|
Interplanetary Monitoring Platform
Interplanetary Monitoring Platform was a program managed by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, as part of the Explorers program, with the primary objectives of investigation of interplanetary space, interplanetary plasma (physics), plasma and the interplanetary magnetic field. The orbiting of IMP satellites in a variety of interplanetary and earth orbits allowed study of spatial and temporal relationships of geophysical and interplanetary phenomena simultaneously by several other NASA satellites. Satellites Technology The IMP program was the first space program to use integrated circuit (IC) chips, which it first launched into space with the IMP-A (Explorer 18) in 1963. This predates the use of IC chips in the Apollo Guidance Computer, used for the Apollo program. The MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor, or MOS transistor) was adopted by NASA for the IMP program in 1964. The use of MOSFETs was a major step forward in spacec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer 21
Explorer 21, also called IMP-B, IMP-2 and Interplanetary Monitoring Platform-2, was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorer program. Explorer 21 was launched on 4 October 1964, at 03:45:00 GMT from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS), Florida, with a Thor-Delta C launch vehicle. Explorer 21 was the second satellite of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform, and used the same general design as its predecessor, Explorer 18 (IMP-A), launched the previous year, in November 1963. The following Explorer 28 (IMP-C), launched in May 1965, also used a similar design. Mission Explorer 21 was a solar cell and chemical-battery powered spacecraft instrumented for interplanetary and distant magnetospheric studies of energetic particles, cosmic rays, magnetic fields, and plasmas. Each normal telemetry sequence of 81.9 seconds in duration consisted of 795 data bits. After every third normal sequence there was an 81.9 seconds interval of rubidium vapor magnetometer analog data transmission. Ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo Guidance Computer
The Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) was a digital computer produced for the Apollo program that was installed on board each Apollo command module (CM) and Apollo Lunar Module (LM). The AGC provided computation and electronic interfaces for guidance, navigation, and control of the spacecraft. The AGC was among the first computers based on silicon integrated circuits (ICs). The computer's performance was comparable to the first generation of home computers from the late 1970s, such as the Apple II, TRS-80, and Commodore PET. At around 2 cubic feet in size, AGC held 4,100 IC packages. The AGC has a 16-bit Word (computer architecture), word length, with 15 data bits and one [ arity bit. Most of the software on the AGC is stored in a special read-only memory known as core rope memory, fashioned by weaving wires through and around magnetic cores, though a small amount of read/write core memory is available. Astronauts communicated with the AGC using a numeric display and keyboard call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
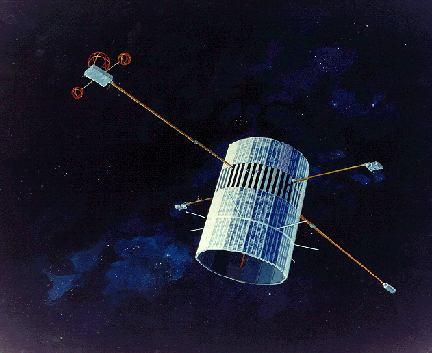
Explorer 50
Explorer 50, also known as IMP-J or IMP-8, was a NASA satellite launched to study the magnetosphere. It was the eighth and last in a series of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform. Spacecraft Explorer 50 was a drum-shaped spacecraft, across and height, with propulsion Star-17A, instrumented for interplanetary medium and magnetotail studies of cosmic rays, energetic solar particles, plasma, and electric and magnetic fields. Its initial orbit was more elliptical than intended, with apogee and perigee distances of about 45.26 Earth radii and 22.11 Earth radii. Its orbital eccentricity decreased after launch. Its orbital inclination varied between 0 deg and about 55° with a periodicity of several years. The spacecraft spin axis was normal to the ecliptic plane, and the spin rate was 23 rpm. The data telemetry rate was 1600 bit/s. The spacecraft was in the solar wind for 7 to 8 days of every 11.99 days orbit. Telemetry coverage was 90% in the early years, but only 60-70% th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer 47
Explorer 47 (IMP-H or IMP-7), was a NASA satellite launched as part of the Explorers program. Explorer 47 was launched on 23 September 1972 from Cape Canaveral, Florida, with a Thor-Delta 1604. Explorer 47 was the ninth overall launch of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform series, but received the launch designation "IMP-7" because two previous "Anchored IMP" flights had used "AIMP" instead. Spacecraft Explorer 47 continued the study begun by earlier IMP spacecraft of the interplanetary space and magnetotail regions from a nearly circular orbit, near 37 Earth radii. This 16 sided drum-shaped spacecraft was in height and in diameter, with propulsion Star-17A. Mission Explorer 47 was designed to measure energetic particles, plasma, electric fields and magnetic fields. The spin axis was normal to the ecliptic plane, and the spin period was 1.3 seconds. The spacecraft was powered by solar cells and a chemical battery. Scientific data were telemetered at 1600 bit/s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer 43
Explorer 43, also called IMP-I and IMP-6, was a NASA satellite launched as part of the Explorers program. Explorer 43 was launched on 13 March 1971 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) with a Delta (rocket family), Thor-Delta M6 launch vehicle. Explorer 43 was the sixth satellite of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform. Spacecraft and mission Explorer 43 continued the study, begun by earlier IMPs, of the interplanetary space, interplanetary and outer Magnetosphere, magnetospheric regions by measuring energetic particles, plasma (physics), plasma, electric fields and magnetic fields. Its orbit took it to cislunar space during a period of decreasing solar activity. A Radio astronomy experiment was also included in the spacecraft payload. The 16-sided spacecraft was high by in diameter. The spacecraft spin axis was normal to the Ecliptic, ecliptic plane, and its spin rate was 5 Revolutions per minute, rpm, with propulsion Star (rocket stage), Star-17A. The init ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
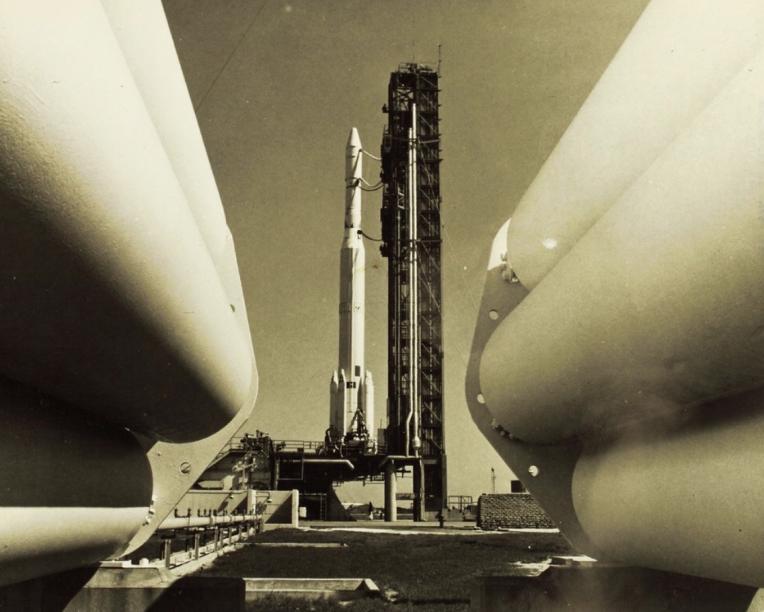
Explorer 41
Explorer 41, also called IMP-G and IMP-5, was a NASA satellite launched as part of the Explorers program. Explorer 41 launched on 21 June 1969 from Vandenberg AFB, California, with a Thor-Delta E1 launch vehicle. Explorer 41 was the seventh satellite launched as part of the overall Interplanetary Monitoring Platform series, though it received the post-launch designation "IMP-5" because two previous flights had used the "AIMP" ("Anchored IMP") designation instead. It was preceded by the second of those flights, Explorer 35 ( MP-E / AIMP-2), launched in July 1967. Its predecessor in the strict IMP series of launches was Explorer 34, launched in May 1967, which shared a similar design to Explorer 41. The next launch of an IMP satellite was Explorer 43 (IMP-I / IMP-6) in 1971. Spacecraft and mission Explorer 41 (IMP-G) was a spin-stabilized satellite placed into a high-inclination, highly elliptical orbit to measure energetic particles, magnetic fields, and plasma in cisluna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
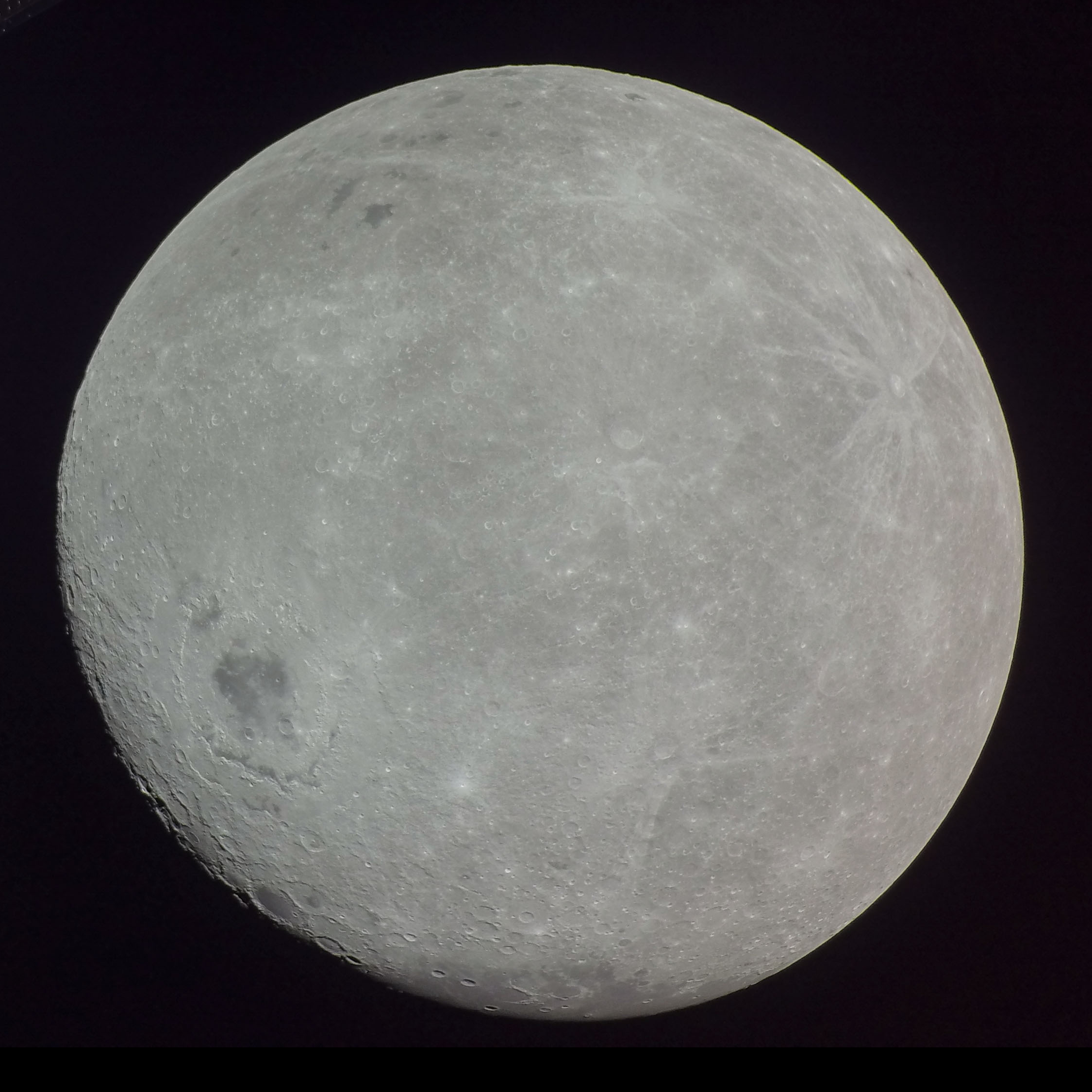
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period (Lunar month#Synodic month, lunar month) of 29.5 Earth days. This is the product of Earth's gravitation having tidal forces, tidally pulled on the Moon until one part of it stopped rotating away from the near side of the Moon, near side, making always the same lunar surface face Earth. Conversley, the gravitational pull of the Moon, on Earth, is the main driver of Earth's tides. In geophysical definition of planet, geophysical terms, the Moon is a planetary-mass object or satellite planet. Its mass is 1.2% that of the Earth, and its diameter is , roughly one-quarter of Earth's (about as wide as the contiguous United States). Within the Solar System, it is the List of Solar System objects by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer 35
Explorer 35, (IMP-E, AIMP-2, Anchored IMP-2, Interplanetary Monitoring Platform-E), was a spin-stabilized spacecraft built by NASA as part of the Explorer program. It was designed for the study of the interplanetary plasma, magnetic field, energetic particles, and solar X-rays, from lunar orbit. Spacecraft Explorer 35 was similar to the earlier Explorer 33. The spacecraft mass was . The main body of the spacecraft was an octagonal prism, across and high. Four arrays containing 6144 n/p solar cells, providing an average of 70 watts power, extended from the main bus, along with two magnetometer booms. Four whip antennas are mounted on top of the spacecraft. A retrorocket was mounted on top of the bus. Power was stored in silver–cadmium batteries (Ag-Cd). Communication (PFM telemetry) was via a 7-watts transmitter and a digital data processor. The science payload had a mass of and included two 3-axis magnetometers, low energy protons and alpha energy analyzer, low energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandenberg AFB Space Launch Complex 2
Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2) is an active rocket launch site at Vandenberg Space Force Base, in California, USA. It consists of two launch pads: Space Launch Complex 2 East (SLC-2E, originally LC 75-1-1), used by the PGM-17 Thor missile and several of its derivatives from 1958 to 1972; and Space Launch Complex 2 West (SLC-2W, originally LC 75-1-2), which has been in use since 1959 to launch the Thor-Delta family and Delta II, and is currently used by the Firefly Alpha. Space Launch Complex 2 was originally part of Launch Complex 75 (LC 75) and was known by designation LC 75-1 or just 75-1 (and the launch pads were designated LC 75-1-1 and LC 75–1–2). The first launch out of the newly designated Space Launch Complex 2 was that of a Delta E with ESSA-3 on 2 October 1966 from SLC-2E. SLC-2E and SLC-2W are located approximately apart. SLC-2W Thor and Thor-Agena (1959–1968) Space Launch Complex 2 West (originally Launch Complex 75-1-2) was built in the late 1950s to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandenberg Air Force Base
Vandenberg may refer to: * Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name * USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida * Vandenberg Space Force Base, a United States military installation with a spaceport * Vandenberg (band), a Dutch hard rock band ** ''Vandenberg'' (album), their 1982 debut album * Vandenberg resolution, a United States Congress resolution passed in 1948 {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |