise written by Sultan Ibrahim Adil Shah II of Bijapur. It was written with the title ''Nauras'', meaining ''Nine Rasas'', but was named as ''Nauras Nama'' or ''Kitab-i Nauras'' later. It is a collection of 59 Manqabat Kalaam (song) and 17 couplets in the Deccani language. Contents Introduction The introduction to the book was not written by Ibrahim; instead, it was written by the poet Muhammad Zuhuri in Persian rather than Deccani. Zuhuri states that the preface is "a worthless stone for the garland made of royal pearls". Songs In the ten known manuscripts, there are fifty-nine songs, although no single copy contains all of them. In addition, there are seventeen dohas. A significant portion of the songs are praises sung for Saraswati, Ganesha, and other Hindu deities. Others praise the prophet Muhammad and Sufi saint Bande Nawaz Syed Muhammad ibn Yousuf al-Hussaini (30 July 1321 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu Alphabet
The Urdu alphabet () is the right-to-left alphabet used for writing Urdu. It is a modification of the Persian alphabet, which itself is derived from the Arabic script. It has co-official status in the republics of Pakistan, India and South Africa. The Urdu alphabet has up to 39 or 40 distinct letters with no distinct letter cases and is typically written in the calligraphic Nastaʿlīq script, whereas Arabic is more commonly written in the Naskh style. Usually, bare transliterations of Urdu into the Latin alphabet (called Roman Urdu) omit many phonemic elements that have no equivalent in English or other languages commonly written in the Latin script. History The standard Urdu script is a modified version of the Perso-Arabic script and has its origins in the 13th century Iran. It is also related to Shahmukhi, used for the Punjabi language varieties in Punjab, Pakistan. It is closely related to the development of the Nastaliq style of Perso-Arabic script. Despite the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deccan Plateau
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura Range, Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound by the mountain ranges of the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats on the sides, which separate the region from the Western Coastal Plains, Western and Eastern Coastal Plains respectively. It covers most of the Indian States of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh excluding the coastal regions, and minor portions of Tamil Nadu and Kerala. The plateau is marked by rocky terrain with an average elevation of about . It is subdivided into Maharashtra Plateau, Karnataka Plateau, and Rayalaseema & Telangana Plateau. The Deccan Traps in the north west were formed by multiple layers of igneous rocks laid down by basaltic lava flows following a massive volcanic eruption that occurred during the end of the Cretaceous period (66 Millio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahmani Sultanate
The Bahmani Kingdom or the Bahmani Sultanate was a late medieval Persianate kingdom that ruled the Deccan plateau in India. The first independent Muslim sultanate of the Deccan, the Bahmani Kingdom came to power in 1347 during the rebellion of Ismail Mukh against Muhammad bin Tughlaq, the Sultan of Delhi. Ismail Mukh then abdicated in favour of Zafar Khan, who established the Bahmani Sultanate. The Bahmani Kingdom was perpetually at war with its neighbours, including its rival to the south, the Vijayanagara Empire, which outlasted the sultanate. The Mahmud Gawan Madrasa was created by Mahmud Gawan, the vizier regent who was prime minister of the sultanate from 1466 until his execution in 1481 during a conflict between the foreign (Afaqis) and local (Deccanis) nobility. Bidar Fort was built by Ahmad Shah I (), who relocated the capital to the city of Bidar. Ahmad Shah led campaigns against Vijayanagara and the sultanates of Malwa and Gujarat. His campaign against V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
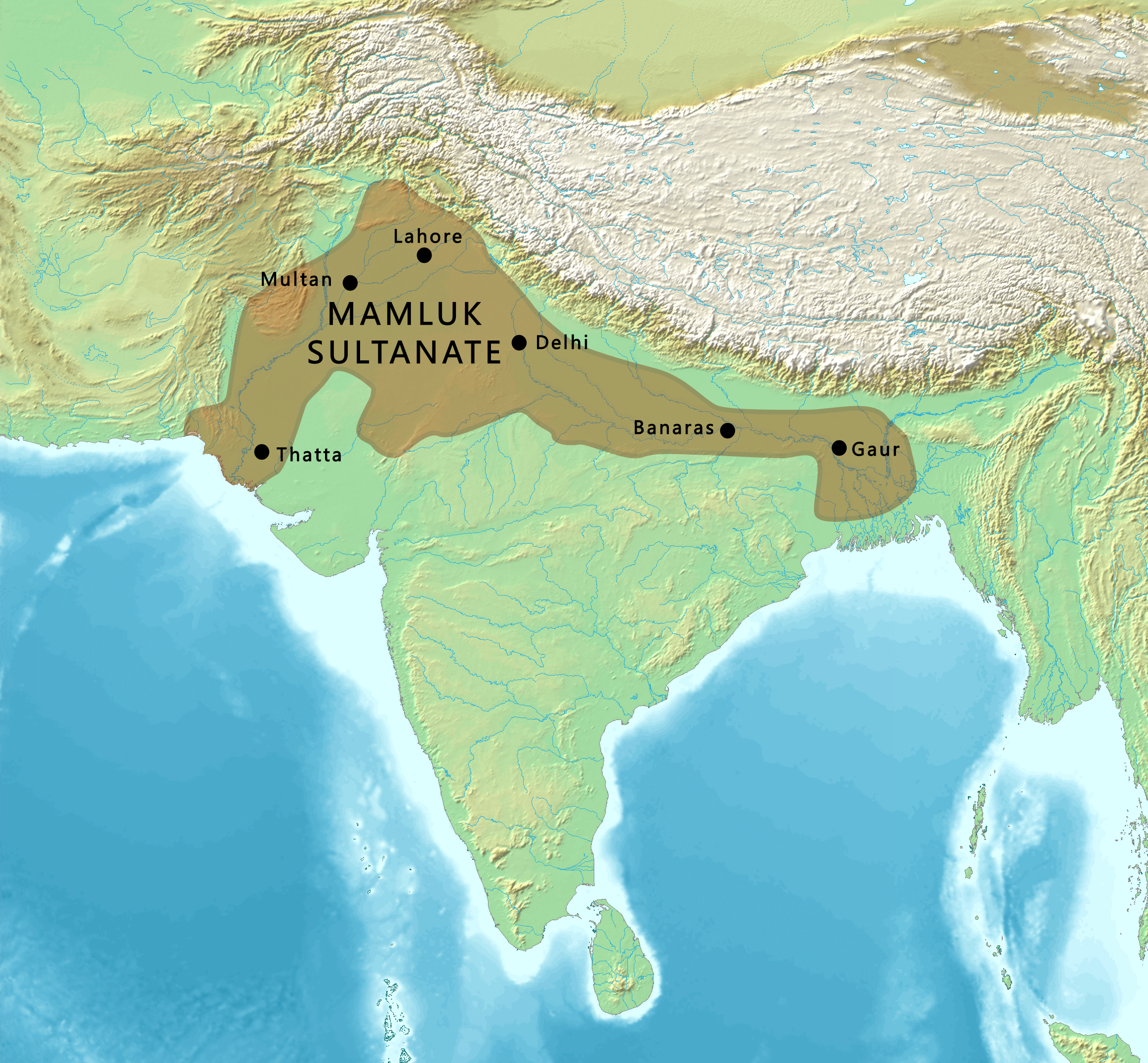
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingua Franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make communication possible between groups of people who do not share a First language, native language or dialect, particularly when it is a third language that is distinct from both of the speakers' native languages. Linguae francae have developed around the world throughout human history, sometimes for commercial reasons (so-called "trade languages" facilitated trade), but also for cultural, religious, diplomatic and administrative convenience, and as a means of exchanging information between scientists and other scholars of different nationalities. The term is taken from the medieval Mediterranean Lingua Franca, a Romance languages, Romance-based pidgin language used especially by traders in the Mediterranean Basin from the 11th to the 19th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan Plateau in South India.. Quote: "The realm so defined and governed was a vast territory of some , ranging from the frontier with Central Asia in northern Afghanistan to the northern uplands of the Deccan plateau, and from the Indus basin on the west to the Assamese highlands in the east." The Mughal Empire is conventionally said to have been founded in 1526 by Babur, a Tribal chief, chieftain from what is today Uzbekistan, who employed aid from the neighboring Safavid Iran, Safavid and Ottoman Empires Quote: "Babur then adroitly gave the Ottomans his promise not to attack them in return for their military aid, which he received in the form of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu Literature
Urdu literature (, ) comprises the literary works, written in the Urdu language. While it tends to be dominated by poetry, especially the verse forms of the ''ghazal'' () and '' nazm'' (), it has expanded into other styles of writing, including the short story, or ''afsana'' (). Urdu literature is popular mostly in Pakistan, where Urdu is the national language, and in India, where it is an Eighth Schedule language. Origin Urdu developed during the 12th to 13th centuries, although the name "Urdu" did not exist at the time for the language. Amir Khusrau, who lived in the thirteenth century, wrote and gave shape to the Rekhta dialect (the Persianized combination of Hindavi), which was the early form of Modern Standard Urdu. He was thus called, the "father of Urdu literature". The continuing traditions of Islam and patronizations of foreign culture centuries earlier by Muslim rulers, usually of Turkic or Afghan descent, marked their influence on the Urdu language given that both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times Of India
''The Times of India'' (''TOI'') is an Indian English-language daily newspaper and digital news media owned and managed by the Times Group. It is the List of newspapers in India by circulation, third-largest newspaper in India by circulation and List of newspapers by circulation, largest selling English-language daily in the world. It is the oldest English-language newspaper in India, and the second-oldest Indian newspaper still in circulation, with its first edition published in 1838. It is nicknamed as "The Old Lady of Bori Bunder", and is a newspaper of record. Near the beginning of the 20th century, Lord Curzon, the Viceroy of India, called ''TOI'' "the leading paper in Asia". In 1991, the BBC ranked ''TOI'' among the world's six best newspapers. It is owned and published by Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. (BCCL), which is owned by the Sahu Jain family. In the Brand Trust Report India study 2019, ''TOI'' was rated as the most trusted English newspaper in India. In a 2021 surve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deccani Muslims
The Deccanis or Deccani people are an Indo-Aryan ethno-religious community of Deccani-speaking Muslims who inhabit or are from the Deccan region of India. The community traces its origins to the shifting of the Delhi Sultanate's capital from Delhi to Daulatabad in 1327 during the reign of Muhammad bin Tughluq. Further ancestry can also be traced from immigrant Muslims referred to as Afaqis, also known as Pardesis who came from Central Asia, Iraq and Iran and had settled in the Deccan region during the Bahmani Sultanate (1347). The migration of Muslim Hindavi-speaking people to the Deccan and intermarriage with the local Hindus who converted to Islam, led to the creation of a new community of Hindustani-speaking Muslims, known as the Deccani, who would come to play an important role in the politics of the Deccan. Their language, Deccani, emerged as a language of linguistic prestige and culture during the Bahmani Sultanate, further evolving in the Deccan Sultanates. Following t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variety (linguistics)
In sociolinguistics, a variety, also known as a lect or an isolect, is a specific form of a language or language cluster. This may include languages, dialects, registers, styles, or other forms of language, as well as a standard variety.Meecham, Marjorie and Janie Rees-Miller. (2001) "Language in social contexts." In W. O'Grady, J. Archibald, M. Aronoff and J. Rees-Miller (eds) ''Contemporary Linguistics''. pp. 537-590. Boston: Bedford/St. Martin's. The use of the word ''variety'' to refer to the different forms avoids the use of the term ''language'', which many people associate only with the standard language, and the term ''dialect'', which is often associated with non-standard language forms thought of as less prestigious or "proper" than the standard.Schilling-Estes, Natalies. (2006) "Dialect variation." In R.W. Fasold and J. Connor-Linton (eds) ''An Introduction to Language and Linguistics''. pp. 311-341. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Linguists speak of both s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Language
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east of the Indus river in Bangladesh, Northern India, Eastern Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives and Nepal. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages. Modern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Old Indo-Aryan languages such as early Vedic Sanskrit, through Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Prakrits). The largest such languages in terms of first-speakers are Hindi–Urdu (),Standard Hindi first language: 260.3 million (2001), as second language: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |