|
De Oratore
''De Oratore'' (''On the Orator'') is a dialogue written by Cicero in 55 BC. It is set in 91 BC, when Lucius Licinius Crassus dies, just before the Social War and the civil war between Marius and Sulla, during which Marcus Antonius, the other great orator of this dialogue, dies. During this year, the author faces a difficult political situation: after his return from exile in Dyrrachium (modern Albania), his house was destroyed by the gangs of Clodius in a time when violence was common. This was intertwined with the street politics of Rome. Amidst the moral and political decadence of the state, Cicero wrote ''De Oratore'' to describe the ideal orator and imagine him as a moral guide of the state. He did not intend ''De Oratore'' as merely a treatise on rhetoric, but went beyond mere technique to make several references to philosophical principles. Cicero believed that the power of persuasion—the ability to verbally manipulate opinion in crucial political decisions—was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialogue
Dialogue (sometimes spelled dialog in American and British English spelling differences, American English) is a written or spoken conversational exchange between two or more people, and a literature, literary and theatrical form that depicts such an exchange. As a philosophy, philosophical or didactic device, it is chiefly associated in the West with the Socratic dialogue as developed by Plato, but antecedents are also found in other traditions including Indian literature. Etymology The term ''dialogue'' stems from the Greek language, Greek (, ); its roots are (, ) and (, ). The first extant author who uses the term is Plato, in whose works it is closely associated with the art of dialectic. Latin took over the word as . As genre Antiquity Dialogue as a genre in the Middle East and Asia dates back to ancient works, such as Sumerian disputations preserved in copies from the late third millennium BC, Rigvedic dialogue hymns, and the ''Mahabharata''. In the West, Plato ( BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Triumvirate
The First Triumvirate was an informal political alliance among three prominent politicians in the late Roman Republic: Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, Marcus Licinius Crassus, and Gaius Julius Caesar. The republican constitution had many veto points. In order to bypass constitutional obstacles and force through the political goals of the three men, they forged an alliance in secret where they promised to use their respective influence to support each other. The "triumvirate" was not a formal magistracy, nor did it achieve a lasting domination over state affairs. It was formed among the three men due to their mutual need to overcome opposition in the senate against their proposals in the previous years. Initially secret, it emerged publicly during Caesar's first consulship in 59 BC to push through legislation for the three allies. Caesar secured passage of an agrarian law which helped resettle Pompey's veterans, a law ratifying Pompey's settlements after the Third Mithridatic War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solon
Solon (; ; BC) was an Archaic Greece#Athens, archaic History of Athens, Athenian statesman, lawmaker, political philosopher, and poet. He is one of the Seven Sages of Greece and credited with laying the foundations for Athenian democracy.Stanton, G. R. ''Athenian Politics c. 800–500 BC: A Sourcebook'', Routledge, London (1990), p. 76.E. Harris, "A New Solution to the Riddle of the Seisachtheia", in ''The Development of the Polis in Archaic Greece'', eds. L. Mitchell and P. Rhodes (Routledge 1997) 103 Solon's efforts to legislate against political, economic and moral declineAristotle, ''Politics'', 1273b 35–1274a 21 resulted in his Solonian Constitution, constitutional reform overturning most of Draco (lawgiver), Draco's Draconian constitution, laws. Solon's reforms included debt relief later known and celebrated among Athenians as the (shaking off of burdens). He is described by Aristotle in the ''Constitution of the Athenians (Aristotle), Athenian Constitution'' as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
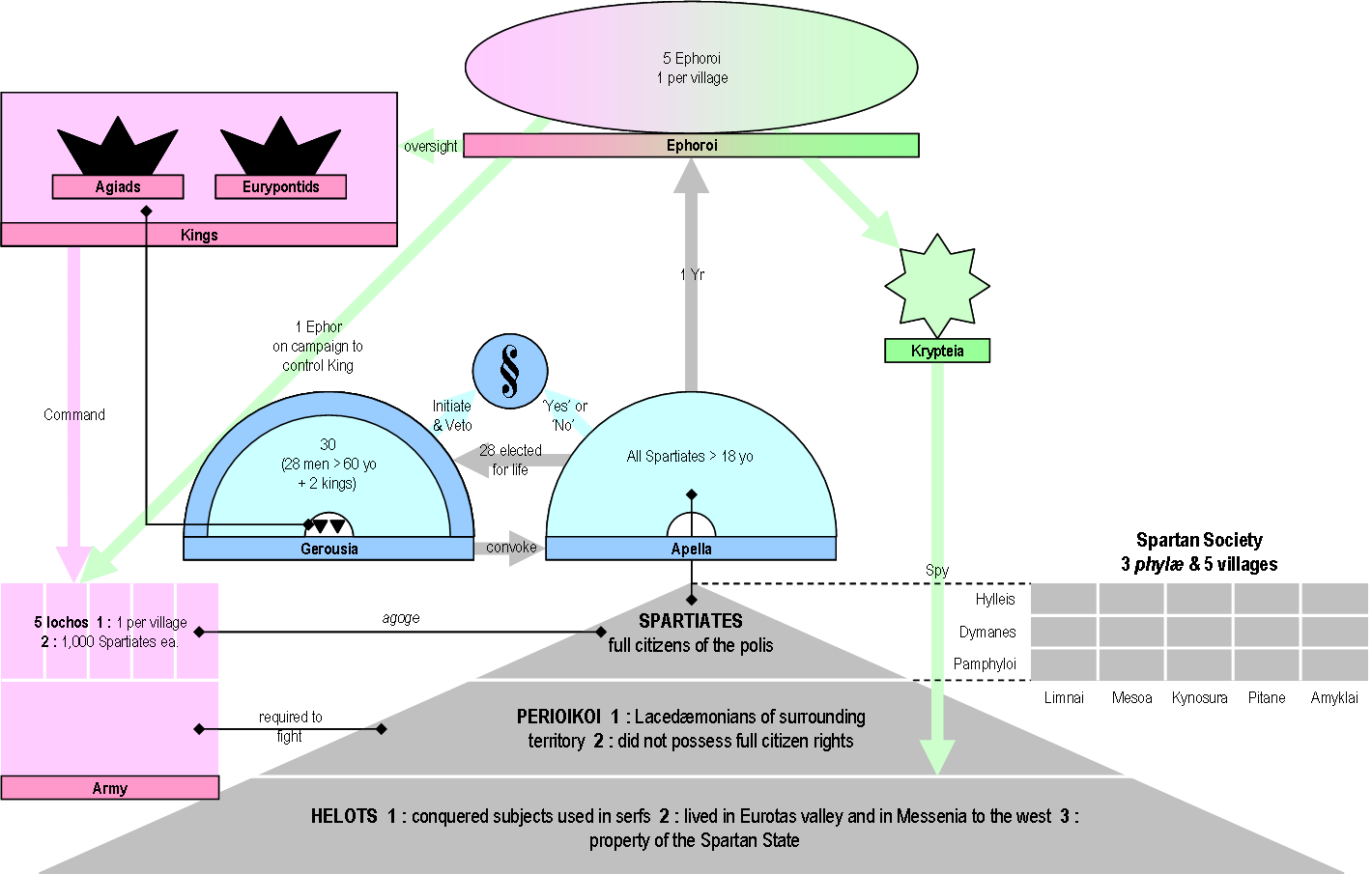
Lycurgus Of Sparta
Lycurgus (; ) was the legendary lawgiver of Sparta, credited with the formation of its (), involving political, economic, and social reforms to produce a military-oriented Spartan society in accordance with the Pythia, Delphic oracle. The Spartans in the historical period honoured him as a god. As a historical figure, almost nothing is known for certain about him, including when he lived and what he did in life. The stories of him place him at multiple times. Nor is it clear when the political reforms attributed to him, called the Great Rhetra, occurred. Ancient dates range from – putting aside the implausibly early Xenophonic 11th century BC – the early ninth century () to as late as early eighth century (). There remains no consensus as to when he lived; some modern scholars deny that he existed at all. The reforms at various times attributed to him touch all aspects of Spartan society. They included the creation of the Spartan constitution (in most trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; ; c. 371 – c. 287 BC) was an ancient Greek Philosophy, philosopher and Natural history, naturalist. A native of Eresos in Lesbos, he was Aristotle's close colleague and successor as head of the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum, the Peripatetic school, Peripatetic school of philosophy in Athens. Theophrastus wrote numerous treatises across all areas of philosophy, working to support, improve, expand, and develop Aristotelian system, the Aristotelian system. He made significant contributions to various fields, including ethics, metaphysics, botany, and natural history. Often considered the "father of botany" for his groundbreaking works "Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus), Enquiry into Plants" () and "On the Causes of Plants", () Theophrastus established the foundations of Botany, botanical science. His given name was (Ancient Greek: ); the nickname Theophrastus ("divine speaker") was reputedly given to him by Aristotle in recognition of his eloquent style. He came to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, and the arts. As the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy in the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum in Athens, he began the wider Aristotelianism, Aristotelian tradition that followed, which set the groundwork for the development of modern science. Little is known about Aristotle's life. He was born in the city of Stagira (ancient city), Stagira in northern Greece during the Classical Greece, Classical period. His father, Nicomachus (father of Aristotle), Nicomachus, died when Aristotle was a child, and he was brought up by a guardian. At around eighteen years old, he joined Plato's Platonic Academy, Academy in Athens and remained there until the age of thirty seven (). Shortly after Plato died, Aristotle left Athens and, at the request ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgias
Gorgias ( ; ; – ) was an ancient Greek sophist, pre-Socratic philosopher, and rhetorician who was a native of Leontinoi in Sicily. Several doxographers report that he was a pupil of Empedocles, although he would only have been a few years younger. W. K. C. Guthrie writes that "Like other Sophists, he was an itinerant that practiced in various cities and giving public exhibitions of his skill at the great pan-Hellenic centers of Olympia and Delphi, and charged fees for his instruction and performances. A special feature of his displays was to ask miscellaneous questions from the audience and give impromptu replies." W. K. C. Guthrie, ''The Sophists'' (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1971), p. 270. He has been called "Gorgias the Nihilist", although the degree to which this epithet adequately describes his philosophy is controversial.Rosenkrantz, G. (2002). The Possibility of Metaphysics: Substance, Identity, and Time*. Philosophy and Phenomenological Research, 64(3), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaedrus (dialogue)
The ''Phaedrus'' (; ), written by Plato, is a dialogue between Socrates and Phaedrus (Athenian), Phaedrus, an interlocutor in several dialogues. The ''Phaedrus'' was presumably composed around 370 BC, about the same time as Plato's ''Republic (Plato), Republic'' and ''Symposium (Plato dialogue), Symposium''. Although ostensibly about the topic of love, the discussion in the dialogue revolves around the art of rhetoric and how it should be practiced, and dwells on subjects as diverse as metempsychosis (the Greek tradition of reincarnation) and erotic love, and the nature of the human soul shown in the famous chariot allegory. Setting Socrates runs into Phaedrus (Athenian), Phaedrus on the outskirts of Athens. Phaedrus has just come from the home of Epicrates of Athens, where Lysias, son of Cephalus, has given a speech on love. Socrates, stating that he is "sick with passion for hearing speeches", walks into the countryside with Phaedrus. Socrates is hoping that Phaedrus will repea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the written dialogue and dialectic forms. He influenced all the major areas of theoretical philosophy and practical philosophy, and was the founder of the Platonic Academy, a philosophical school in History of Athens, Athens where Plato taught the doctrines that would later become known as Platonism. Plato's most famous contribution is the theory of forms, theory of forms (or ideas), which aims to solve what is now known as the problem of universals. He was influenced by the pre-Socratic thinkers Pythagoras, Heraclitus, and Parmenides, although much of what is known about them is derived from Plato himself. Along with his teacher Socrates, and his student Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Western philosophy. Plato's complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Sulpicius Rufus
Publius Sulpicius Rufus (124–88 BC) was a Roman politician and orator whose attempts to pass controversial laws with the help of mob violence helped trigger the first civil war of the Roman Republic. His actions kindled the deadly rivalry between Gaius Marius and Sulla, and provided the pretext for Sulla's unexpected March on Rome (88 BC), march on Rome. Life Background and early career Publius Sulpicius Rufus was probably born in 124 BC. His precise background is unclear: It is unknown if he was related to the jurist and near-contemporary Servius Sulpicius Rufus, and, like him, he might not have been a patrician (ancient Rome), patrician, despite their matching family names. It is likely, nevertheless, that he was of high birth, as he was personally acquainted to some of the most important aristocrats of the day. These included the orators Lucius Licinius Crassus and Marcus Antonius (orator), Marcus Antonius, of whom Sulpicius was a close friend as well as disciple. Sulpicius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintus Mucius Scaevola Augur
Quintus Mucius Scaevola Augur (c. 169 – 88 BC) was a politician of the Roman Republic, Stoic, and an early authority on Roman law. He was first educated in law by his father (whose name he shared) and in philosophy by the Stoic Panaetius of Rhodes. Both Augur and his relative Quintus Mucius Scaevola Pontifex, father-in-law of Pompey, were prominent Optimates. Scaevola was made tribune in 128 BC, aedile in 125, and praetor in 121, in which capacity he acted as governor of Asia. Upon his return to Rome the following year he faced a charge of extortion brought by Titus Albucius (probably on personal grounds) which he successfully defended. In 117, he was elected consul. In his old age, Scaevola vigorously maintained his interest in the law and in the affairs of Rome. He also passed on his knowledge of law to some of Rome's most celebrated orators, as the teacher of Cicero and Atticus. In 88 BC, he alone defended Gaius Marius against Sulla's motion to have him named an enemy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Livius Drusus (tribune)
Marcus Livius Drusus (before 122 BC – 91 BC) was a Roman politician and reformer. He is most famous for his legislative programme during his term as tribune of the plebs in 91 BC. During his year in office, Drusus proposed wide-ranging legislative reforms, including offering citizenship to Rome's Italian allies. The failure of these reforms, and Drusus' subsequent murder at the hands of an unknown assassin in late 91 BC, are often seen as an immediate cause of the Social War. Early life Marcus Livius Drusus was born before 122 or 124 BC. He was the son of Cornelia (precise identity unknown) and the Marcus Livius Drusus who had served as tribune in 122 BC, consul in 112 BC, and censor in 109 BC. His father died in office during his censorship in 109. If the younger Marcus was the eldest son, he would now have become the '' pater familias'' of the Drusi and the provider for his two siblings, Mamercus and Livia. However, certain scholars beli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |