|
Nitrobenzenes
Nitrobenzenes are a group of nitro compounds consisting of one or more Nitro compound, nitro groups as substituents on a benzene core. They have the formula C6H6–''n''(NO2)''n'', where ''n'' = 1–6 is the number of nitro groups. Depending on the number of nitro groups, there may be several constitutional isomers possible. * Mononitrobenzene * Dinitrobenzene ** 1,2-Dinitrobenzene ** 1,3-Dinitrobenzene ** 1,4-Dinitrobenzene * Trinitrobenzene ** 1,2,3-Trinitrobenzene ** 1,2,4-Trinitrobenzene ** 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene * Tetranitrobenzene ** 1,2,3,4-Tetranitrobenzene ** 1,2,3,5-Tetranitrobenzene ** 1,2,4,5-Tetranitrobenzene * Pentanitrobenzene * Hexanitrobenzene Nitrobenzenes, {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
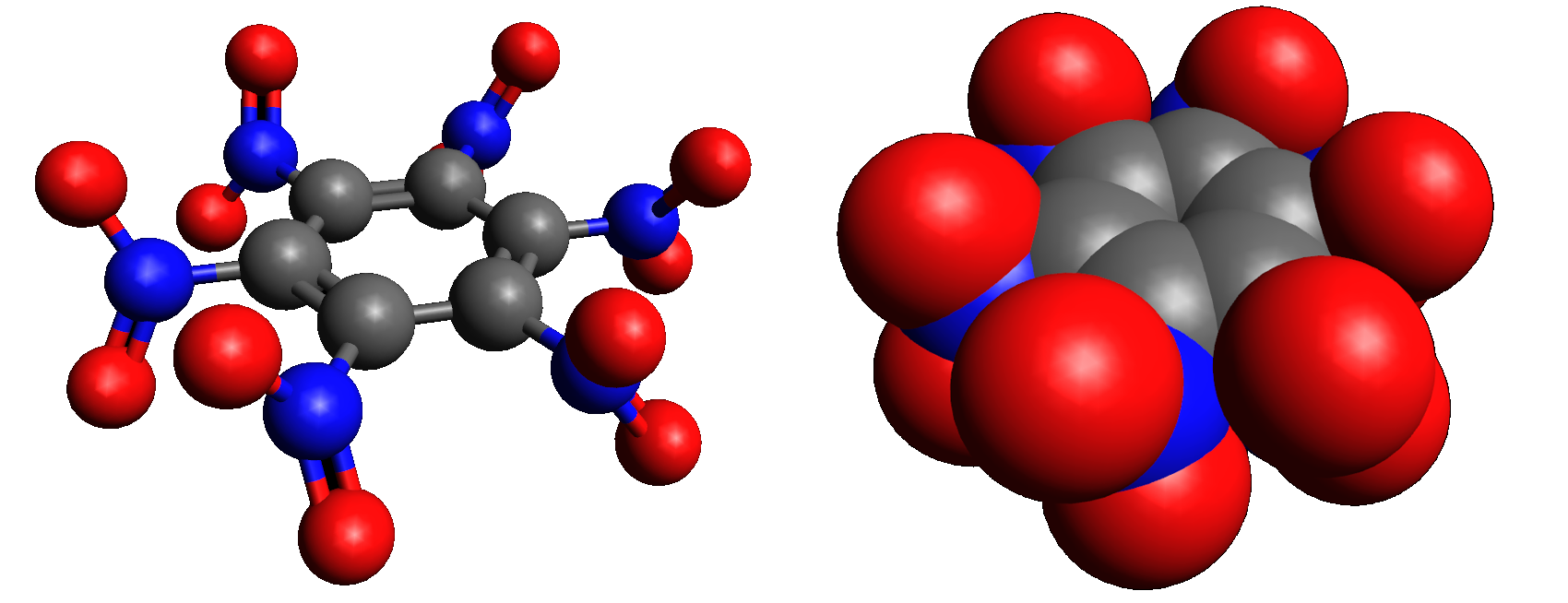
Hexanitrobenzene
Hexanitrobenzene, also known as HNB, is a nitrobenzenes, nitrobenzene compound in which six Nitro compound, nitro groups are bonded to all six positions of a central benzene ring. It is a high-density explosive compound (chemistry), compound with chemical formula , obtained by oxidation, oxidizing the amine group of pentanitroaniline with hydrogen peroxide in sulfuric acid. Properties The stable Conformational isomerism, conformation of this molecule has the nitro groups rotated out of the plane of the central benzene ring. The molecule adopts a propeller-like conformation in which the nitro groups are rotated about 53° from planar. HNB has the undesirable property of being moderately sensitive to light and, therefore, hard to utilize safely. As of 2021, it is not used in any production explosives applications, though it is used as a precursor chemical in one method of production of TATB, another explosive. HNB was experimentally used as a gas source for explosively pumped ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,2-Dinitrobenzene
1,2-Dinitrobenzene is one of three isomers of dinitrobenzene Dinitrobenzenes are nitrobenzenes composed of a benzene ring and two nitro group (-NO2) substituents. The three possible arrangements of the nitro groups afford three isomers, 1,2-dinitrobenzene, 1,3-dinitrobenzene, and 1,4-dinitrobenzene. Each iso ..., with the formula C6H4(NO2)2. The compound is a white or colorless solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is prepared from 2-nitroaniline by diazotization and treatment with sodium nitrite in the presence of a copper catalyst. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Dinitrobenzene, 1,2- Nitrobenzenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene
1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene is one of three isomers of trinitrobenzene with the formula C6H3(NO2)3. A pale yellow solid, the compound is highly explosive. Synthesis and reactions 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene is produced by decarboxylation of 2,4,6-trinitrobenzoic acid. 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene forms charge-transfer complexes with electron-rich arenes. Reduction of 1,3,5-trinitrobenzene gives 1,3,5-triaminobenzene, a precursor to phloroglucinol. Uses and applications Trinitrobenzene is more explosive than TNT, but more expensive. It is primarily used as a high explosive compound for commercial mining and military applications. It has also been used as a narrow-range pH indicator, an agent to vulcanize natural rubber, and a mediating agent to mediate the synthesis of other explosive compounds. See also * 1,2,3-Trinitrobenzene * TNT equivalent * RE factor TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. A ton of TNT equ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,2,3-Trinitrobenzene
1,2,3-Trinitrobenzene is an isomer of trinitrobenzene. See also * 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene is one of three isomers of trinitrobenzene with the formula C6H3(NO2)3. A pale yellow solid, the compound is highly explosive. Synthesis and reactions 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene is produced by decarboxylation of 2,4,6-trinitrob ... References Nitrobenzenes {{aromatic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,4-Dinitrobenzene
1,4-Dinitrobenzene is one of three isomers of dinitrobenzene, with the formula C6H4(NO2)2. The 1,4-isomer is most symmetrical. The compound is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is prepared from 4-nitroaniline by diazotization followed by treatment with sodium nitrite Sodium nitrite is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a white to slightly yellowish crystalline powder that is very soluble in water and is hygroscopic. From an industrial perspective, it is the most important nitrite sa ... in the presence of a copper catalyst. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Dinitrobenzene, 1,4- Nitrobenzenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,3-Dinitrobenzene
1,3-Dinitrobenzene is one of three isomers of dinitrobenzene, with the formula C6H4(NO2)2. It is one of three isomers of dinitrobenzene. The compound is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Preparation 1,3-Dinitrobenzene is accessible by nitration of nitrobenzene. The reaction proceeds under acid catalysis using sulfuric acid. The directing effect of the nitro group of nitrobenzene leads to 93% of the product resulting from nitration at the ''meta''-position. The ''ortho''- and ''para''-products occur in only 6% and 1%, respectively. : Reactions Reduction of 1,3-dinitrobenzene with sodium sulfide in aqueous solution leads to 3-nitroaniline. Further reduction with iron and hydrochloric acid Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ... (HCl) gives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinitrobenzene
Trinitrobenzenes are nitrobenzenes consisting of three nitro groups bonded to a central benzene ring. There are three isomers of trinitrobenzene: * 1,2,3-Trinitrobenzene * * 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene is one of three isomers of trinitrobenzene with the formula C6H3(NO2)3. A pale yellow solid, the compound is highly explosive. Synthesis and reactions 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene is produced by decarboxylation of 2,4,6-trinitrob ... Nitrobenzenes {{chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrobenzene
Dinitrobenzenes are nitrobenzenes composed of a benzene ring and two nitro group (-NO2) substituents. The three possible arrangements of the nitro groups afford three isomers, 1,2-dinitrobenzene, 1,3-dinitrobenzene, and 1,4-dinitrobenzene. Each isomer has the chemical formula C6H4N2O4 and a molar mass of about 168.11 g/mol. 1,3-Dinitrobenzene is the most common isomer and it is used in the manufacture of Explosive material, explosives. Properties The dinitrobenzenes are all crystalline solids. The boiling points of the three isomers are relatively close; however, the melting points significantly differ. 1,4-Dinitrobenzene, which has the highest symmetry, has the highest melting point. References {{reflist Nitrobenzenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mononitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene is an aromatic nitro compound and the simplest of the nitrobenzenes, with the chemical formula C6H5 NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline. In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent, especially for electrophilic reagents. As confirmed by X-ray crystallography, nitrobenzene is a planar molecule. Production Nitrobenzene is prepared by nitration of benzene with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid, water, and nitric acid. This mixture is sometimes called "mixed acid." The production of nitrobenzene is one of the most dangerous processes conducted in the chemical industry because of the exothermicity of the reaction (Δ''H'' = −117 kJ/mol). World capacity for nitrobenzene in 1985 was about 1,700,000 tonnes. The nitration process involves formation of the nitronium ion (NO2+), followed by an electrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Isomer
In chemistry, a structural isomer (or constitutional isomer in the IUPAC nomenclature) of a compound is a compound that contains the same number and type of atoms, but with a different connectivity (i.e. arrangement of bonds) between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept. For example, butanol , methyl propyl ether , and diethyl ether have the same molecular formula but are three distinct structural isomers. The concept applies also to polyatomic ions with the same total charge. A classical example is the cyanate ion and the fulminate ion . It is also extended to ionic compounds, so that (for example) ammonium cyanate and urea are considered structural isomers,William F. Bynum, E. Janet Browne, Roy Porter (2014)''Dictionary of the History of Science'' page 218. and so are methylammonium formate and ammonium acetate . Structural isomerism is the most radical type of isomerism. It is opposed to stereoisomerism, in which the atoms and bonding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitro Compound
In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups (). The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used globally. The nitro group is also strongly electron-withdrawing. Because of this property, bonds alpha (adjacent) to the nitro group can be acidic. For similar reasons, the presence of nitro groups in aromatic compounds retards electrophilic aromatic substitution but facilitates nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Nitro groups are rarely found in nature. They are almost invariably produced by nitration reactions starting with nitric acid. Synthesis Preparation of aromatic nitro compounds Aromatic nitro compounds are typically synthesized by nitration. Nitration is achieved using a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid, which produce the nitronium ion (), which is the electrophile: + The nitration product produced on the largest scale, by f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon. Benzene is a natural constituent of petroleum and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. Due to the cyclic continuous pi bonds between the carbon atoms, benzene is classed as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Benzene is a colorless and highly Combustibility and flammability, flammable liquid with a sweet smell, and is partially responsible for the aroma of gasoline. It is used primarily as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to the manufacture of chemicals with more complex structures, such as ethylbenzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are produced annually. Although benzene is a major Chemical industry, industrial che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |