|
Vehicle Telematics
Telematics is an interdisciplinary field encompassing telecommunications, vehicular technologies (road transport, road safety, etc.), electrical engineering (sensors, instrumentation, wireless communications, etc.), and computer science (multimedia, Internet, etc.). Telematics can involve any of the following: * The technology of sending, receiving, and storing information using telecommunication devices to control remote objects * The integrated use of telecommunications and informatics for application in vehicles and to control vehicles on the move * Satellite navigation, Global navigation satellite system technology integrated with computers and mobile communications technology in automotive navigation systems * (Most narrowly) The use of such systems within road vehicles (also called vehicle telematics) History Telematics is a translation of the French language, French word ''télématique,'' which was first Protologism, coined by Simon Nora and Alain Minc in a 1978 report to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunication
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent Session (computer science), communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the electrical telegraph, telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Informatization
Informatization or informatisation refers to the extent by which a geographical area, an economy or a society is becoming information-based, i.e. the increase in size of its information labor force. Usage of the term was inspired by Marc Porat’s categories of ages of human civilization: the Agricultural Age, the Industrial Age and the Information Age (1978). Informatization is to the Information Age what industrialization was to the Industrial Age. It has been stated that: :The Agricultural Age has brought about the agriculturization of the planet. The Industrial Age has caused among other things the industrialization of agriculture. The Information Age has resulted to the informatization of the agricultural industry (Flor, 1993). The term has mostly been used within the context of national development. Everett Rogers defines informatization as the process through which new communication technologies are used as a means for furthering development as a nation becomes more and more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
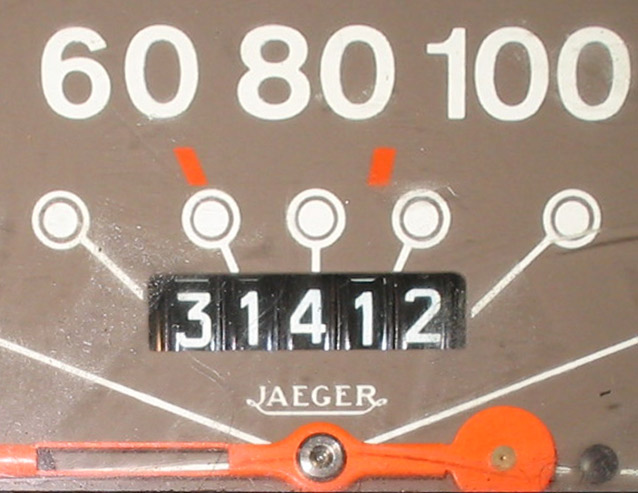
Odometry
Odometry is the use of data from motion sensors to estimate change in position over time. It is used in robotics by some legged or wheeled robots to estimate their position relative to a starting location. This method is sensitive to errors due to the integration of velocity measurements over time to give position estimates. Rapid and accurate data collection, instrument calibration, and processing are required in most cases for odometry to be used effectively. The word ''odometry'' is composed of the Greek words ''odos'' (meaning "route") and ''metron'' (meaning "measure"). Example Suppose a robot has rotary encoders on its wheels or on its legged joints. It drives forward for some time and then would like to know how far it has traveled. It can measure how far the wheels have rotated, and if it knows the circumference of its wheels, compute the distance. Train operations are also frequent users of odometrics. Typically, a train gets an absolute position by passing over stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPRS
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), also called 2.5G, is a mobile data standard on the 2G cellular communication network's Global System for Mobile Communications, global system for mobile communications (GSM). Networks and mobile devices with GPRS started to roll out around the year 2001; it offered, for the first time on GSM networks, seamless data transmission using Packet switching, packet data for an "always-on" connection (eliminating the need to "dial-up"), so providing improved Internet access for World Wide Web, web, email, Wireless Application Protocol, WAP services, Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) and others. Up until the rollout of GPRS, only circuit switched data was used in cellular networks, meaning that one or more radio channels were occupied for the entire duration of a data connection. On the other hand, on GPRS networks, data is broken into small packets and transmitted through available channels. This increased efficiency also gives it theoretical data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNSS
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geopositioning. A satellite navigation system with global coverage is termed global navigation satellite system (GNSS). , four global systems are operational: the United States's Global Positioning System (GPS), Russia's Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS), China's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), and the European Union's Galileo. Two regional systems are operational: India's NavIC and Japan's QZSS. ''Satellite-based augmentation systems'' (SBAS), designed to enhance the accuracy of GNSS, include Japan's Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), India's GAGAN and the European EGNOS, all of them based on GPS. Previous iterations of the BeiDou navigation system and the present Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), operationally known as NavIC, are examples of stand-alone operating regional navigation satellite systems (RNSS). Satellite navigation devic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle Tracking
A vehicle tracking system combines the use of automatic vehicle location in individual vehicles with software that collects these fleet data for a comprehensive picture of vehicle locations. Modern vehicle tracking systems commonly use GPS or GLONASS technology for locating the vehicle, but other types of automatic vehicle location technology can also be used. Vehicle information can be viewed on electronic maps via the Internet or specialized software. Urban public transit authorities are an increasingly common user of vehicle tracking systems, particularly in large cities. Active versus passive tracking Several types of vehicle tracking devices exist. Typically they are classified as "passive" and "active". "Passive" devices store GPS location, speed, heading and sometimes a trigger event such as key on/off, door open/closed. Once the vehicle returns to a predetermined point, the device is removed and the data downloaded to a computer for evaluation. Passive systems includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligent Transportation System
An intelligent transportation system (ITS) is an advanced application that aims to provide services relating to different modes of transport and traffic management and enable users to be better informed and make safer, more coordinated, and 'smarter' use of transport networks. Some of these technologies include calling for emergency services when an accident occurs, using cameras to enforce traffic laws or signs that mark speed limit changes depending on conditions. Although ITS may refer to all modes of transport, the directive of the European Union 2010/40/EU, made on July 7, 2010, defined ITS as systems in which information and communication technologies are applied in the field of road transport, including infrastructure, vehicles and users, and in traffic management and mobility management, as well as for interfaces with other modes of transport. ITS may be used to improve the efficiency and safety of transport in many situations, i.e. road transport, traffic management, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless Access For The Vehicular Environment
IEEE 802.11p is an approved amendment to the IEEE 802.11 standard to add wireless access in vehicular environments (WAVE), a vehicular communication system. It defines enhancements to 802.11 (the basis of products marketed as Wi-Fi) required to support intelligent transportation systems (ITS) applications. This includes data exchange between high-speed vehicles and between the vehicles and the roadside infrastructure, so called vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, in the licensed ITS band of 5.9 GHz (5.85–5.925 GHz). IEEE 1609 is a higher layer standard based on the IEEE 802.11p. It is also the basis of a European standard for vehicular communication known as ETSI ITS-G5. Description 802.11p is the basis for dedicated short-range communications (DSRC), a U.S. Department of Transportation project based on the Communications Access for Land Mobiles (CALM) architecture of the International Organization for Standardization for vehicle-based communication network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dedicated Short-range Communications
Dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) is a technology for direct wireless exchange of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) and other intelligent transportation systems (ITS) data between vehicles, other road users (pedestrians, cyclists, etc.), and roadside infrastructure (traffic signals, electronic message signs, etc.). DSRC, which can be used for both one- and two-way data exchanges, uses channels in the licensed 5.9 GHz band. DSRC is based on IEEE 802.11p. History In October 1999, the United States Federal Communications Commission (FCC) allocated 75 MHz of spectrum in the 5.9 GHz band for DSRC-based ITS uses. By 2003, DSRC was used in Europe and Japan for electronic toll collection. In August 2008, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) allocated 30 MHz of spectrum in the 5.9 GHz band for ITS. In November 2020, the FCC reallocated the lower 45 MHz of the 75 MHz spectrum to the neighboring 5.8 GHz ISM band for unlicensed non-ITS uses, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automation In Automobiles
Vehicular automation is using technology to assist or replace the operator of a vehicle such as a car, truck, aircraft, rocket, military vehicle, or boat. Assisted vehicles are ''semi-autonomous'', whereas vehicles that can travel without a human operator are autonomous robot, ''autonomous''. The degree of autonomy may be subject to various constraints such as conditions. Autonomy is enabled by advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) of varying capacity. Related technology includes advanced software, maps, vehicle changes, and outside vehicle support. Autonomy presents varying issues for road, air, and marine travel. Roads present the most significant complexity given the unpredictability of the driving environment, including diverse road designs, driving conditions, traffic, obstacles, and geographical/cultural differences. Autonomy implies that the vehicle is responsible for all perception, monitoring, and control functions. SAE autonomy levels The Society of Aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle Telematics
Telematics is an interdisciplinary field encompassing telecommunications, vehicular technologies (road transport, road safety, etc.), electrical engineering (sensors, instrumentation, wireless communications, etc.), and computer science (multimedia, Internet, etc.). Telematics can involve any of the following: * The technology of sending, receiving, and storing information using telecommunication devices to control remote objects * The integrated use of telecommunications and informatics for application in vehicles and to control vehicles on the move * Satellite navigation, Global navigation satellite system technology integrated with computers and mobile communications technology in automotive navigation systems * (Most narrowly) The use of such systems within road vehicles (also called vehicle telematics) History Telematics is a translation of the French language, French word ''télématique,'' which was first Protologism, coined by Simon Nora and Alain Minc in a 1978 report to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |