|
Quintus Mucius Scaevola Augur
Quintus Mucius Scaevola Augur (c. 169 – 88 BC) was a politician of the Roman Republic and an early authority on Roman law. He was first educated in law by his father (whose name he shared) and in philosophy by the stoic Panaetius of Rhodes. Scaevola was made tribune in 128 BC, aedile in 125, and praetor in 121, in which capacity he acted as governor of Asia. Upon his return to Rome the following year he faced a charge of extortion brought by Titus Albucius (probably on personal grounds) which he successfully defended. In 117, he was elected consul. In his old age, Scaevola vigorously maintained his interest in the law and in the affairs of Rome. He also passed on his knowledge of law to some of Rome's most celebrated orators, as the teacher of Cicero and Atticus. In 88 BC, he defended Gaius Marius against Sulla's motion to have him named an enemy of the people, saying that he would never agree to have this done to a man who had saved Rome. Cicero used the persona of his o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
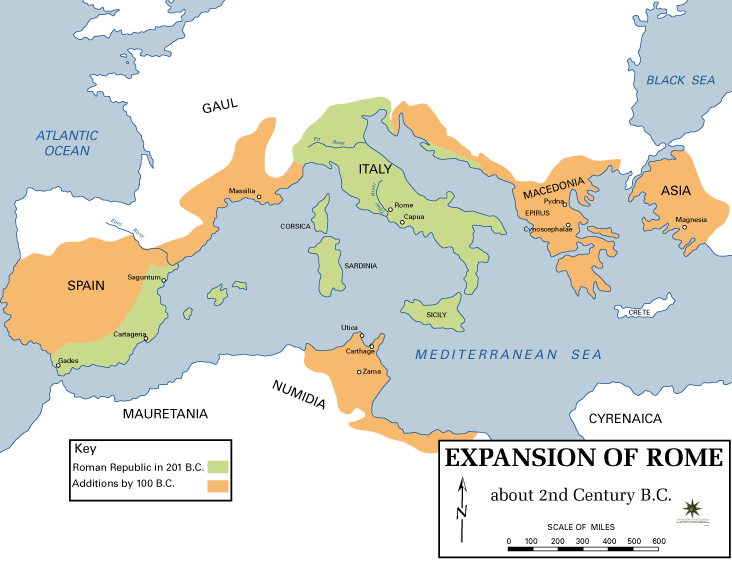
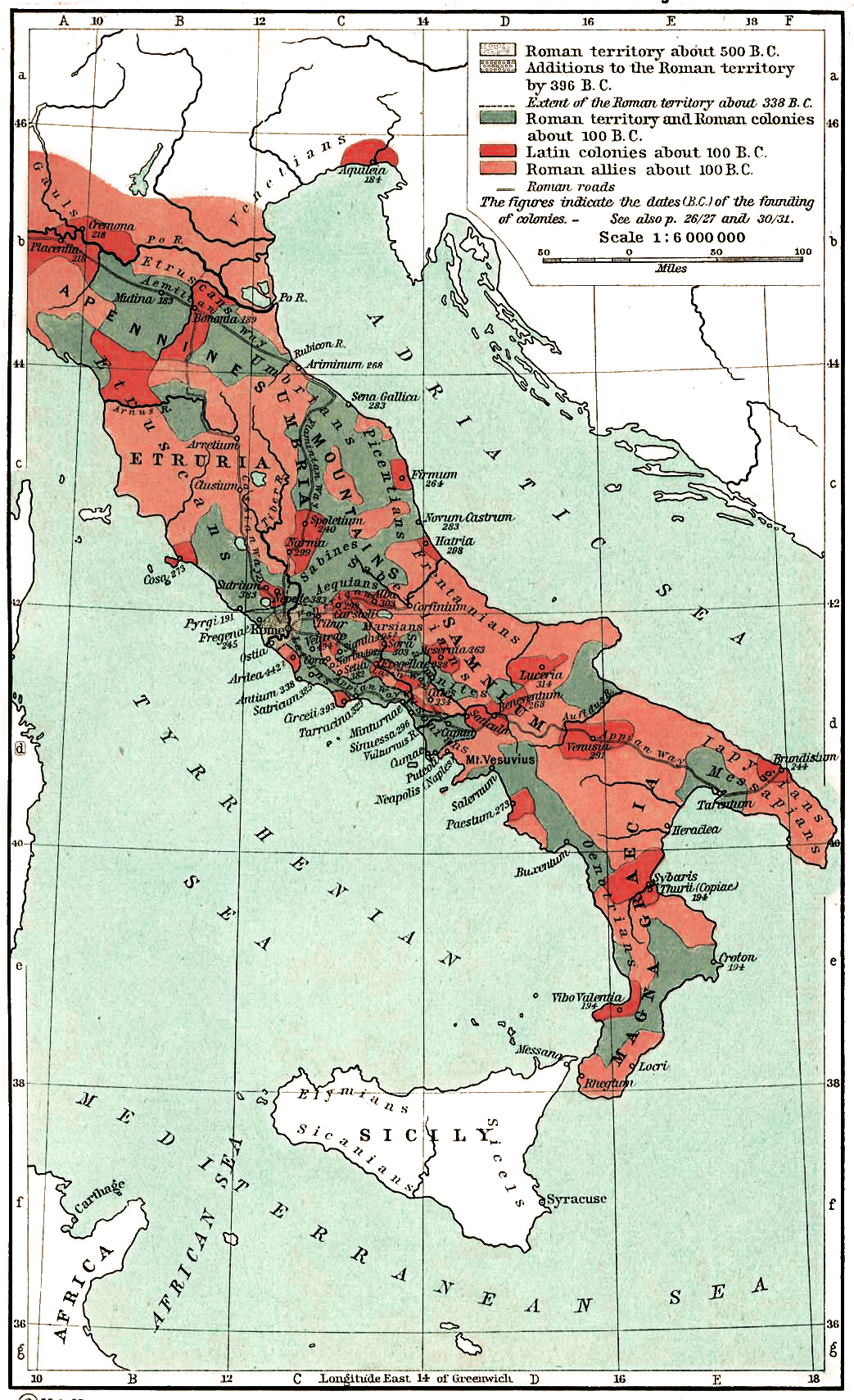
Social War (91–87 BC)
The Social War (from Latin , properly 'war of the allies'), also called the Italian War or the Marsic War, was fought from 91 to 87 BC between the Roman Republic and several of its autonomous allies () in Italy. The Italian allies wanted Roman citizenship, not only for the status and influence that came with it, but also for the right to vote in Roman elections and laws. They believed that they should be treated equally to the Romans, given that they had formed cultural and linguistic connections with the Roman civilization, and had been their loyal allies for over two centuries. The Romans strongly opposed their demands, and refused to grant them citizenship, thus leaving the ''socii'' with fewer rights and privileges. The situation escalated in 91 BC, leading to the outbreak of a devastating war, in which many of the Italian allies, headed by the Samnites and the Marsi, staged a four-year revolt against Roman rule. Most of the Etruscan, Umbrian and Latin allies did not j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Amicitia
''Laelius de Amicitia'' (or simply ''De Amicitia'') is a treatise on friendship (''amicitia'') by the Roman statesman and author Marcus Tullius Cicero, written in 44 BC. Background The work is written as a dialogue between prominent figures of the Middle Roman Republic and is set after the death of the younger Scipio Africanus (otherwise known as Scipio Aemilianus, Scipio Africanus Minor or Scipio the Younger) in 129 BC. The interlocutors of the dialogue chosen by Cicero are Gaius Laelius, a close friend of the late statesman, and Laelius's two sons-in-law, Gaius Fannius, and Quintus Mucius Scaevola. Cicero in his youth knew Scaevola, and states that Scaevola described to him the substance of the conversation on Friendship which he and Fannius had held with Laelius a few days after the death of Scipio. ''De Amicitia'' is addressed to Atticus, who, as Cicero tells him in his dedication, could not fail to discover his own portrait in the study of a perfect friend. Summary In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintus Marcius Rex (consul 118 BC)
Quintus Marcius Rex was a member of the ''Marcii Reges'', the family founded by the Roman King Ancus Marcius. His father Quintus Marcius Rex, the praetor in 144 BC, built the Aqua Marcia aqueduct, the longest aqueduct of ancient Rome. The aqueduct was known for its water purity and its cold temperature. Marcius carried on a war against the Stoeni, a Ligurian people at the foot of the Alps, and obtained a triumph in the following year on account of his victories over them. During his consulship in 118 BC, Marcius lost his only son, a youth of great promise, but had such mastery over his feelings as to meet the senate on the day of his son's burial, and perform his regular official duties. His sister Marcia was the mother of Sextus Julius Caesar; Julia, wife of Gaius Marius; and Gaius Julius Caesar, father of Julius Caesar the dictator. Through his son, possibly named Quintus Marcius Rex, he had a grandson also named Quintus Marcius Rex, who was the consul in 68 BC. Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Porcius Cato (consul 118 BC)
Marcus Porcius Cato (died 118 BC) was a member of the Roman plebeian gens Porcii and consul in 118 BC. Marcus Porcius Cato was the elder son of Marcus Porcius Cato Licinianus and the grandson of the famous conservative Roman politician Cato the Elder. Nothing is known about his early life. In 121 BC at the latest he was praetor. In 118 BC he became consul; his colleague was Quintus Marcius Rex. He went to Africa, perhaps to settle the dispute between the heirs of king Micipsa of Numidia, the son of Masinissa Masinissa ( nxm, , ''MSNSN''; ''c.'' 238 BC – 148 BC), also spelled Massinissa, Massena and Massan, was an ancient Numidian king best known for leading a federation of Massylii Berber tribes during the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), ulti ..., but Cato died during his consulate. Cato was a powerful orator. He left some posthumous speeches, which were preserved for some time.Aulus Gellius, ''Noctes Atticae'' 13.20.10 Notes References *Franz Miltner: ''Porcius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Gracchus
Gaius Sempronius Gracchus ( – 121 BC) was a reformist Roman politician in the 2nd century BC. He is most famous for his tribunate for the years 123 and 122 BC, in which he proposed a wide set of laws, including laws to establish colonies outside of Italy, engage in further land reform, reform the judicial system, and create a subsidised grain supply for Rome. The year after his tribunate, his political enemies used political unrest – which he and his political allies had caused – as an excuse to declare martial law and march on his supporters, leading to his death. After his death, his political allies were purged in a series of trials, but most of his legislation was undisturbed. His brother was the reformer Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus. Both were the sons of the Gracchus who was consul in 177 and 163 BC. Background Gaius Gracchus was born into a very well-connected political family. His father, Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus, was a very successf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Licinia
Licinia is the name used by ancient Roman women of the '' gens Licinia''. Known individuals Daughter of Gaius Licinius Varus Licinia (flourished 188 BC–180 BC) was the daughter of Gaius Licinius Varus and the sister of Publius Licinius Crassus (consul 171 BC) and Gaius Licinius Crassus (consul 168 BC). She married Publius Mucius Scaevola (consul 175 BC) and bore him at least two sons Publius Mucius Scaevola and Publius Licinius Crassus Dives Mucianus. The younger son was adopted by her elder brother as his heir. Both sons were well-educated and both became Pontifex Maximus successively. Wife of Claudius Asellus Licinia (died 153 BC), a woman killed by her relatives in 153 BC for allegedly murdering her husband Claudius Asellus; another woman similarly accused was Publicia, wife of the consul Lucius Postumius Albinus (consul 154 BC). Both women assigned real estate as bail to the urban praetor, but were killed (strangled) by their relatives before coming to trial. Daughter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Mucius Scaevola (pontifex Maximus)
Publius Mucius Scaevola (c. 176 BC115 BC) was a prominent Roman politician and jurist who was consul in 133 BC. In his earlier political career he served as tribune of the plebs in 141 BC and praetor in 136 BC. He also held the position of '' pontifex maximus'' for sixteen years after his consulship. He died around 115 BC. Scaevola was consul at the time of Tiberius Gracchus' tribuneship and murder, and was heavily involved in reconciling the Senate following Gracchus' death. According to Cicero, Scaevola supported Gracchus' land reforms (''Lex Sempronia Agraria''), but the extent of his involvement has been debated by some historians. Family Publius belonged to the gens Mucia, a noble plebeian family of Rome, of which the Scaevolae were the main branch. Several Scaevolae appear in Roman magistracies before the appearance of Publius Mucius, including a certain Publius Mucius Scaevola who served as a tribune of the plebs in 486 BC and a Publius Mutius Scaevola—who, while not of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Licinius Crassus Dives Mucianus
Publius Licinius Crassus Dives Mucianus (c. 180 BC – 130 BC) was the natural son of Publius Mucius Scaevola and Licinia, and brother of Publius Mucius Scaevola. He was adopted at an unknown date by Publius Licinius Crassus (consul 171 BC), his mother's brother, or (although improbable) by a son of the consul of 205 BC, Publius Licinus Crassus Dives. Career Mucianus became Pontifex Maximus in 132 BC after the death of the exiled Pontifex Publius Cornelius Scipio Nasica Serapio. In 131 BC he was elected consul along with Lucius Valerius Flaccus, the Flamen Martialis. Mucianus forbade his colleague to fight against Aristonicus and fined him for neglecting his sacred duties. The people remitted the fine but wished Flaccus to submit to his religious superior. Mucianus, nevertheless, went to fight Aristonicus, who had occupied the kingdom of Pergamum, after it had been left to Rome in the will of Attalus III. He was the first Pontifex Maximus to leave Italy voluntarily (w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Licinius Crassus
Lucius Licinius Crassus (140–91 BC) was a Roman orator and statesman. He was considered the greatest orator of his day, most notably by his pupil Cicero. Crassus is also famous as one of the main characters in Cicero's work '' De Oratore'', a dramatic dialogue on the art of oratory set just before Crassus' death in 91 BC. Early life Lucius Licinius Crassus was born in 140 BC. It is not known exactly which Licinius Crassus his father was, as there are a number of similarly named Licinii Crassi active in the mid-second century BC. However, prosopographical investigation by scholars has established that he must have been a grandson of Gaius Licinius Crassus, the consul of 168 who marched his army from Gallia Cisalpina to Macedonia against the will of the Senate. Lucius was, therefore, the child of one of this Gaius Crassus' sons. Lucius was taught at a young age by the Roman historian and jurist Lucius Coelius Antipater. He also studied law under two eminent statesmen, bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scipio Aemilianus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus Aemilianus (185–129 BC), known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a Roman general and statesman noted for his military exploits in the Third Punic War against Carthage and during the Numantine War in Spain. He oversaw the final defeat and destruction of the city of Carthage. He was a prominent patron of writers and philosophers, the most famous of whom was the Greek historian Polybius. In politics, he opposed the populist reform program of his murdered brother-in-law, Tiberius Gracchus. Family Scipio Aemilianus was the second son of Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus, the commander of the Romans' victorious campaign in the Third Macedonian War, and his first wife, Papiria Masonis. Scipio was adopted by his first cousin, Publius Cornelius Scipio, the eldest son of his aunt Aemilia Tertia and her husband Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus, the acclaimed commander who won the decisive battle of the Second Pun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |