|
Organorhenium Compounds
Organorhenium chemistry describes the compounds with Re−C bonds. Because rhenium is a rare element, relatively few applications exist, but the area has been a rich source of concepts and a few useful catalysts. General features Rhenium exists in ten known oxidation states from −3 to +7 except −2, and all but Re(−3) are represented by organorhenium compounds. Most are prepared from salts of perrhenate and related binary oxides.O. Glemser "Ammonium Perrhenate" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. p. 1476-85. The halides, e.g., ReCl5 are also useful precursors as are certain oxychlorides. A noteworthy feature of organorhenium chemistry is the coexistence of oxide and organic ligands in the same coordination sphere. Carbonyl compounds Dirhenium decacarbonyl is a common entry point to other rhenium carbonyls. The general patterns are similar to the related manganese carbonyls. It is possible to redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhenium
Rhenium is a chemical element; it has symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-gray, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an estimated average concentration of 1 part per billion (ppb), rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth's crust. It has one of the highest melting and boiling points of any element. It resembles manganese and technetium chemically and is mainly obtained as a by-product of the extraction and refinement of molybdenum and copper ores. It shows in its compounds a wide variety of oxidation states ranging from −1 to +7. Rhenium was originally discovered in 1908 by Masataka Ogawa, but he mistakenly assigned it as element 43 (now known as technetium) rather than element 75 and named it ''nipponium''. It was rediscovered in 1925 by Walter Noddack, Ida Tacke and Otto Berg, who gave it its present name. It was named after the river Rhine in Europe, from which the earliest samples had been obtained and worked co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-sandwich Compound
Half sandwich compounds, also known as piano stool complexes, are organometallic complexes that feature a cyclic polyhapto ligand bound to an MLn center, where L is a unidentate ligand. Thousands of such complexes are known. Well-known examples include cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl and (C5H5)TiCl3. Commercially useful examples include (C5H5)Co(CO)2, which is used in the synthesis of substituted pyridines, and methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl, an antiknock agent in petrol. MMT-2D-skeletal.png, MMT is a commercially useful antiknock compound. Cpco(CO)2.png, CpCo(CO)2 is a catalyst for the synthesis of pyridines. Cyclobutadiene-iron-tricarbonyl-from-xtal-3D-balls.png, (C4H4)Fe(CO)3. Cp2Fe(CO)2I-2D-skeletal.png, CpFe(CO)2I is an example of a piano stool complex with two different monodentate ligands. RuCymCl2.png, The diruthenium of cymene is readily cleaved by ligands to give monoRu half-sandwich derivatives. CHTMo(CO)3.png, Cycloheptatriene molybdenum tricarbonyl CPP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
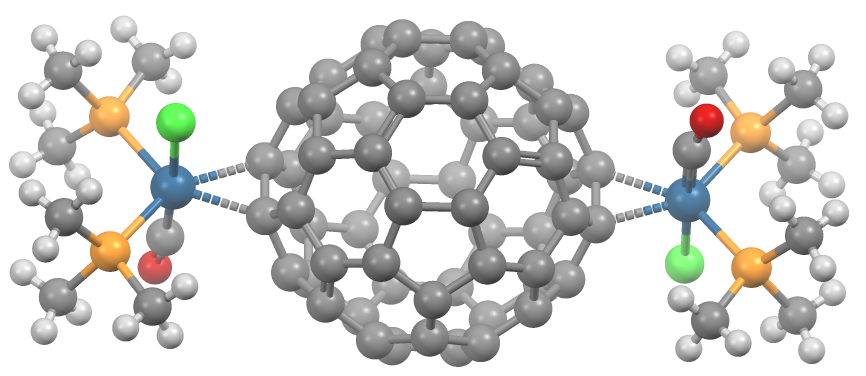
Fullerene Ligands
A transition metal fullerene complex is a coordination complex wherein fullerene serves as a ligand. Fullerenes are typically spheroidal carbon compounds, the most prevalent being buckminsterfullerene, C60. One year after it was prepared in milligram quantities in 1990, C60 was shown to function as a ligand in the complex [Ph3P]2Pt(η2-C60). Since this report, a variety of transition metals and binding modes were demonstrated. Most transition metal fullerene complex are derived from C60, although other fullerenes also coordinate to metals as seen with C70Rh(H)(CO)(PPh3)2. Binding modes As ligands, fullerenes behave similarly to electron-deficient alkenes such as tetracyanoethylene. Thus, their complexes are a subset of metal-alkene complexes. They almost always coordinate in a Hapticity, dihapto fashion and prefer electron-rich metal centers.Spessard, p. 162 This binding occurs on the junction of two 6-membered rings. Hexahapto and pentahapto bonding is rarely observed.Spessard, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazoalkane
In organic chemistry, the diazo group is an organic moiety (chemistry), moiety consisting of two linked nitrogen atoms at the terminal position. Overall charge-neutral organic compounds containing the diazo group bound to a carbon atom are called diazo compounds or diazoalkanes and are described by the general structural formula . The simplest example of a diazo compound is diazomethane, . Diazo compounds () should not be confused with azo compounds () or with diazonium compounds (). Structure The electronic structure of diazo compounds is characterized by π electron density delocalized over the α-carbon and two nitrogen atoms, along with an orthogonal π system with electron density delocalized over only the terminal nitrogen atoms. Because all octet rule-satisfying resonance forms of diazo compounds have formal charges, they are members of a class of compounds known as 1,3-dipoles. Some of the most stable diazo compounds are α-diazo-β-diketones and α-diazo-β-dieste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology. Structure and bonding Aldehyde molecules have a central carbon atom that is connected by a double bond to oxygen, a single bond to hydrogen and another single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2- hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar. The bond length is about 120–122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes such as formaldehyde and acetaldehyde are solubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Preferred IUPAC name, recommends using the name "alkene" only for Open-chain compound, acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for Cyclic compound, cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with ''n'' being a >1 natural number (which is two hydrogens less than the corresponding alkane). When ''n'' is four or more, isomers are possible, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 118 picometers (for C2H2) is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (132 pm, for C2H4) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or "high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as both a monopropellant and an oxidizer in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly into water and elemental oxygen when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a Stabilizer (chemistry), stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in an opaque bottle. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetramethyltin
Tetramethyltin is an organometallic compound with the formula (CH3)4Sn. This liquid, one of the simplest organotin compounds, is useful for transition-metal mediated conversion of acid chlorides to methyl ketones and aryl halides to aryl methyl ketones. It is volatile and toxic, so care should be taken when using it in the laboratory. Synthesis and structure Tetramethyltin is synthesized by reaction of the Grignard reagent methylmagnesium iodide, with tin tetrachloride, which is synthesized by reacting tin metal with chlorine gas. :4 CH3MgI + SnCl4 → (CH3)4Sn + 4 MgICl In tetramethyltin, the metal surrounded by four methyl groups in a tetrahedral structure is a heavy analogue of neopentane. Applications Precursor to methyltin compounds Tetramethyltin is a precursor to trimethyltin chloride (and related methyltin halides), which are precursors to other organotin compounds. These methyltin chlorides are prepared via the so-called Kocheshkov redistribution reaction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylrhenium Trioxide
Methylrhenium trioxide, also known as methyltrioxorhenium(VII), is an organometallic compound with the formula . It is a volatile, colourless solid that has been used as a catalyst in some laboratory experiments. This chemical substance adopts a tetrahedral molecular geometry with rhenium surrounded by one methyl and three oxo ligands. The oxidation state of rhenium is +7. Synthesis Methylrhenium trioxide is commercially available. It can be prepared by many routes, a typical method is the reaction of rhenium heptoxide and tetramethyltin: : Analogous alkyl and aryl derivatives are known. Compounds of the type are Lewis acids, forming both 1:1 and 1:2 adducts with halides and amines. Uses Methylrhenium trioxide serves as a heterogeneous catalyst for a variety of transformations. Supported on alumina/silica, it catalyzes olefin metathesis at 25 °C. In solution, methylrhenium trioxide catalyses for the oxidations with hydrogen peroxide. Terminal alkynes yield the correspondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |