|
Dean, Cumbria
Dean is a village and civil parish in the county of Cumbria, England. Dean has a Church of England school, a church called St Oswald's. Nearby settlements include the towns of Workington and Cockermouth. Location Dean is located in Cumberland, in the west of Cumbria in the North West of England. It is situated south-west of Cockermouth, on a minor road off the A5086. It is about west of the nearest part of the Lake District National Park. The nearest tourist information centre is in Cockermouth. The village The village contains The Royal Yew Inn, a traditional country pub. Dean is also home to the Dean Church of England Primary School, which also serves three other small villages. Dean is situated in fertile farming land; it has existed for a long time, dating back to the 12th century through the evidence of the 12th century church, and a grammar school founded in 1596. Forms of agriculture in the 19th century include wheat, oats and potatoes. The Curwens of Workington a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumberland (unitary Authority)
Cumberland is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Cumbria, England, and a non-metropolitan county and Districts of England, district. It borders Scotland, Northumberland, Westmorland and Furness, and the Irish Sea. Part of the area is in the Lake District National Park and notable landmarks include Carlisle Cathedral, Carlisle Castle and Hadrian's Wall. In comparison to the Cumberland, historic county of Cumberland that existed before 1974, the district covers 77% of its area (excluding Penrith, Cumbria, Penrith area) and 90% of its population. When created, in April 2023, it took over the northern and western part of the 1974–2023 Cumbria non-metropolitan county's administration and the corresponding former Allerdale, City of Carlisle, Carlisle and Borough of Copeland, Copeland districts, while the new Westmorland and Furness unitary authority took over the remainder. History Elections to Cumbria County Council were due to take place in May 2021 but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ullock
Ullock is a village in Cumbria, England, located at National Grid reference NY076239, approximately south west of Cockermouth and south east of Workington. The River Marron flows through the village. It is located just outside the Lake District National Park. In 1870-72 the township had a population of 353. The village was once served by Ullock railway station on the Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway. Governance Ullock is in the parliamentary constituency of Whitehaven and Workington. The former Labour MP for what was the neighbouring constituency of Workington from 2015-2019, Sue Hayman, was elevated to the House of Lords in 2020 under the title ''Baroness Hayman of Ullock''. For Local Government purposes it is in the Cumberland unitary authority area A unitary authority is a type of local authority in New Zealand and the United Kingdom. Unitary authorities are responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Wales
North Wales ( ) is a Regions of Wales, region of Wales, encompassing its northernmost areas. It borders mid Wales to the south, England to the east, and the Irish Sea to the north and west. The area is highly mountainous and rural, with Snowdonia, Snowdonia National Park ( and the Clwydian Range and Dee Valley (), known for its mountains, waterfalls and trails, wholly within the region. Its population is concentrated in the North East Wales, north-east and northern coastal areas, with significant Welsh-speaking populations in its North West Wales, western and rural areas. North Wales is imprecisely defined, lacking any exact definition or administrative structure. It is commonly defined administratively as its six most northern Principal areas of Wales, principal areas, but other definitions exist, with Montgomeryshire historically considered to be part of the region. Those from North Wales are sometimes referred to as "Gogs" (); in turn, those from South Wales are sometimes cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
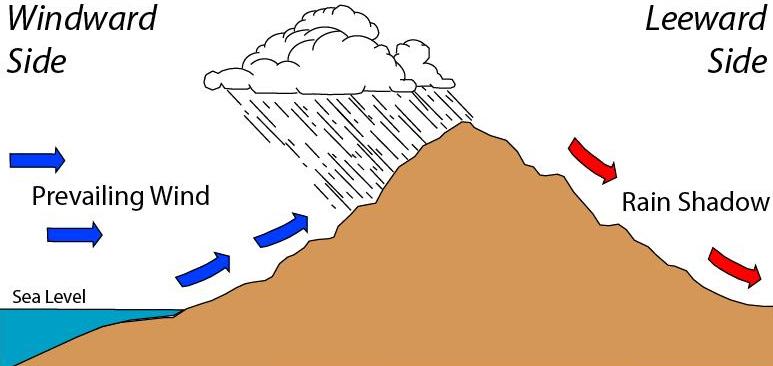
Rain Shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from body of water, bodies of water (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing sea breeze, onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is orographic lift, driven upslope towards the summit, peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to Precipitation, precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing Foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of arid, dry climate region behind the ridge, mountain crests. This climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drier
Dryer (or drier) may refer to: Drying equipment * Hair dryer * Hand dryer * Clothes dryer, also known as a tumble-dryer * Belt dryer * Desiccant, a substance that absorbs or adsorbs water * Grain dryer, for storage grain bins * Oil drying agent, an additive which accelerates the film formation of a drying oil Other * Dryer (surname) * Dryer (band), a Saratoga Springs, NY based band See also * * * Drying * Dreier (other) Dreier is German for "three-er" and may refer to: * Dreier (coin), an historical German coin * Dreier (Königrufen), a contract in the Tarot game of Königrufen * Dreier (surname), people with the surname * Dreier (Tapp Tarock), a contract in t ... * Dreyer {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature dates from the mid-7th century. After the Norman Conquest of 1066, English was replaced for several centuries by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, type of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during the subsequent period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into what is now known as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles (tribe), Angles, Saxons and Jutes. As the Germanic settlers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calciferous Sandstone
Calciferous sandstone is an obsolete geological term relating to strata at the base of the Carboniferous formation, below the coal measures. The rocks of this formation are now considered part of the Inverclyde Group and Strathclyde Group. Typically this geological sequence, as in the Touch Hills and Fintry Hills to the west of Stirling contains a mixture of lavas and sedimentary rocks, including sandstone and mudstone, and lies unconformably on top of older Devonian The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ... strata. References Carboniferous geology {{UK-geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calder Abbey
Calder Abbey in Cumbria was a Savigniac monastery founded in 1134 by Ranulph de Gernon, 2nd Earl of Chester, and moved to this site following a refoundation in 1142. It became Cistercian in 1148. It is near the village of Calderbridge. History Ranulf de Gernon (also known as Ranulph le Meschines) founded the abbey on 10 January 1134, and gave a site and a mill to the monks. It was a wooden building and occupied by twelve Savigniac monks from Furness Abbey under the abbot Gerold. Only four years later, in the midst of the political instability following the death of Henry I, David King of Scots sent Scottish raiders under William Fitz Duncan to raid the northern English counties. Calder Abbey was one of the victims, and the Scots raided they despoiled the Abbey and drove out the monks. This, and the poor endowment, led the monks to abandon the site, and they sought sanctuary at Furness Abbey. However, as Abbot Gerold would not resign his abbacy, a dispute arose and they we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross
A cross is a religious symbol consisting of two Intersection (set theory), intersecting Line (geometry), lines, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a saltire in heraldic terminology. The cross shape has been widely officially recognized as an absolute and exclusive religious symbol of Christianity from an early period in that religion's history.''Christianity: an introduction'' by Alister E. McGrath 2006 pages 321-323 Before then, it was used as a religious or cultural symbol throughout Europe, in West Asia, west and south Asia (the latter, in the form of the original Swastika); and in Ancient Egypt, where the Ankh was a hieroglyph that represented "life" and was used in the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preaching
A sermon is a religious discourse or oration by a preacher, usually a member of clergy. Sermons address a scriptural, theological, or moral topic, usually expounding on a type of belief, law, or behavior within both past and present contexts. Elements of the sermon often include Expository preaching, exposition, exhortation, and practical application. The act of delivering a sermon is called preaching. In secular usage, the word ''sermon'' may refer, often disparagingly, to a lecture on morals. In Christianity, Christian practice, a sermon is usually preached to a church (congregation), congregation in a place of worship, either from an elevated architectural feature, known as a pulpit or an ambon (liturgy), ambo, or from behind a lectern. The word ''sermon'' comes from a Middle English word which was derived from Old French, which in turn originates from the Latin word meaning 'discourse.' A ''sermonette'' is a short sermon (usually associated with television broadcasting, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulpit
A pulpit is a raised stand for preachers in a Christian church. The origin of the word is the Latin ''pulpitum'' (platform or staging). The traditional pulpit is raised well above the surrounding floor for audibility and visibility, accessed by steps, with sides coming to about waist height. From the late Middle Ages, late medieval period onwards, pulpits have often had a canopy known as the sounding board, ''tester'' or ''abat-voix'' above and sometimes also behind the speaker, normally in wood. Though sometimes highly decorated, this is not purely decorative, but can have a useful acoustic effect in projecting the preacher's voice to the Church (congregation), congregation below, especially prior to the invention of modern audio equipment. Most pulpits have one or more book-stands for the preacher to rest his bible, notes or texts upon. The pulpit is generally reserved for clergy. This is mandated in the regulations of the Catholic Church, and several others (though not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |