|
Speech Synthesis
Speech synthesis is the artificial production of human speech. A computer system used for this purpose is called a speech synthesizer, and can be implemented in software or hardware products. A text-to-speech (TTS) system converts normal language text into speech; other systems render symbolic linguistic representations like phonetic transcriptions into speech. The reverse process is speech recognition. Synthesized speech can be created by concatenating pieces of recorded speech that are stored in a database. Systems differ in the size of the stored speech units; a system that stores phones or diphones provides the largest output range, but may lack clarity. For specific usage domains, the storage of entire words or sentences allows for high-quality output. Alternatively, a synthesizer can incorporate a model of the vocal tract and other human voice characteristics to create a completely "synthetic" voice output. The quality of a speech synthesizer is judged by its similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, such as informing, declaring, asking, persuading, directing; acts may vary in various aspects like enunciation, Intonation (linguistics), intonation, loudness, and Speech tempo, tempo to convey meaning. Individuals may also unintentionally communicate aspects of their social position through speech, such as sex, age, place of origin, physiological and mental condition, education, and experiences. While normally used to facilitate communication with others, people may also use speech without the intent to communicate. Speech may nevertheless express emotions or desires; people Talking to oneself, talk to themselves sometimes in acts that are a development of what some psychologists (e.g., Lev Vygotsky) have maintained is the use of silent spee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text Normalization
Text normalization is the process of transforming text into a single canonical form that it might not have had before. Normalizing text before storing or processing it allows for separation of concerns, since input is guaranteed to be consistent before operations are performed on it. Text normalization requires being aware of what type of text is to be normalized and how it is to be processed afterwards; there is no all-purpose normalization procedure. Applications Text normalization is frequently used when converting text to speech. Numbers, dates, acronyms, and abbreviations are non-standard "words" that need to be pronounced differently depending on context.Sproat, R.; Black, A.; Chen, S.; Kumar, S.; Ostendorf, M.; Richards, C. (2001). "Normalization of non-standard words." ''Computer Speech and Language'' 15; 287–333. doibr>10.1006/csla.2001.0169 For example: * "$200" would be pronounced as "two hundred dollars" in English, but as "lua selau tālā" in Samoan. * "vi" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the Scholastic accolades, scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English polymath, philosopher, scientist, theologian and Franciscans, Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through empiricism. Intertwining his Catholic faith with scientific thinking, Roger Bacon is considered one of the greatest polymaths of the Medieval Period, medieval period. In the Early modern period, early modern era, he was regarded as a Wizard (paranormal), wizard and particularly famed for the story of his History of robots, mechanical or necromancy, necromantic brazen head. He is credited as one of the earliest European advocates of the modern scientific method, along with his teacher Robert Grosseteste. Bacon applied the empirical method of Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) to observations in texts attributed to Aristotle. Bacon discovered the importance of empirical testing when the results he obt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albertus Magnus
Albertus Magnus ( 1200 – 15 November 1280), also known as Saint Albert the Great, Albert of Swabia, Albert von Bollstadt, or Albert of Cologne, was a German Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and bishop, considered one of the greatest medieval philosophers and thinkers. Canonized in 1931, he was known during his lifetime as ''Doctor universalis'' and ''Doctor expertus''; late in his life the sobriquet ''Magnus'' was appended to his name. Scholars such as James A. Weisheipl and Joachim R. Söder have referred to him as the greatest German philosopher and theologian of the Middle Ages. The Catholic Church distinguishes him as one of the Doctors of the Church. Biography It seems likely that Albertus Magnus was born sometime before 1200, given well-attested evidence that he was aged over 80 on his death in 1280. Two later sources say that Albert was about 87 on his death, which has led 1193 to be commonly given as the date of Albert's birth, but this information doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silvester II
Pope Sylvester II (; – 12 May 1003), originally known as Gerbert of Aurillac, was a scholar and teacher who served as the bishop of Rome and ruled the Papal States from 999 to his death. He endorsed and promoted study of Moorish and Greco-Roman arithmetic, mathematics and astronomy, reintroducing to Western Christendom the abacus, armillary sphere, and water organ, which had been lost to Latin Europe since the fall of the Western Roman Empire. He is said to be the first in Christian Europe (outside of Al-Andalus) to introduce the decimal numeral system using the Hindu-Arabic numeral system. Early life Gerbert was born about 946, or at any rate between 945 and 950. His exact birthplace is unknown, but it must have been in what was then the Duchy of Aquitaine, part of the Kingdom of France. More precise proposals include the town of Belliac, near the present-day commune of Saint-Simon, Cantal, or Aurillac. Another speculated location is the province of Auvergne. Gerbert's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, Scalar potential, potential fields, Seismic tomography, seismic signals, Altimeter, altimetry processing, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, Data storage, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, improve subjective video quality, and to detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal. History According to Alan V. Oppenheim and Ronald W. Schafer, the principles of signal processing can be found in the classical numerical analysis techniques of the 17th century. They further state that the digital refinement of these techniques can be found in the digital control systems of the 1940s and 1950s. In 1948, Claude Shannon wrote the influential paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication" which was publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield of physics and electrical engineering which uses Passivity (engineering), active devices such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to control and amplify the flow of electric current and to convert it from one form to another, such as from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or from analog signal, analog signals to digital signal, digital signals. Electronic devices have significantly influenced the development of many aspects of modern society, such as telecommunications, entertainment, education, health care, industry, and security. The main driving force behind the advancement of electronics is the semiconductor industry, which continually produces ever-more sophisticated electronic devices and circuits in respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosody (linguistics)
In linguistics, prosody () is the study of elements of speech, including intonation, stress, rhythm and loudness, that occur simultaneously with individual phonetic segments: vowels and consonants. Often, prosody specifically refers to such elements, known as ''suprasegmentals'', when they extend across more than one phonetic segment. Prosody reflects the nuanced emotional features of the speaker or of their utterances: their obvious or underlying emotional state, the form of utterance (statement, question, or command), the presence of irony or sarcasm, certain emphasis on words or morphemes, contrast, focus, and so on. Prosody displays elements of language that are not encoded by grammar, punctuation or choice of vocabulary. Attributes of prosody In the study of prosodic aspects of speech, it is usual to distinguish between auditory measures ( subjective impressions produced in the mind of the listener) and objective measures (physical properties of the sound wave and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grapheme
In linguistics, a grapheme is the smallest functional unit of a writing system. The word ''grapheme'' is derived from Ancient Greek ('write'), and the suffix ''-eme'' by analogy with ''phoneme'' and other emic units. The study of graphemes is called '' graphemics''. The concept of graphemes is abstract and similar to the notion in computing of a character. (A specific geometric shape that represents any particular grapheme in a given typeface is called a glyph.) Conceptualization There are two main opposing grapheme concepts. In the so-called ''referential conception'', graphemes are interpreted as the smallest units of writing that correspond with sounds (more accurately phonemes). In this concept, the ''sh'' in the written English word ''shake'' would be a grapheme because it represents the phoneme /ʃ/. This referential concept is linked to the ''dependency hypothesis'' that claims that writing merely depicts speech. By contrast, the ''analogical concept'' defines gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentence (linguistics)
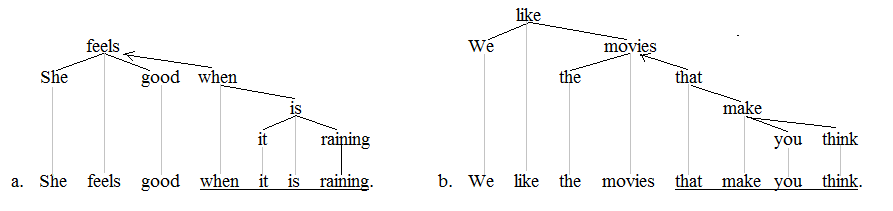
In linguistics and grammar, a sentence is a Expression (linguistics), linguistic expression, such as the English example "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog." In traditional grammar, it is typically defined as a string of words that expresses a complete thought, or as a unit consisting of a Subject (grammar), subject and Predicate (grammar), predicate. In non-functional linguistics it is typically defined as a maximal unit of syntactic structure such as a Constituent_(linguistics), constituent. In functional linguistics, it is defined as a unit of written texts delimited by writing, graphological features such as upper-case letters and markers such as periods, question marks, and exclamation marks. This notion contrasts with a curve, which is delimited by phonologic features such as pitch and loudness and markers such as pauses; and with a clause, which is a sequence of words that represents some process going on throughout time. A sentence can include words grouped meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clause
In language, a clause is a Constituent (linguistics), constituent or Phrase (grammar), phrase that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic Predicate (grammar), predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject (grammar), subject and a syntactic Predicate (grammar), predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with or without any object (grammar), objects and other Grammatical modifier, modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unexpressed if it is easily deducible from the context, especially in null-subject languages but also in other languages, including instances of the imperative mood in English grammar, English. A complete simple sentence contains a single clause with a finite verb. Complex sentences contain at least one clause subordinated (dependent clause, ''dependent'') to an ''independent clause'' (one that could stand alone as a simple sentence), which may be co-ordinated with other independents with or without dependents. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |