|
Karelia
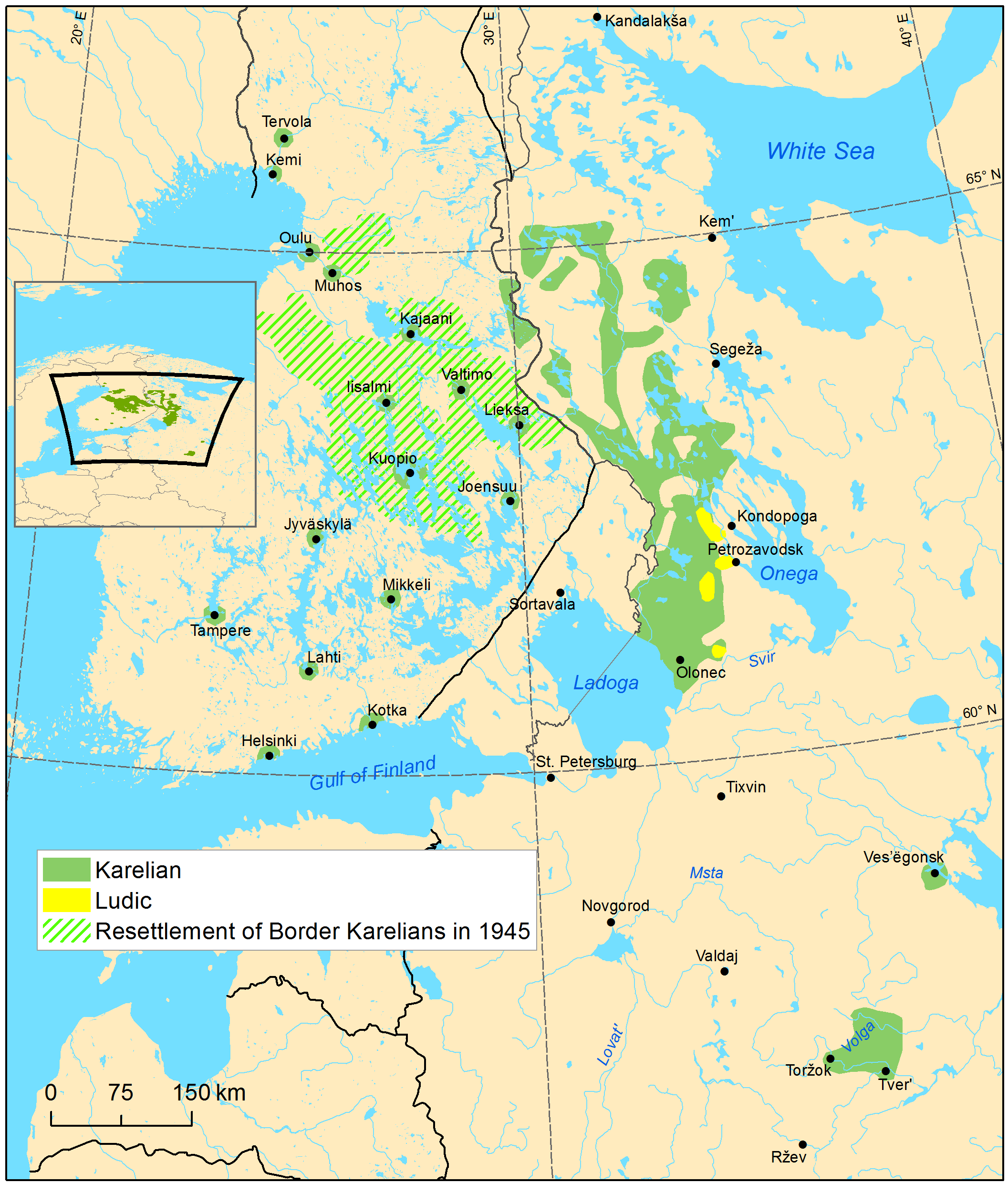
Karelia (; Karelian language, Karelian and ; , historically Коре́ла, ''Korela'' []; ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia (the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast) and Finland (the Regions of Finland, regions of South Karelia, North Karelia, and the eastern portion of Kymenlaakso). Use of name Various regions may be called Karelia. Finnish Karelia is a historical province of Finland and is now divided between Finland and Russia, often called just ''Karjala'' in Finnish. The eastern part of this chiefly Lutheran area was ceded to Russia after the Winter War of 1939–40. The Republic of Karelia is a Russian federal subject, including East Karelia, with a chiefly Russian Orthodox population. Within present-day Finland, ''Karjala'' refers to the Regions of Finland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia, or simply Karelia or Karjala (; ) is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia situated in the Northwest Russia, northwest of the country. The republic is a part of the Northwestern Federal District, and covers an area of , with a population of 533,121 residents. Its capital city, capital is Petrozavodsk. The modern Karelian Republic was founded as an autonomous republic within the Russian SFSR, by the Resolution of the Presidium of the All-Russian Central Executive Committee (VTsIK) on 27 June 1923 and by the Decree of the VTsIK and the Council of People's Commissars of 25 July 1923, from the Karelian Labor Commune, Karelian Labour Commune. From 1940 to 1956, it was known as the Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic, one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, republics of the Soviet Union. In 1956, it was once again made an autonomous republic and remained part of Russia following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Etymology "Karelia" deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelian Language
Karelian (; ; ; ) is a Finnic language spoken mainly by the Karelians, Karelian people in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish language, Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, but nowadays it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the South Karelian dialects, Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as ("Karelian dialects") in Finland. In the Russian 2020–2021 census, around 9,000 people spoke Karelian natively, but around 14,000 said they were able to speak the language. There are around 11,000 speakers of Karelian in Finland, and around 30,000 people in Finland have at least some knowledge of Karelian. The Karelian language is a group of two supradialects. The two supradialects are Karelian Proper language, Karelian Proper (which comprises Northern Karelian dialect, Northern Kareli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
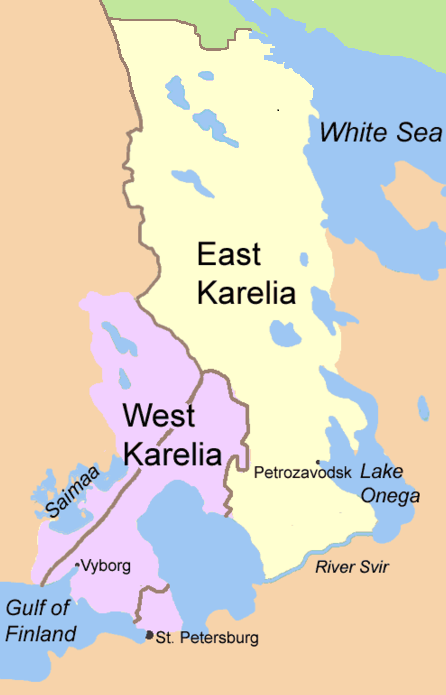
Finnish Karelia
Karelia (: ) is a historical province of Finland, consisting of the modern-day Finnish regions of South Karelia and North Karelia plus the historical regions of Ladoga Karelia and the Karelian Isthmus, which are now in Russia. Historical Karelia also extends to the regions of Kymenlaakso (east of the River Kymi), Northern Savonia ( Kaavi, Rautavaara and Säyneinen) and Southern Savonia ( Mäntyharju). Karelia may also refer to the region as a whole, including the portion of Karelia within Russia. The term "Finnish Karelia" refers specifically to the historical Finnish province, while East Karelia or "Russian Karelia" refers to the portion of Karelia within Russia. Finland ceded a portion of Finnish Karelia to the Soviet Union after the Winter War of 1939–40. More than 400,000 evacuees from the ceded territories re-settled in various parts of Finland. Finnish Karelians include the present-day inhabitants of South Karelia and North Karelia, as well as the still-surviving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Karelia
North Karelia (or ''Northern Karelia'', ; ) is a region in eastern Finland. It borders the regions of Kainuu, North Savo, South Savo and South Karelia, as well as Russia's Republic of Karelia. It is the easternmost region of Finland and shares a border with Russia. The city of Joensuu is the capital and the largest settlement of the region. North Karelia has successfully reduced chronic diseases through public health measures. In the 1960s Finland led industrialized nations in heart disease mortality rates; North Karelia had Finland's highest incidence. In 1972 a long-term project was undertaken which targeted this risk in North Karelia. The resulting improvement in public health is still considered remarkable, a model for the rest of the nation. North Karelia is also known as the most sociable region in Finland. History The borders of remote North Karelia were formed gradually. Important border foundations were the Treaty of Stolbovo (1617) for the eastern border and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peace Treaty on 13 March 1940. Despite superior military strength, especially in tanks and aircraft, the Soviet Union suffered severe losses and initially made little headway. The League of Nations deemed the attack illegal and expelled the Soviet Union from its organization. The Soviets made several demands, including that Finland cede substantial border territories in exchange for land elsewhere, claiming security reasonsprimarily the protection of Leningrad, from the Finnish border. When Finland refused, the Soviets invaded. Most sources conclude that the Soviet Union had intended to conquer all of Finland, and cite the establishment of the Finnish Democratic Republic, puppet Finnish Communist government and the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Karelia
South Karelia (or ''Southern Karelia'', ; ) is a Regions of Finland, region of Finland. It borders the regions of Kymenlaakso, Southern Savonia, South Savo and North Karelia, as well as Russia (Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast). Historical province ''For history, geography and culture see: Finnish Karelia'' Heraldry The coat of arms of South Karelia is composed of the arms of Finnish Karelia, Karelia. Nature The ground in the region consists of loose soil types accumulated on top of bedrock during the Last Glacial Period, last ice age, as the ice sheet retreated to the northwest. The soil shaped by the Last Glacial Period, Ice Age is still clearly visible in the South Karelian environment and scenery. The greatest natural wonder in South Karelia consists of the parallel dividers called Salpausselkä, which transect the region, and their large edge formations. At its steepest, the divider plunges into Lake Saimaa in Kyläniemi village of Taipalsaari. The variable t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Karelia
East Karelia (, ), also rendered as Eastern Karelia or Russian Karelia, is a name for the part of Karelia that is beyond the eastern border of Finland and since the Treaty of Stolbovo in 1617 has remained Eastern Orthodox and a part of Russia. It is separate from the western part of Karelia, called '' Finnish Karelia'' or historically ''Swedish Karelia'' (before 1808). Most of East Karelia has become part of the Republic of Karelia within the Russian Federation. It consists mainly of the old historical regions of Viena Karjala ( English: White Karelia) and Aunus Karjala ( English: Olonets Karelia). Culture and ideology 19th-century ethnic-nationalist Fennomans saw East Karelia as the ancient home of Finnic culture, "un-contaminated" by either Scandinavians or Slavs. In the sparsely populated East Karelian backwoods, mainly in White Karelia, Elias Lönnrot (1802–1884) collected the folk tales that ultimately would become Finland's national epic, the Kalevala (published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, opposite Estonia. Finland has a population of 5.6 million. Its capital and largest city is Helsinki. The majority of the population are Finns, ethnic Finns. The official languages are Finnish language, Finnish and Swedish language, Swedish; 84.1 percent of the population speak the first as their mother tongue and 5.1 percent the latter. Finland's climate varies from humid continental climate, humid continental in the south to boreal climate, boreal in the north. The land cover is predominantly boreal forest biome, with List of lakes of Finland, more than 180,000 recorded lakes. Finland was first settled around 9000 BC after the Last Glacial Period, last Ice Age. During the Stone Age, various cultures emerged, distinguished by differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of The Province Of Karelia
The coat of arms of Karelia in Finland were first used in 1562, although the arms were likely presented at the burial of Gustav Vasa in 1560. The arms were used for the Swedish province of Karelia {{Heraldry-stub}">; ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currentl ... {{Heraldry-stub} ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currentl ... and they have been used continuously since then. Variations of the arms are still used in two regions of Finland: North Karelia and South Karelia, in which the North Karelian version is the original one. North Karelia was not part of the Swedish Kingdom until 1617, when Sweden gained the area from Russia following the Treaty of Stolbovo. South Karelia belonged to Sweden from 1323 to 1743, when Russia annexed territory from Sweden following t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Onega
Lake Onega (; also known as Onego; , ; ; Livvi-Karelian language, Livvi: ''Oniegujärvi''; ) is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic Sea, and is the second-largest lake in Europe after Lake Ladoga, slightly smaller than Lebanon. The lake is fed by about 50 rivers and is drained by the Svir. There are about 1,650 islands on the lake. They include Kizhi, which hosts a historical complex of 89 Orthodox churches and other wooden structures of the 15th–20th centuries. The complex includes a UNESCO World Heritage Site, Kizhi Pogost. The eastern shores of the lake contain about 1,200 petroglyphs (rock engravings) dated to the 4th–2nd millennia BC, which have Petroglyphs of Lake Onega and the White Sea, also been inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The major cities on the lake are Petrozavodsk, Kondopoga and Medvezhyegorsk. Geological history The lake is of Glacial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of The Republic Of Karelia
The coat of arms of the Russian Republic of Karelia is crossed in three equal parts with the colors of the flag of Karelia on a shield with a profile of a rampant Asian black bear, black bear. The golden frame of the shield comes into stylized image of a fir tree on the left and a pine tree on the right. In the upper part of the shield there is an octagonal star (doubled cross) of gold. The arms were created by . The current coat of arms of Karelia has much resemblance with the coat of arms of the independent Republic of Uhtua, the national symbol of East Karelia created by Finnish artist Akseli Gallen-Kallela. The main difference is that the bear was holding a billhook. The shield had the traditional Varangian colours and there were Aurora (astronomy), polar lights above of shield. Sources * Constitution of the Republic of Karelia, paragraph 13. The official site of the republic See also * Emblem of the Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic, Emblem of the Karelo-Finnish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast (, ; ; ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). The oblast has an area of and a population of 2,000,997 (2021 Russian census, 2021 Census); up from 1,716,868 recorded in the 2010 Russian census, 2010 Census. Leningrad Oblast is highly industrialized. Its administrative center and largest city is Gatchina. The oblast was established on 1 August 1927, although it was not until 1946 that the oblast's borders had been mostly settled in their present position. The oblast was named after the city of Saint Petersburg, Leningrad. In 1991, the city restored its original name, Saint Petersburg, but the oblast retains the name of Leningrad. It overlaps the historical region of Ingria, and is bordered by Finland (Kymenlaakso and South Karelia) in the northwest and Estonia (Ida-Viru County) in the west, as well as five federal subjects of Russia: the Republic of Karelia in the northeast, Vologda Oblast in the east, Novgorod Oblast in the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |