|
Datong River
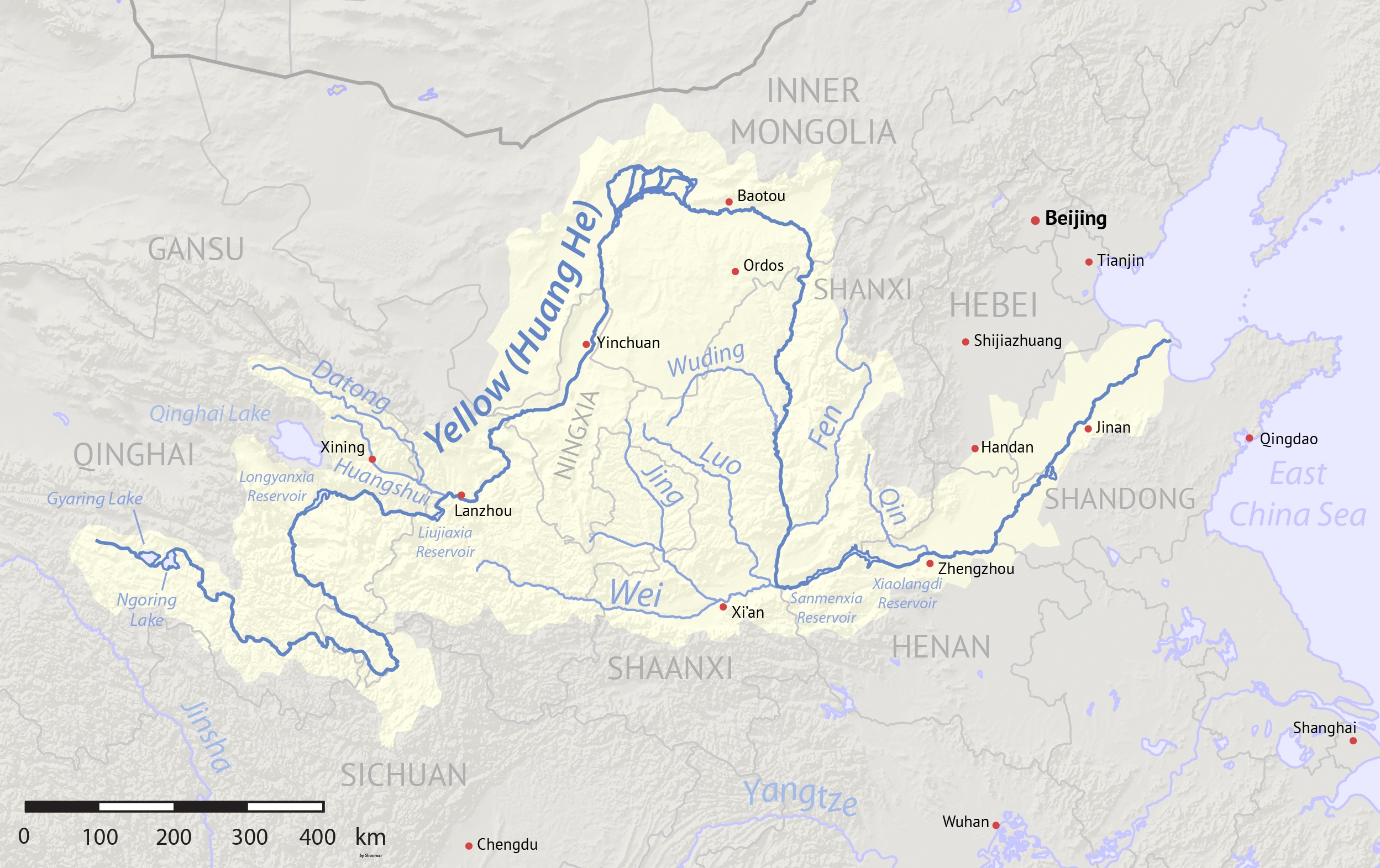
The Datong River (), known as the Julak Chu ( Tibetan: འཇུ་ལག་ཆུ་) in Amdo Tibetan, is a river of Qinghai in the Yellow River basin. It has a total length of , and a basin area of . It has an average annual flow of 90.5 cubic meters per second. It was previously spelled Tatung in English. The river forms in Tianjun County, part of Qinghai Province's Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. It then flows easterly separating the Qilian Mountains from the Daban Mountains. The main centre of population along its length here is Menyuan. The Datong River meets the Huangshui River at Qinghai's border with Gansu Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti .... While it is a tributary of the Huangshui in name, the Datong River is actually the main stem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Script
The Tibetan script is a segmental writing system, or '' abugida'', forming a part of the Brahmic scripts, and used to write certain Tibetic languages, including Tibetan, Dzongkha, Sikkimese, Ladakhi, Jirel and Balti. Its exact origins are a subject of research but is traditionally considered to be developed by Thonmi Sambhota for King Songtsen Gampo. The printed form is called uchen script while the hand-written form used in everyday writing is called umê script. This writing system is especially used across the Himalayan Region. History Little is known about the exact origins of Tibetan script. According to Tibetan historiography, it was developed during the reign of King Songtsen Gampo by his minister Thonmi Sambhota, who was sent to India along with other scholars to study Buddhism along with Sanskrit and other brahmi languages. They developed the Tibetan script from the Gupta script while at the Pabonka Hermitage. This occurred , towards the beginning of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amdo Tibetan
Amdo Tibetan (; also called ''Am kä'') is the Tibetic language spoken in Amdo (now mostly in Qinghai, some in Ngawa and Gannan). It has two varieties, the farmer dialects and the nomad dialects. Amdo is one of the three branches of traditional classification of Tibetic languages (the other two being Khams Tibetan and Ü-Tsang). In terms of mutual intelligibility, Amdo speakers cannot communicate even at a basic level with the Ü-Tsang branch (including Lhasa Tibetan). Amdo Tibetan has 70% lexical similarity with Central Tibetan and Khams Tibetan. The nomad dialect of Amdo Tibetan is closer to classical written Tibetan as it preserves the word-initial consonant clusters and it is non- tonal, both now elided in the Ü-Tsang branch (including Lhasa Tibetan). Hence, its conservatism in phonology has become a source of pride among Amdo Tibetans. Amdo is one of the Tibetic languages that have undergone a spelling reform to make the written form closer to the spoken language: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Hui people, Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese language, Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat language, Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River
The Yellow River, also known as Huanghe, is the second-longest river in China and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system on Earth, with an estimated length of and a Drainage basin, watershed of . Beginning in the Bayan Har Mountains, the river flows generally eastwards before entering the long Ordos Loop, which runs northeast at Gansu through the Ordos Plateau and turns east in Inner Mongolia. The river then turns sharply southwards to form the border between Shanxi and Shaanxi, turns eastwards at its confluence with the Wei River, and flows across the North China Plain before emptying into the Bohai Sea. The river is named for the yellow color of its water, which comes from the large amount of sediment discharged into the water as the river flows through the Loess Plateau. The Yellow River basin was the birthplace of Yellow River civilization, ancient Chinese civilization. According to traditional Chinese historiography, the Xia dynasty originated on it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianjun County
Tianjun County, in Tibetan Themchen, is a county of Qinghai Province, China, bordering Gansu Province to the north. It is under the administration of the Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. The county seat in Xinyuan Town. Administrative divisions Tianjun County is divided into 3 towns and 7 townships A township is a form of human settlement or administrative subdivision. Its exact definition varies among countries. Although the term is occasionally associated with an urban area, this tends to be an exception to the rule. In Australia, Canad .... Climate Economy The county is served by the Qinghai–Tibet Railway; its Tianjun railway station is located near the county seat, Xinyuan Town. Large coalfields are worked near Muli Town in the northern part of the county, at the elevation around 4,000 m above the sea level. The Muli coal fields are connected with the Ha'ergai railway station on the Qinghai–Tibet Railway by a long branch railway, whose two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haixi Mongol And Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture
Haixi Mongolian and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture ( zh, c=海西蒙古族藏族自治州; ; ), locally also known as Qaidam Prefecture (; ; zh, s=柴达木), is an autonomous prefecture occupying much of the northern half of (as well as part of the southwest of) Qinghai, Qinghai Province, China. It has an area of and its Capital (political), seat is Delingha. The name of the prefecture literally means "west of Qinghai Lake, (Qinghai) Lake." Geladaindong Peak, Geladandong Mountain, the source of the Yangtze River, is located here. History After 1949, the People's Government of Dulan County was founded and the area was renamed Dulan Autonomous District ( zh, labels=no, s=都兰自治区); in 1954, Dulan was renamed Haixi Mongol, Tibetan and Kazakh Autonomous District ( zh, labels=no, s=海西蒙藏哈萨克族自治区) and in 1955, Haixi Mongol, Tibetan and Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture ( zh, labels=no, c=海西蒙藏哈萨克族自治州). In 1963, it was renamed " zh, labels= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qilian Mountains
The Qilian Mountains (), together with the Altyn-Tagh sometimes known as the Nan Shan, as it is to the south of the Hexi Corridor, is a northern outlier of the Kunlun Mountains, forming the border between Qinghai and the Gansu provinces of northern China. Geography The range stretches from the south of Dunhuang some 800 km to the southeast, forming the northeastern escarpment of the Tibetan Plateau and the southwestern border of the Hexi Corridor. The eponymous Qilian Shan peak, situated some 60 km south of Jiuquan, at , rises to 5,547 m. It is the highest peak of the main range, but there are two higher peaks further south, Kangze'gyai at wit5,808 mand Qaidam Shan peak at wit5,759 m Other major peaks include Gangshiqia Peak in the east. The Nan-Shan range continues to the west as Yema Shan (5,250 m) and Altun Shan (Altyn Tagh) (5,798 m). To the east, it passes north of Qinghai Lake, terminating as Daban Shan and Xinglong Shan near Lanzhou, with Maoma Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daban Mountains
Daban may refer to: Places * Daban, China, a village in Fujian, China *Daban, Kati Cercle, a village and rural commune in the Kati Cercle in the Koulikoro Region, Mali *Daban, Russia, a ''selo'' in Olyokminsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia *The Chinese name for Osaka is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the List of cities in Japan, third-most populous city in J ..., a city in Osaka Prefecture, Japan People *Jacques Tisné Daban, mayor of Aast, a commune in the Aquitane region of France, in 1871–1881 See also * {{Disambiguation, geo, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menyuan
Menyuan Hui Autonomous County ( zh, s=门源回族自治县, t=門源回族自治縣, p=Ményuán Huízú Zìzhìxiàn, Xiao'erjing: ; ) is a county in the northeast of Qinghai Province, China, bordering Gansu Province to the north. It is under the administration of Haibei Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. Menyuan is situated on the Datong River between the Qilian Mountains and Daban Mountains. Gangshiqia Peak rises dramatically in the north of the county. It used to be called Menyuan () in Chinese, with a different first character from the current name. Administrative divisions Haiyan County is made up of 4 towns, 7 townships, and 1 ethnic township: Others: *Menyuan Prison (门源监狱) *Menyuan Stallion Ranch (门源种马场) Climate Transportation * Lanzhou–Xinjiang High-Speed Railway ( Menyuan railway station) * China National Highway 227 See also * List of administrative divisions of Qinghai Qinghai, a province of the People's Republic of China, is made up of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huangshui River
The Huangshui River, Huang Shui, or Tsong Chu is a river in Qinghai and Gansu, China. It is a left tributary of the Yellow River and its total length is with a basin area of . Etymology The Huangshui River () is also referred to simply as Huang Shui () in China. The river was formerly romanized as the Hwong-Choui. In Amdo Tibetan, the Huangshui River is known as the Tsong Chu ( Tibetan: ཙོང་ཆུ་). History The Huangshui River Valley, also known as Tsongkha ( Tibetan: ཙོང་ཁ་), has long been important as a route between Chinese, Tibetan, and Mongolian cultures. As one of the few fertile valleys on the northeast edge of the Tibetan Plateau, the river's basin has supported agriculture for various Neolithic and Bronze Age civilizations including the Majiayao culture, Qijia culture, Xindian culture, and Kayue culture. Huangshui River Valley was also one of the routes utilized by travelers on the Northern Silk Road. The city of Xining formed on the Huangsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Tibetan and Loess Plateau, Loess plateaus and borders Mongolia's Govi-Altai Province, Inner Mongolia and Ningxia to the north, Xinjiang and Qinghai to the west, Sichuan to the south and Shaanxi to the east. The Yellow River passes through the southern part of the province. Part of Gansu's territory is located in the Gobi Desert. The Qilian Mountains, Qilian mountains are located in the south of the Province. Gansu has a population of 26 million, ranking List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, 22nd in China. Its population is mostly Han Chinese, Han, along with Hui people, Hui, Dongxiangs, Dongxiang and Tibetan people, Tibetan minorities. The most common language is Mandarin. Gansu is among the poorest administrative divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |