|
David Vigor
David Bernard Vigor (26 June 1939 – 9 April 1998) was an Australian politician. He was a member of the Australian Senate, representing the Australian Democrats and the Unite Australia Party. Born in Elbeuf, France to an English mother and French father, the infant Vigor and his family caught the last ferry to England prior to the start of World War II. After returning to France at war's end, the Vigor family migrated to Adelaide, Australia in 1951. Vigor attended Adelaide Boys High School and the University of Adelaide, graduating in pure mathematics and French, and then transferred to Monash University as one of its first intake of research students. It was here Vigor met his future wife, Susan. Following his period at Monash, Vigor lectured in Glasgow for three years while he conducted ground breaking research into data representation and machine intelligence, placing him at the forefront of Information Technology research. After a period based in London working as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Senate
The Senate is the upper house of the Bicameralism, bicameral Parliament of Australia, the lower house being the Australian House of Representatives, House of Representatives. The powers, role and composition of the Senate are set out in Chapter I of the Constitution of Australia, federal constitution as well as federal legislation and Constitutional convention (political custom), constitutional convention. There are a total of 76 senators: twelve are elected from each of the six states and territories of Australia, Australian states, regardless of population, and two each representing the Australian Capital Territory (including the Jervis Bay Territory and Norfolk Island) and the Northern Territory (including the Australian Indian Ocean Territories). Senators are popularly elected under the single transferable vote system of proportional representation in state-wide and territory-wide districts. Section 24 of the Constitution of Australia, Section 24 of the Constitution provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Information technology is an application of computer science and computer engineering. The term is commonly used as a synonym for computers and computer networks, but it also encompasses other information distribution technologies such as television and telephones. Several products or services within an economy are associated with information technology, including computer hardware, software, electronics, semiconductors, internet, Telecommunications equipment, telecom equipment, and e-commerce.. An information technology system (IT system) is generally an information system, a communications system, or, more specifically speaking, a Computer, computer system — including all Computer hardware, hardware, software, and peripheral equipment � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Labor Party
The Australian Labor Party (ALP), also known as the Labor Party or simply Labor, is the major Centre-left politics, centre-left List of political parties in Australia, political party in Australia and one of two Major party, major parties in Politics of Australia, Australian politics, along with the Centre-right politics, centre-right Liberal Party of Australia. The party has been in government since the 2022 Australian federal election, 2022 federal election, and with List of state and territory branches of the Australian Labor Party, political branches active in all the States and territories of Australia, Australian states and territories, they currently hold government in New South Wales, South Australia, Victoria (state), Victoria, Western Australia, and the Australian Capital Territory. As of 2025, Queensland, Tasmania and Northern Territory are the only states or territories where Labor currently forms the opposition. It is the oldest continuously operating political party ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bob Hawke
Robert James Lee Hawke (9 December 1929 – 16 May 2019) was an Australian politician and trade unionist who served as the 23rd prime minister of Australia from 1983 to 1991. He held office as the Australian Labor Party, leader of the Labor Party (ALP), having previously served as president of the Australian Council of Trade Unions from 1969 to 1980 and president of the Australian Labor Party National Executive, Labor Party national executive from 1973 to 1978. Hawke was born in Bordertown, South Australia, Border Town, South Australia. He attended the University of Western Australia and went on to study at University College, Oxford as a Rhodes Scholarship, Rhodes Scholar. In 1956, Hawke joined the Australian Council of Trade Unions (ACTU) as a research officer. Having risen to become responsible for national wage case arbitration, he was elected as president of the ACTU in 1969, where he achieved a high public profile. In 1973, he was appointed as president of the Labor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia Card
The Australia Card was a proposal for a national identification card for Australian citizens and resident foreigners. The proposal was made in 1985, and abandoned in 1987. History The idea for the card was raised at the national Tax Summit in 1985 convened by the then Federal Labor government led by Bob Hawke. The card was to amalgamate other government identification systems and act against tax avoidance, and health and welfare fraud. The government introduced legislation in the parliament in 1986, but it did not have a majority in the Senate and was repeatedly blocked by the opposition and minor parties. Due to his opposition to the card, ALP senator George Georges resigned from the party to sit as an independent in December 1986. In the House of Representatives, ALP backbencher Lewis Kent said the card was un-Australian and that it would be more appropriate to call it a "Hitlercard or Stalincard". In response, Hawke asked the Governor-General Sir Ninian Stephen for a do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory until 1938, is an internal States and territories of Australia, territory of Australia. Canberra, the capital city of Australia, is situated within the territory, and is the territory's primate city. It is located in southeastern Australian mainland as an enclave and exclave, enclave surrounded by the state of New South Wales (NSW). Exclaved from NSW after Federation of Australia, federation as the seat of government for the new nation, the territory hosts Parliament House, Canberra, parliament house, High Court of Australia and the head offices of many Australian Government agencies. On 1 January 1901, Federation of Australia, federation of the colonies of Australia was achieved. Section 125 of the new Constitution of Australia, Australian Constitution provided that land, situated in New South Wales and at least from Sydney, would be ceded to the new Government of Australia, federal government. Foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1984 Australian Federal Election
The 1984 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 1 December 1984. All 148 seats in the House of Representatives (24 of them newly created) and 46 of 76 seats in the Senate (12 of them newly created) were up for election. The incumbent Labor Party led by Prime Minister Bob Hawke defeated the opposition Liberal–National coalition, led by Andrew Peacock. The election was held in conjunction with two referendum questions, neither of which was carried. Background and issues The election had a long campaign and a high rate of informal voting for the House of Representatives, but decreased rate in the Senate (due to the introduction of the Group voting ticket). Although a House election was not due until 1986, Hawke opted to call an election 18 months early in part to bring the elections for the House and Senate back into line following the double dissolution election of 1983. The legislated increase in the size of the House by 24 seats and the Senate by 12 seats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
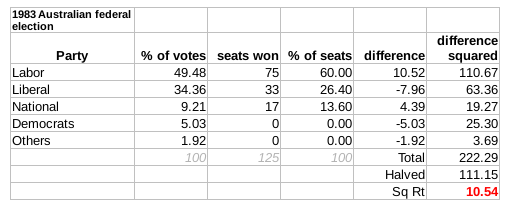
1983 Australian Federal Election
The 1983 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 5 March 1983. All 125 seats in the House of Representatives and all 64 seats in the Senate were up for election, following a double dissolution. The incumbent Coalition government which had been in power since 1975, led by Malcolm Fraser (Liberal Party) and Doug Anthony ( National Party), was defeated in a landslide by the opposition Labor Party led by Bob Hawke. This election marked the end of the seven year Liberal–National Coalition Fraser government and the start of the 13 year Hawke-Keating Labor government. The Coalition would spend its longest ever period in opposition and the Labor party would spend its longest ever period of government at a federal level. The Coalition would not return to government until the 1996 election. Hawke became the second Labor leader after World War II to lead the party to victory from opposition, after Gough Whitlam in 1972 and before Kevin Rudd in 2007 and Anthony Albanese i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
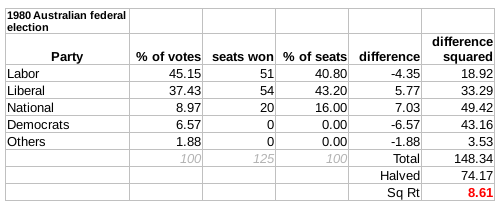
1980 Australian Federal Election
The 1980 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 18 October 1980. All 125 seats in the House of Representatives and 34 of the 64 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Liberal–NCP coalition government, led by Prime Minister Malcolm Fraser, was elected to a third term with a much reduced majority, defeating the opposition Labor Party led by Bill Hayden. This was the last federal election victory for the Coalition until the 1996 election. Future Prime Minister Bob Hawke and future opposition leader and future Deputy Prime Minister Kim Beazley entered parliament at this election. Issues and significance The Fraser Government had lost a degree of popularity within the electorate by 1980. The economy had been performing poorly since the 1973 oil shock. However, Hayden was not seen as having great electoral prospects. Perhaps as evidence of this, then ACTU President Bob Hawke (elected to parliament in the election as the member for Wills) and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robin Millhouse
Robin Rhodes Millhouse, QC (9 December 1929 – 28 April 2017) was, at various times, the 39th Attorney-General of South Australia, the first Australian Democrats parliamentarian, and the Chief Justice of both Kiribati and Nauru and a judge of the High Court of Tuvalu. Early life and career Millhouse was born in Adelaide, to lawyer Vivian Rhodes Millhouse (1902–1963), and Grace Lily (often Lilly) Millhouse, née Ayliffe (1900–1990). Millhouse gained an LLB from the University of Adelaide in 1951 after attending St Peter's College, Adelaide. Political career While practising as a barrister, Millhouse entered the South Australian House of Assembly on 7 May 1955 as the Liberal and Country League (LCL) member for Mitcham, a safe LCL seat in southeastern Adelaide. Millhouse rapidly gained a reputation as both the intellectual driving force behind the LCL and an outspoken spokesperson for the urban middle class faction of the LCL, a group under-represented within the part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New LM
The New Liberal Movement (New LM) was a South Australian political party which existed from 1976 to 1977, with one member of parliament. In 1976 the Liberal Movement dissolved and three of its four parliamentary members rejoined the Liberal Party. However the remaining member, Robin Millhouse, argued that the South Australian Division of the Liberal Party of Australia was no longer worthy of the descriptor ''liberal'', and instead founded the New LM in May 1976. Millhouse kept a high profile for the New LM until the party merged with the Australia Party to form the Australian Democrats in 1977, thus causing it to cease to exist. The New LM had had some reservations about merging with the Australia Party, but the resignation of prominent politician Don Chipp from the Liberal Party represented an opportunity to expand the reach of the two parties. Chipp had agreed to become leader of the Australia Party only if it merged with the New LM, thus motivating the two parties to do so. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |