|
Dave The Resurrector
Dave the Resurrector was a so-called "resurrector bot" that responded to any attempts at canceling a message on the usenet newsgroup news.admin.net-abuse by re-posting the message. Ohm, Paul K Skirvin, Tim It was written by Chris Lewis. The bot is notable as one of the first escalations in the spam Spam most often refers to: * Spam (food), a consumer brand product of canned processed pork of the Hormel Foods Corporation * Spamming, unsolicited or undesired electronic messages ** Email spam, unsolicited, undesired, or illegal email messages ... arms race. See also * Cancelbot, a process that sends out cancel messages Notes References * * Anti-spam Newsgroups {{Compu-network-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Bot
An Internet bot, web robot, robot, or simply bot, is a software application that runs automated tasks ( scripts) on the Internet, usually with the intent to imitate human activity, such as messaging, on a large scale. An Internet bot plays the client role in a client–server model whereas the server role is usually played by web servers. Internet bots are able to perform simple and repetitive tasks much faster than a person could ever do. The most extensive use of bots is for web crawling, in which an automated script fetches, analyzes and files information from web servers. More than half of all web traffic is generated by bots. Efforts by web servers to restrict bots vary. Some servers have a robots.txt file that contains the rules governing bot behavior on that server. Any bot that does not follow the rules could, in theory, be denied access to or removed from the affected website. If the posted text file has no associated program/software/app, then adhering to the rules i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancel Message
Control messages are a special kind of Usenet post that are used to control news servers. They differ from ordinary posts by a header field named Control. The body of the field contains control name and arguments. There are two historical alternatives to header field Control. They are not supported by contemporary software and forbidden according to RFC 5537. However, the traditional format of the subject line is widely used in addition to the Control header: the subject line consists of the word "cmsg" followed by control name and arguments. Types cancel A cancel message requests the deletion of a specific article. The body of the Control field contains one argument, the Message-ID of the article to delete. According to RFC 1036 only the author of the target message or the local news administrator is allowed to send a cancel (cancels not meeting this condition are called "rogue cancels"). To verify authorization the line (or line, if it exists) of the cancel message must ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
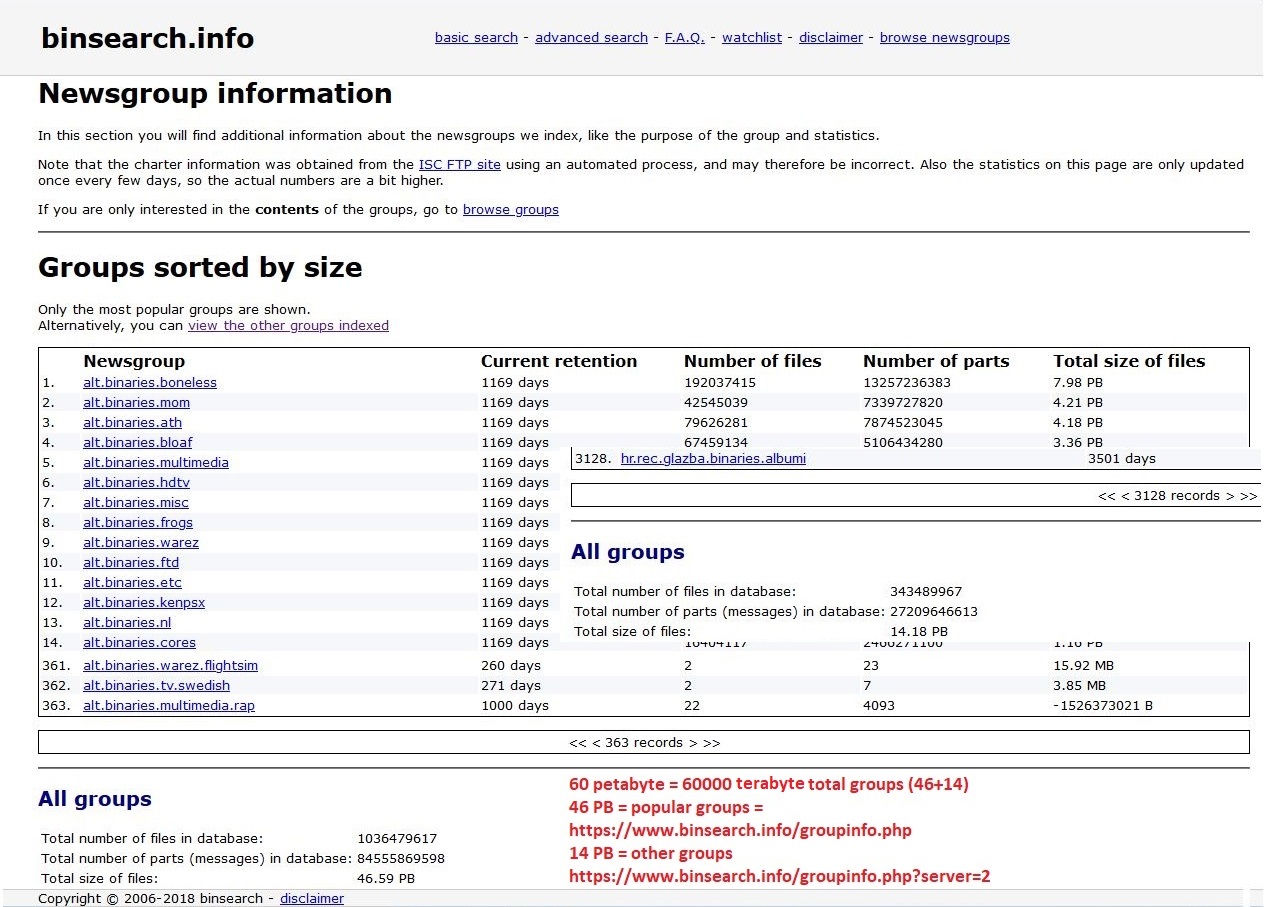
Usenet Newsgroup
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are not only discussion groups or conversations, but also a repository to publish articles, start developing tasks like creating Linux, sustain mailing lists and file uploading. That’s thank to the protocol that poses no article size limit, but are to the providers to decide. In the late 1980s, Usenet articles were often limited by the providers to 60,000 characters, but in time, Usenet groups have been split into two types: ''text'' for mainly discussions, conversations, articles, limited by most providers to about 32,000 characters, and ''binary'' for file transfer, with providers setting limits ranging from less than 1 MB to about 4 MB. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read the content of newsgroups. Before the adoption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faqs
A frequently asked questions (FAQ) list is often used in articles, websites, electronic mailing list, email lists, and online forums where common questions tend to recur, for example through posts or queries by new users related to common knowledge gaps. The purpose of a FAQ is generally to provide information on frequent questions or concerns; however, the format is a useful means of organizing information, and text consisting of questions and their answers may thus be called a FAQ regardless of whether the questions are actually ''frequently'' asked. Since the acronym ''FAQ'' originated in textual media, its pronunciation varies. FAQ can be pronounced as an initialism, "F-A-Q", or as an acronym, "FAQ". Web designers often label a single list of questions as a "FAQ", such as on Google Search, while using "FAQs" to denote multiple lists of questions such as on United States Department of the Treasury, United States Treasury sites. Use of "FAQ" to refer to a single frequently asked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chris Lewis (Usenet)
Christopher Lewis is a Canadian computer security consultant from Ottawa, who fought Spamming, spam on Usenet and the early Internet. Active in volunteer anti-spam efforts in the late 1990s and early 2000s, Lewis was described in ''Net.wars'' (1997) as "the best known active canceler of spam and other mass postings" at the time. In April 1998, he organized an unsuccessful moratorium with forty other anti-spam volunteers in an attempt to boycott Internet service provider, internet service providers into doing their share against spam. He worked as a systems architect for Nortel and, as of 2017, is Chief Scientist at The Spamhaus Project, SpamhausTechnology. Career Lewis worked as a senior security architect at Bell-Northern Research, Bell Northern Research, then as a systems architect for Nortel from 1991 to 2012. In 2002, Lewis led a five-man Anti-spam techniques, spam-filtering team at a major telecommunications company with over 45,000 employees. His unofficial title was "sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spam (electronic)
Spamming is the use of messaging systems to send multiple unsolicited messages (spam) to large numbers of recipients for the purpose of commercial advertising, non-commercial proselytizing, or any prohibited purpose (especially phishing), or simply repeatedly sending the same message to the same user. While the most widely recognized form of spam is email spam, the term is applied to similar abuses in other media: messaging spam, instant messaging spam, Newsgroup spam, Usenet newsgroup spam, spamdexing, Web search engine spam, spam in blogs, wiki spam, classified advertising, online classified ads spam, mobile phone spam, mobile phone messaging spam, Forum spam, Internet forum spam, junk fax, junk fax transmissions, social spam, spam mobile apps, television advertising and file sharing spam. It is named after Spam (food), Spam, a luncheon meat, by way of a Spam (Monty Python sketch), Monty Python sketch about a restaurant that has Spam in almost every dish in which Vikings annoyi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancelbot
A cancelbot is an automated or semi-automated process for sending out third-party cancel messages over Usenet, commonly as a stopgap measure to combat spam. History One of the earliest uses of a cancelbot was by microbiology professor Richard DePew, to remove anonymous postings in science newsgroups. Perhaps the most well known early cancelbot was used in June 1994 by Arnt Gulbrandsen within minutes of the first post of Canter & Siegel's second spam wave, as it was created in response to their "Green Card spam" in April 1994. Usenet spammers have alleged that cancelbots are a tool of the mythical Usenet cabal. Rationale Cancelbots must follow community consensus to be able to serve a useful purpose, and historically, technical criteria have been the only acceptable criteria for determining if messages are cancelable, and only a few active cancellers ever obtain the broad community support needed to be effective. Pseudosites are referenced in cancel headers by legitimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UCLA Law Review
The ''UCLA Law Review'' is a bimonthly law review established in 1953 and published by students of the UCLA School of Law, where it also sponsors an annual symposium. Originally, UCLA Law proposed in 1950 that either Berkeley and UCLA should publish a joint law review or that all law schools in the state should jointly publish a law review. After Berkeley shot down both proposals, UCLA Law persuaded the Board of Regents in 1952 to provide a full subsidy for the launch of its own law review. Membership is decided based on performance on a write-on competition. The editorial board is selected from the staff. Past editors have included federal judges Paul J. Watford, Sandra Segal Ikuta, and Kim McLane Wardlaw. The UCLA Law Review ranks 10th in the nation among all legal law journals. Bryce Clayton of the University of Oregon noted that as of 2023, it ranks 16th per US News Peer Reputation score (averaged over 10 years), 7th per Washington and Lee Law Journal Ranking, 15th pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-spam
Various anti-spam techniques are used to prevent email spam (unsolicited bulk email). No technique is a complete solution to the spam problem, and each has trade-offs between incorrectly rejecting legitimate email ( false positives) as opposed to not rejecting all spam email ( false negatives) – and the associated costs in time, effort, and cost of wrongfully obstructing good mail. Anti-spam techniques can be broken into four broad categories: those that require actions by individuals, those that can be automated by email administrators, those that can be automated by email senders and those employed by researchers and law enforcement officials. End-user techniques There are a number of techniques that individuals can use to restrict the availability of their email addresses, with the goal of reducing their chance of receiving spam. Discretion Sharing an email address only among a limited group of correspondents is one way to limit the chance that the address will be "harv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |