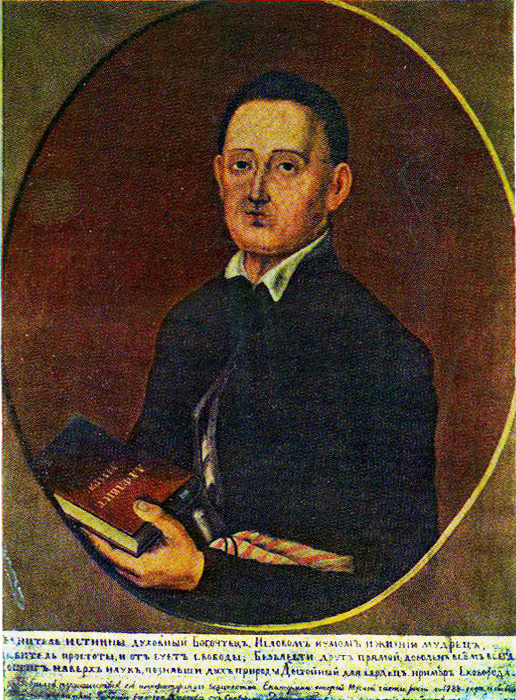|
Ukrainian Composers
This is a list of Ukrainian composers of European classical music, classical music who were either born on the territory of modern-day Ukraine or were ethnically Ukrainian. List by century of birth 15th century 16th century 17th century 18th century 19th century 20th century See also A–D * (1868, Оdesа1942, Tbilisi) * (1816, Voronovytsia1881, Boguslav) * Alexandre Barjansky, Barjansky, Alexandre (1883, Odesa–1961, Brussels) * Felix Blumenfeld, Blumenfeld, Felix (19 April 1863 [O.S. 7 April]21 January 1931) * (1852, Verkhniachka1920, Petrograd) * (1850, Kyiv province1898) * Platon Gregoriewitch Brounoff, Brounoff, Platon Gregoriewitch (1859, Brounoff1924, New York) * (1882, Odesa1943, Auschwitz) E–G * Konstantin Eiges , Eiges, Konstantin (1875, Bogodukhov–1950, Moscow) * Alexander Gauk , Gauk, Alexander (1893, Odesa–1963, Moscow) * Yefim Golyshev (1897, Kherson–1970, Paris) * (1903, Kyiv–1961, Novosibirsk, Russia) References Sourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Classical Music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" can also be applied to List of classical and art music traditions, non-Western art musics. Classical music is often characterized by formality and complexity in its musical form and Harmony, harmonic organization, particularly with the use of polyphony. Since at least the ninth century, it has been primarily a written tradition, spawning a sophisticated music notation, notational system, as well as accompanying literature in music analysis, analytical, music criticism, critical, Music history, historiographical, musicology, musicological and Philosophy of music, philosophical practices. A foundational component of Western culture, classical music is frequently seen from the perspective of individual or com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherkasy
Cherkasy (, ) is a city in central Ukraine. Cherkasy serves as the administrative centre of Cherkasy Oblast as well as Cherkasy Raion within the oblast. The city has a population of Cherkasy is the cultural, educational and industrial centre of Cherkasy Oblast and Central Economical Region of Ukraine. Cherkasy has been known since the 13th century and played a great role in the history of Ukraine. The city was the centre of the land of the Cossacks; its citizens took part in Khmelnytsky Uprising, Khmelnychchyna and Koliivshchyna Cossack and peasant rebellions. The city is located on the right bank of Dnieper River (specifically at the Kremenchuk Reservoir), about south of the nation's capital, Kyiv. Cherkasy is divided into 2 Urban districts of Ukraine, urban districts: Sosnivskyi (with Orshanets village) and Prydniprovskyi. It hosts the administration of Cherkasy urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. In June 2011, the city celebrated its 725th anniversary. Geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maksym Berezovsky
Maxim Sozontovich Berezovsky ( ; ; ) was a composer of secular and liturgical music, and a conductor and opera singer, who worked at the Saint Petersburg Court Chapel in the Russian Empire, but who also spent much of his career in Italy. He made an important contribution in the music of Ukraine. Together with Artemy Vedel and Dmitry Bortniansky, both of whom have cited him as an influence, Berezovsky is considered by musicologists as one of the three great composers of 18th-century Ukrainian classical music, and one of the Russian Empire's first composers. Berezovsky's place of birth and his father's name are known only from verbal accounts. He is traditionally thought to have been educated at the ; he may have also attended the Kyiv-Mohyla Academy, although this is uncertain. In 1758, he was accepted as a singer into the capella at Oranienbaum, before being employed at the imperial court of Catherine II in Saint Petersburg, where he received lessons from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasily Pashkevich
Vasily Alexeyevich Pashkevich also Paskevich () (c. 1742, probably Ukraine – March 20, 1797 in St. Petersburg) was a Russian composer, singer, violinist and teacher of Ukrainian origin who lived during the time of Catherine the Great. Biography Vasily Pashkevich was of Ukrainian originShuliar, Orest: History of Vocal Art. Ivano-Frankivsk: Institute of Arts of Vasyl Stefanyk Precarpathian National University, 2013. P. 13. and according to some sources was born in Ukraine. Vasily Pashkevich entered court service in 1756 becoming a court composer to Tsar Peter III of Russia and later to his widow, Catherine the Great. He also played violin, and taught singing in the Academy of Arts 1773-1774 and later in the court capella. Between 1780 and 1783 he managed the Karl Kniper Theatre and in 1789 he became the first violin of the court orchestra, remaining in charge of imperial ballroom music until his death. Pashkevich wrote important comic operas, often re-working them at len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloboda Ukraine Governorate
Kharkov Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Russian Empire founded in 1835. It embraced the historical region of Sloboda Ukraine. From 1765 to 1780 and from 1796 to 1835 the governorate was called Sloboda Ukraine Governorate. In 1780–1796 there existed the Kharkov Vicegerency (; ). From 1765 to 1780, the Sloboda Ukraine Governorate existed. In 1780, the Kharkov Viceroyalty was established and lasted until 1796. In 1835, the Viceroyalty was again reorganized into the Sloboda-Ukrainian Governorate, and from 1835 onwards, the Kharkov Governorate was formed, which existed until 1925. With each reorganization, the boundaries and administrative structure change significantly. The main state tax implementation, processing, and publishing of statistical information for the Kharkov governorate was the Kharkov Governorate Statistical Committee. History Sloboda Ukraine Governorate (1765–1780) After the abolition of the Cossack system in Sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgorod
Belgorod (, ) is a city that serves as the administrative center of Belgorod Oblast, Russia, located on the Seversky Donets River, approximately north of the border with Ukraine. It has a population of It was founded in 1596 as a defensive fort on the southern border of Russia. Contested by various Russian and Ukrainian factions during World War I and the Russian Civil War, the city served as the temporary Soviet Ukrainian capital at the turn of 1918 and 1919. Etymology The name ''Belgorod'' (Белгород) in Russian literally means "white city", a compound of "" (''bely'', "white, light") and "" (''gorod'', "town, city"). The name is a reference to the region's historical abundance of limestone. Demographics The population of Belgorod is 339,978 as of the most recent censuses: As of the 2021 Census, the ethnic composition of Belgorod was: 1149,931 people (or 44.1% of the population) residing in Belgorod did not state their ethnicity in the 2021 census. Geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yelizaveta Belogradskaya
Yelizaveta Osipovna Belogradskaya (1739 – ca. 1764 was a Russian Imperial Court opera singer and composer for keyboard. She was born in St. Petersburg in 1739, the daughter of Osip Bilohradsky, a court singer and choral conductor, and niece of Timofiy Bilohradsky, the court lute player. She was a kammermädchen at the court of the Empress Elizaveta Petrovna. In 1753 she performed the part of Procris in Francesco Araja's opera '' Cephalus and Procris'', which was the first opera set in Russian, accessed 11 December 2014. with the text by Aleksandr Sumarokov. She sang in G.P. Raupach's "The Refuge of Virtue" and "Alcesta". She appeared at court concerts and festivities as a singer and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Razumovsky
The House of Razumovsky or Rozumovsky (, Ukrainian: ''Розумовський'', German: ''Razumofsky'') is the name of an Imperial Russian noble family of Zaporozhian Cossack origin from Siveria. The main family line became extinct in the 19th century, while its Austrian branch exists to this day. The Austrian branch was started by Grigory Razumovsky, who was forced to relocate to the Austrian Empire in 1816, after he received the hereditary title of Prince in 1815 from Francis I, Emperor of Austria. History The family traces its origin to a khutir called Lemeshi (today a village in Chernihiv Raion, Chernihiv Oblast). Yakiv Rozum and his son Hryhoriy were registered Cossacks of the Kiev Regiment.Rozumovsky at the |
Velyki Mosty
Velyki Mosty (, , ; ; ) is a city in Sheptytskyi Raion of Lviv Oblast (oblast, region) of western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Velyki Mosty urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Its population is History In the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland, the village of Mosty was a royal property, with its own starostas. The village itself was established in 1472, and was part of Belz Voivodeship in the Lesser Poland Province, Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Lesser Poland Province. In the late 15th century, Mosty was ransacked and destroyed in a Crimean Tatars raid, and in July 1497, during the Moldavian expedition of John I Albert, a unit of Teutonic Knights under Johann von Tiefen, called upon by the Polish king, marched through the village. On 23 July 1549, during the period known as the Polish Golden Age, Mosty received Magdeburg rights. It was a royal city in Poland, royal town. Following the order of King Sigismund II Augustus, a szlachta, nobleman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossack Hetmanate
The Cossack Hetmanate (; Cossack Hetmanate#Name, see other names), officially the Zaporozhian Host (; ), was a Ukrainian Cossacks, Cossack state. Its territory was located mostly in central Ukraine, as well as in parts of Belarus and southwestern Russia. It existed between 1649 and 1764, although its administrative-judicial system persisted until 1781. The Hetmanate was founded in the eastern territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by the Treaty of Zboriv, signed on August 18, 1649 by Bohdan Khmelnytsky (Hetman of the Zaporizhian Host) and Adam Kysil (representing Crown Forces), as a result of Khmelnytsky Uprising. Establishment of vassal relations with the Tsardom of Russia in the Pereiaslav Agreement, Treaty of Pereiaslav of 1654 is considered a benchmark of the Cossack Hetmanate in Soviet, Ukrainian, and Russian historiography. The second Pereiaslav Articles, Pereiaslav Council in 1659 restricted the independence of the Hetmanate, and from the Russian side there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiev Governorate (1708–1764)
Kiev Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire. It was established in December 1708 as one of the eight ''guberniyas'' first created during the reforms of Peter the Great. The first established Kiev Governorate was located east of Dnieper, unlike the second ( Kiev Governorate) which was established west of Dnieper in 1802 after the partitions of Poland. Description The Government of Kiev in the 18th century greatly differed from the Government of Kiev in the 19th century. When one was exclusively located on the left banks of Dnieper, the other one happened to be located across the river. In territorial reform of Catherine the Great changed the name for government to the Russian vice royalty in 1781. The first Government of Kiev was established on the most part of the Cossack Hetmanate including a vast territory to east of the Hetmanate as well, while the Zaporizhian Sich was in a condominium of the Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |