|
DRG Class 80
The Class 80 tank engines were German standard locomotives ('' Einheitsloks'') with the Deutsche Reichsbahn. They were intended to replace the aging, rickety state railway line engines performing shunting duties in their dotage at large stations. History Between 1927 and 1928, 39 vehicles were produced, having been built in the locomotive factories of Jung in Jungenthal, Union Gießerei in Königsberg, Wolf and Hohenzollern. With the development of the Class 80, a relatively economical and simple locomotive class, it was hoped that the cost of shunting duties would come down. After they had been on duty, prior to the Second World War, primarily in the area of Leipzig (including the shunting of post vans) and Cologne, 22 units went into the DR in East Germany, post-1945, and 17 to the Deutsche Bundesbahn. They were in service with the DR until 1968. In the Federal Republic of Germany, the last Bundesbahn engine was taken out of service in 1965. Several examples survived i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aktiengesellschaft Für Lokomotivbau Hohenzollern
The Hohenzollern Locomotive Works (Aktiengesellschaft für Lokomotivbau Hohenzollern) was a German locomotive-building company which operated from 1872 to 1929. The Hohenzollern works was a manufacturer of standard gauge engines and about 400 fireless locomotives as well as diesel locomotives of various rail gauges. The company was founded on 8 June 1872 in Düsseldorf-Grafenberg, Grafenberg near Düsseldorf. The firm produced around 4,600 locomotives. After the increasingly critical situation in the German locomotive building industry around 1929 the works was closed in November 1929. The Hohenzollern AG had hoped in vain for follow-on orders for the DRG Class 80 from the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG). Locomotive number 80 030 in the Bochum-Dahlhausen Railway Museum was one of the last built by the Lokomotivbau Hohenzollern and is preserved today in photograph-grey livery. The last locomotives left the factory in September 1929; it was immediately torn down. Fireless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on 3 October 1990. Until 1989, it was generally viewed as a communist state and described itself as a Socialist state, socialist "workers' and peasants' state". The Economy of East Germany, economy of the country was Central planning, centrally planned and government-owned corporation, state-owned. Although the GDR had to pay substantial war reparations to the Soviets, its economy became the most successful in the Eastern Bloc. Before its establishment, the country's territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the Berlin Declaration (1945), Berlin Declaration abolishing German sovereignty in World War II. The Potsdam Agreement established the Soviet occupation zone in Germany, Soviet-occupied zone, bounded on the east b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veluwsche Stoomtrein Maatschappij
Veluwse Stoomtrein Maatschappij () (VSM) is a Dutch heritage railway between Apeldoorn and Dieren. It passes through the villages of Lieren/Beekbergen, Loenen, and Eerbeek. Rides on steam trains are popular with tourists visiting the region, and that is why VSM operates mainly during the summer vacation. VSM, founded in 1975, is operated by volunteers. In March 2011 one of the individuals who possessed a number of locomotives decided to sell his collection. This could have meant that VSM would lose some of the biggest and most popular locomotives in their collection. VSM decided to buy the whole collection in order to keep for future generations. Back to Then Each year, on the first full weekend of September, the "Back to Then" (Dutch: ''Terug naar Toen'') event is held, using everything that will run. Usually a number of guest locomotives appear as well. The last run on Saturday used to be the highlight of the event until 2007, originating in Apeldoorn. The train was pushed and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bochum Dahlhausen Railway Museum
The Eisenbahnmuseum Bochum-Dahlhausen is a railway museum situated south of the city of Bochum in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It was founded by DGEG, the German Railway History Company in 1977 and is based in a locomotive depot that was built between 1916 and 1918 and ceased operation in 1969. Then DGEG took over the whole area of 46,000 square metres and built up the biggest railway museum in Germany. In the middle of the museum, there is an engine shed with fourteen tracks. A preserved turntable, coaling, watering, and sanding facilities are still in operation. This museum is integrated into The Industrial Heritage Trail (''Route der Industriekultur'') a route of monuments from the history of the industry. Exhibits The origins of the vehicle collection go back to 1967. A variety of steam locomotives and other technically interesting railway vehicles from different epochs are displayed. There are over 200 exhibits in total. The stars of the exhibition are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg, and Cologne), and the third-most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Saxony, Coswig, Radeberg, and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Dresden Basin, Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated, area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden Transport Museum
The Dresden Transport Museum (German: Verkehrsmuseum Dresden) displays vehicles of all modes of transport, such as railway, shipping, road and air traffic, under one roof. The museum is housed in the Johanneum at the Neumarkt in Dresden. The Johanneum was built between 1586 and 1590; it is one of the oldest museum buildings in Dresden.Fritz Löffler: ''Das alte Dresden - Geschichte seiner Bauten''. 16th ed. Leipzig: Seemann, 2006, History The history of the Dresden Transport Museum begins on 1 May 1952. On that day, negotiations started between the Hochschule für Verkehrswesen (High School for Transportation) and the Ministry of Transport for the construction of a transport museum in the German Democratic Republic. The museum was mainly intended to house the exhibits of the Saxon Railway Museum that had been evacuated during the Second World War. After Dresden was confirmed as the location, the first vehicles were stabled in a locomotive shed at Dresden's Neustadt stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
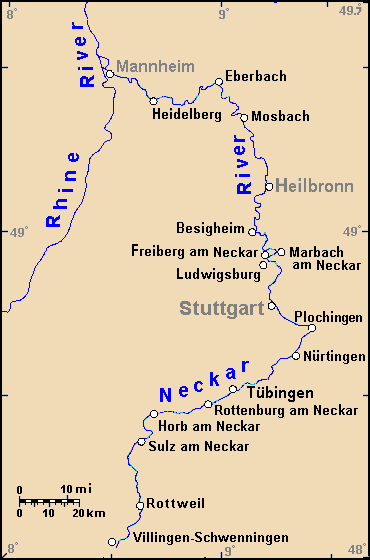
Heilbronn
Heilbronn () is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, surrounded by Heilbronn (district), Heilbronn District. From the late Middle Ages on, it developed into an important trading centre. At the beginning of the 19th century, Heilbronn became one of the centres of early industrialisation in Württemberg. Heilbronn's old town was completely destroyed during the air raid of 4 December 1944 and rebuilt in the 1950s. Today Heilbronn is the economic centre of the Heilbronn-Franconia, Heilbronn-Franken region. Heilbronn is known for its wine industry and is nicknamed ''Käthchenstadt'', after Heinrich von Kleist's ''Das Käthchen von Heilbronn''. Geography Heilbronn is located in the northern corner of the Neckar Sedimentary basin, basin at the bottom of the Wartberg (Heilbronn), Wartberg (308 m). It occupies both banks of the Neckar, and the highest spot inside city limits is the Schweinsberg (mountain), Schweinsberg with a height of 372 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South German Railway Museum
The South German Railway Museum (''Süddeutsches Eisenbahnmuseum Heilbronn'' or SEH) is a railway museum at Heilbronn in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwestern Germany.225 It was founded in 1998. Aims The museum has the following aims:1. To preserve the site of the former Heilbronn locomotive depot, part of which is under historic building protection. 2. To preserve historical railway vehicles and their associated infrastructure and to display them to the general public. The members of the board of trustees work for the museum as volunteers. Site and description of the museums The museum is located in the former Deutsche Bundesbahn locomotive depot at Heilbronn in the Böckingen district of the town. The depot was opened in 1893 by the Royal Württemberg State Railways (''Königlich Württembergische Staats-Eisenbahnen'' or K.W.St.E.), and owned in succession by the Deutsche Reichsbahn, Deutsche Bundesbahn and Deutsche Bahn, before being taken over in 2000 by the mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuenmarkt
Neuenmarkt is a municipality in the district of Kulmbach in Bavaria in Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu .... City arrangement Neuenmarkt is arranged in the following boroughs: References Kulmbach (district) {{Kulmbachdistrict-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Steam Locomotive Museum
The German Steam Locomotive Museum (''Deutsches Dampflokomotiv-Museum'') or DDM is located at the foot of the famous '' Schiefe Ebene'' ramp on the Ludwig South-North Railway in Neuenmarkt, Upper Franconia. This region is in northern Bavaria, Germany. The DDM was founded in 1977. Facilities The museum is in the former locomotive shed (''Bahnbetriebswerk'') at Neuenmarkt- Wirsberg station. It comprises a 15-road roundhouse, water cranes, a turntable with an off-centre pivot, a coaling facility and a ''Ruge'' coal crane in a newly built 'old fashioned' working coal yard. History The locomotive shed was built in 1895 by the Royal Bavarian State Railways and extended in 1923 by the Deutsche Reichsbahn. Amongst others, pusher locomotives e. g. DRG Class 95s (ex- Prussian T 20s) and Class 96s (ex- Bavarian Gt 2x4/4 Mallet locomotives) were stationed there. One example of a Class 95 may be seen in the museum. Locomotives Around 30 steam locomotives may be seen, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maschinenfabrik Christian Hagans
Maschinenfabrik Christian Hagans (Christian Hagans Engineering Works) was a German locomotive manufacturer founded on 1 July 1857 in Erfurt, Germany, by Christian Hagans. By the mid-1860s, the company had started building locomotive boilers and other components; in 1872 the first locomotive followed, a narrow gauge engine for a rail gauge of 750 mm. As a result of shortages of space, Hagans often had to limit its operations. For example, the T 15 was built by Henschel because Hagans did not have the necessary capacity. In 1903 the factory site was moved to Ilversgehofen north of the city; only then was large-scale production possible. On 30 June 1915 the locomotive factory was sold, with effect from 1 April 1916, to the ''Maschinenbau R. Wolf Magdeburg-Buckau''. In 1928, steam locomotive manufacture finally came to an end in Erfurt. By then Hagans had built 1,251 locomotives. The last Hagans engine was a DRG Class 64. Hagans locomotive A type of articulated steam locomotive is na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |