Apollo Guidance Computer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) was a
 Each lunar mission had two additional computers:
* The
Each lunar mission had two additional computers:
* The

 The AGC was designed at the
The AGC was designed at the


 The AGC had additional registers that were used internally in the course of operation:
* S: 12-bit memory address register, the lower portion of the memory address
* Bank/Fbank: 4-bit ROM bank register, to select the 1
The AGC had additional registers that were used internally in the course of operation:
* S: 12-bit memory address register, the lower portion of the memory address
* Bank/Fbank: 4-bit ROM bank register, to select the 1
 Block I AGC memory was organized into 1 kiloword banks. The lowest bank (bank 0) was erasable memory (RAM). All banks above bank 0 were fixed memory (ROM). Each AGC instruction had a 12-bit address field. The lower bits (1-10) addressed the memory inside each bank. Bits 11 and 12 selected the bank: 00 selected the erasable memory bank; 01 selected the lowest bank (bank 1) of fixed memory; 10 selected the next one (bank 2); and 11 selected the ''Bank'' register that could be used to select any bank above 2. Banks 1 and 2 were called ''fixed-fixed'' memory, because they were always available, regardless of the contents of the Bank register. Banks 3 and above were called ''fixed-switchable'' because the selected bank was determined by the bank register.
The Block I AGC initially had 12 kilowords of fixed memory, but this was later increased to 24 kilowords. Block II had 36 kilowords of fixed memory and 2 kilowords of erasable memory.
The AGC transferred data to and from memory through the G register in a process called the ''memory cycle''. The memory cycle took 12 timing pulses (11.72 μs). The cycle began at timing pulse 1 (TP1) when the AGC loaded the memory address to be fetched into the S register. The memory hardware retrieved the data word from memory at the address specified by the S register. Words from erasable memory were deposited into the G register by timing pulse 6 (TP6); words from fixed memory were available by timing pulse 7. The retrieved memory word was then available in the G register for AGC access during timing pulses 7 through 10. After timing pulse 10, the data in the G register was written back to memory.
The AGC memory cycle occurred continuously during AGC operation. Instructions needing memory data had to access it during timing pulses 7–10. If the AGC changed the memory word in the G register, the changed word was written back to memory after timing pulse 10. In this way, data words cycled continuously from memory to the G register and then back again to memory.
The lower 15 bits of each memory word held AGC instructions or data, with each word being protected by a 16th odd parity bit. This bit was set to 1 or 0 by a parity generator circuit so a count of the 1s in each memory word would always produce an odd number. A parity checking circuit tested the parity bit during each memory cycle; if the bit didn't match the expected value, the memory word was assumed to be corrupted and a ''parity alarm'' panel light was illuminated.
Block I AGC memory was organized into 1 kiloword banks. The lowest bank (bank 0) was erasable memory (RAM). All banks above bank 0 were fixed memory (ROM). Each AGC instruction had a 12-bit address field. The lower bits (1-10) addressed the memory inside each bank. Bits 11 and 12 selected the bank: 00 selected the erasable memory bank; 01 selected the lowest bank (bank 1) of fixed memory; 10 selected the next one (bank 2); and 11 selected the ''Bank'' register that could be used to select any bank above 2. Banks 1 and 2 were called ''fixed-fixed'' memory, because they were always available, regardless of the contents of the Bank register. Banks 3 and above were called ''fixed-switchable'' because the selected bank was determined by the bank register.
The Block I AGC initially had 12 kilowords of fixed memory, but this was later increased to 24 kilowords. Block II had 36 kilowords of fixed memory and 2 kilowords of erasable memory.
The AGC transferred data to and from memory through the G register in a process called the ''memory cycle''. The memory cycle took 12 timing pulses (11.72 μs). The cycle began at timing pulse 1 (TP1) when the AGC loaded the memory address to be fetched into the S register. The memory hardware retrieved the data word from memory at the address specified by the S register. Words from erasable memory were deposited into the G register by timing pulse 6 (TP6); words from fixed memory were available by timing pulse 7. The retrieved memory word was then available in the G register for AGC access during timing pulses 7 through 10. After timing pulse 10, the data in the G register was written back to memory.
The AGC memory cycle occurred continuously during AGC operation. Instructions needing memory data had to access it during timing pulses 7–10. If the AGC changed the memory word in the G register, the changed word was written back to memory after timing pulse 10. In this way, data words cycled continuously from memory to the G register and then back again to memory.
The lower 15 bits of each memory word held AGC instructions or data, with each word being protected by a 16th odd parity bit. This bit was set to 1 or 0 by a parity generator circuit so a count of the 1s in each memory word would always produce an odd number. A parity checking circuit tested the parity bit during each memory cycle; if the bit didn't match the expected value, the memory word was assumed to be corrupted and a ''parity alarm'' panel light was illuminated.
 AGC software was written in AGC assembly language and stored on
AGC software was written in AGC assembly language and stored on
"NASA Honors Apollo Engineer"
(September 03, 2003) When the design requirements for the AGC were defined, necessary software and programming techniques did not exist so they had to be designed from scratch. Many of the trajectory and guidance algorithms used were based on earlier work by
"About Margaret Hamilton"
(Last Revised: February 03, 2010)By ''A.J.S. Rayl'
/ref> The Apollo Guidance computer has been called "The fourth astronaut" for its role in helping the three astronauts who relied on it
 PGNCS generated unanticipated warnings during Apollo 11's lunar descent, with the AGC showing a ''1202 alarm'' ("Executive overflow - NO CORE SETS"), and then a ''1201 alarm'' ("Executive overflow - NO VAC AREAS"). The response of the AGC to either alarm was a soft restart. The cause was a rapid, steady stream of spurious cycle steals from the rendezvous radar (tracking the orbiting command module), intentionally left on standby during the descent in case it was needed for an abort.
During this part of the approach, the processor would normally be almost 85% loaded. The extra 6,400 cycle steals per second added the equivalent of 13% load, leaving just enough time for all scheduled tasks to run to completion. Five minutes into the descent, Buzz Aldrin gave the computer the command ''1668'', which instructed it to periodically calculate and display DELTAH (the difference between altitude sensed by the radar and the computed altitude).More specifically, verb 16 instructs the AGC to print the ''noun'' (in this case, 68, DELTAH) approximately twice per second. Had Aldrin known this, a simple ''0668'' (calculate and display DELTAH, once) would have only added approximately 5% load to the system, and would have only done so once, when ENTER was pressed. The ''1668'' added another 10% to the processor workload, causing executive overflow and a ''1202'' alarm. After being given the "GO" from Houston, Aldrin entered ''1668'' again and another ''1202'' alarm occurred. When reporting the second alarm, Aldrin added the comment "It appears to come up when we have a ''1668'' up". The AGC software had been designed with priority scheduling, and automatically recovered, deleting lower priority tasks including the ''1668'' display task, to complete its critical guidance and control tasks. Guidance controller Steve Bales and his support team that included Jack Garman issued several "GO" calls and the landing was successful. For his role, Bales received the US
PGNCS generated unanticipated warnings during Apollo 11's lunar descent, with the AGC showing a ''1202 alarm'' ("Executive overflow - NO CORE SETS"), and then a ''1201 alarm'' ("Executive overflow - NO VAC AREAS"). The response of the AGC to either alarm was a soft restart. The cause was a rapid, steady stream of spurious cycle steals from the rendezvous radar (tracking the orbiting command module), intentionally left on standby during the descent in case it was needed for an abort.
During this part of the approach, the processor would normally be almost 85% loaded. The extra 6,400 cycle steals per second added the equivalent of 13% load, leaving just enough time for all scheduled tasks to run to completion. Five minutes into the descent, Buzz Aldrin gave the computer the command ''1668'', which instructed it to periodically calculate and display DELTAH (the difference between altitude sensed by the radar and the computed altitude).More specifically, verb 16 instructs the AGC to print the ''noun'' (in this case, 68, DELTAH) approximately twice per second. Had Aldrin known this, a simple ''0668'' (calculate and display DELTAH, once) would have only added approximately 5% load to the system, and would have only done so once, when ENTER was pressed. The ''1668'' added another 10% to the processor workload, causing executive overflow and a ''1202'' alarm. After being given the "GO" from Houston, Aldrin entered ''1668'' again and another ''1202'' alarm occurred. When reporting the second alarm, Aldrin added the comment "It appears to come up when we have a ''1668'' up". The AGC software had been designed with priority scheduling, and automatically recovered, deleting lower priority tasks including the ''1668'' display task, to complete its critical guidance and control tasks. Guidance controller Steve Bales and his support team that included Jack Garman issued several "GO" calls and the landing was successful. For his role, Bales received the US
 The AGC formed the basis of an experimental fly-by-wire (FBW) system installed into an
The AGC formed the basis of an experimental fly-by-wire (FBW) system installed into an
Virtual AGC Project
and
''AGC4 Memo #9, Block II Instructions''
– The infamous memo that served as de facto official documentation of the instruction set
– By James Tomayko (Chapter 2, Part 5, ''The Apollo guidance computer: Hardware'')
''Computers Take Flight''
– By James Tomayko
''The Apollo Guidance Computer - A Users View''
(
''Lunar Module Attitude Controller Assembly Input Processing''
(
The MIT AGC Project
– With comprehensive document archive
for Lunar Module guidance computer. (nb. 622 Mb)
for Command Module guidance computer. (nb. 83 Mb)
National Air and Space Museum's AGC Block I
an
Dsky
– An AGC system programmer discusses some obscure details of the development of AGC, including specifics of Ed's Interrupt ;Documentation of AGC hardware design, and particularly the use of the new integrated circuits in place of transistors
Integrated Circuits in the Apollo Guidance Computer
;Documentation of AGC software operation
Delco Electronics, Apollo 15
- Manual for CSM and LEM AGC software used on the Apollo 15 mission, including detailed user interface procedures, explanation of many underlying algorithms and limited hardware information. Note that this document has over 500 pages and is over 150 megabytes in size.
for Command Module code (Comanche054) and Lunar Module code (Luminary099) as text.
GitHub Complete Source Code
Original Apollo 11 Guidance Computer (AGC) source code for the command and lunar modules. ;Some AGC-based projects and simulators
AGC Replica
– John Pultorak's successful project to build a hardware replica of the Block I AGC in his basement. Mirror site
AGC Replica
– Ronald Burkey's AGC simulator, plus source and binary code recovery for the Colossus (CSM) and Luminary (LEM) SW.
– A web-based AGC simulator based on Virtual AGC.
Eagle Lander 3D
Shareware Lunar Lander Simulator with a working AGC and DSKY (Windows only).
AGC restarted 45 years later
Feature Stories
Weaving the way to the Moon
(BBC News)
(Wall Street Journal)
''Computer for Apollo'' video
{{CPU technologies Guidance computers Apollo program hardware Computer-related introductions in 1966 Assembly language software Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1975 disestablishments Spacecraft navigation instruments
digital computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These progra ...
produced for the Apollo program that was installed on board each Apollo command module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother shi ...
(CM) and Apollo Lunar Module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed s ...
(LM). The AGC provided computation and electronic interfaces for guidance, navigation, and control of the spacecraft. The AGC was the first computer based on silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
integrated circuits. The computer's performance was comparable to the first generation of home computers from the late 1970s, such as the Apple II
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-mold ...
, TRS-80
The TRS-80 Micro Computer System (TRS-80, later renamed the Model I to distinguish it from successors) is a desktop microcomputer launched in 1977 and sold by Tandy Corporation through their Radio Shack stores. The name is an abbreviation of ...
, and Commodore PET
The Commodore PET is a line of personal computers produced starting in 1977 by Commodore International. A single all-in-one case combines a MOS Technology 6502 microprocessor, Commodore BASIC in read-only memory, keyboard, monochrome monitor, ...
.
The AGC has a 16-bit word
A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consen ...
length, with 15 data bits and one parity bit
A parity bit, or check bit, is a bit added to a string of binary code. Parity bits are a simple form of error detecting code. Parity bits are generally applied to the smallest units of a communication protocol, typically 8-bit octets (bytes) ...
. Most of the software on the AGC is stored in a special read-only memory
Read-only memory (ROM) is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be electronically modified after the manufacture of the memory device. Read-only memory is useful for storing s ...
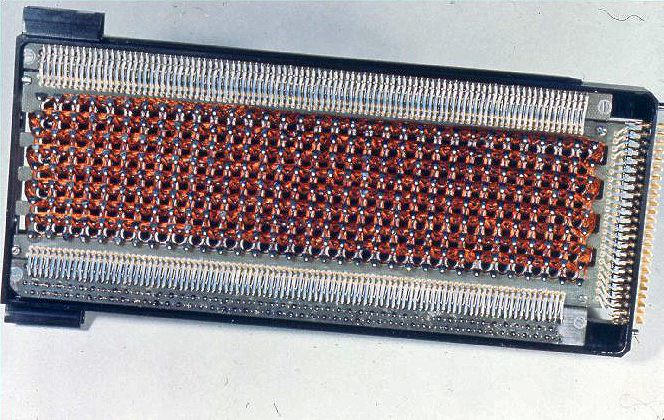
known as core rope memory
Core rope memory is a form of read-only memory (ROM) for computers, first used in the 1960s by early NASA Mars space probes and then in the Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) and programmed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Ins ...
, fashioned by weaving wires through and around magnetic core
A magnetic core is a piece of magnetic material with a high magnetic permeability used to confine and guide magnetic fields in electrical, electromechanical and magnetic devices such as electromagnets, transformers, electric motors, generators, ...
s, though a small amount of read/write core memory
Core or cores may refer to:
Science and technology
* Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages
* Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding
* Core (optical fiber), the signal-carrying portion of an optical fiber
* Core, the centr ...
is available.
Astronauts communicated with the AGC using a numeric display and keyboard called the DSKY (for "display and keyboard", pronounced "DIS-kee"). The AGC and its DSKY user interface were developed in the early 1960s for the Apollo program by the MIT Instrumentation Laboratory
Draper Laboratory is an American non-profit research and development organization, headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts; its official name is The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory, Inc (sometimes abbreviated as CSDL). The laboratory specialize ...
and first flew in 1966.
Operation
Astronauts manually flewProject Gemini
Project Gemini () was NASA's second human spaceflight program. Conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo, Gemini started in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual ...
with control stick
A joystick, sometimes called a flight stick, is an input device consisting of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling. A joystick, also known as the control column, is the principal cont ...
s, but computers flew most of Project Apollo except briefly during lunar landings. Each Moon flight carried two AGCs, one each in the command module and the Apollo Lunar Module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed s ...
, with the exception of Apollo 8
Apollo 8 (December 21–27, 1968) was the first crewed spacecraft to leave low Earth orbit and the first human spaceflight to reach the Moon. The crew orbited the Moon ten times without landing, and then departed safely back to Earth. The ...
which did not need a lunar module for its lunar orbit mission. The AGC in the command module was the center of its guidance, navigation and control (GNC) system. The AGC in the lunar module ran its Apollo PGNCS
The Apollo primary guidance, navigation, and control system (PGNCS, pronounced ''pings'') was a self-contained inertial guidance system that allowed Apollo spacecraft to carry out their missions when communications with Earth were interrupted, ...
(primary guidance, navigation and control system), with the acronym pronounced as ''pings''.
 Each lunar mission had two additional computers:
* The
Each lunar mission had two additional computers:
* The Launch Vehicle Digital Computer
The Launch Vehicle Digital Computer (LVDC) was a computer that provided the autopilot for the Saturn V rocket from launch to Earth orbit insertion. Designed and manufactured by IBM's Electronics Systems Center in Owego, New York, it was one of th ...
(LVDC) on the Saturn V
Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, with three stages, and powered with liquid fuel. It was flown from 1 ...
booster instrumentation ring
* the Abort Guidance System (AGS, pronounced ''ags'') of the lunar module, to be used in the event of failure of the LM PGNCS. The AGS could be used to take off from the Moon, and to rendezvous with the command module, but not to land.
Design

 The AGC was designed at the
The AGC was designed at the MIT Instrumentation Laboratory
Draper Laboratory is an American non-profit research and development organization, headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts; its official name is The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory, Inc (sometimes abbreviated as CSDL). The laboratory specialize ...
under Charles Stark Draper
Charles Stark "Doc" Draper (October 2, 1901 – July 25, 1987) was an American scientist and engineer, known as the "father of inertial navigation". He was the founder and director of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Instrumen ...
, with hardware design led by Eldon C. Hall
Eldon Hall was the leader of hardware design efforts for the Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) at MIT, and advocated the use of integrated circuits for this task. He wrote extensively of the development of the AGC, culminating in his 1996 book, ''J ...
. Early architectural work came from J. H. Laning Jr., Albert Hopkins, Richard Battin
Richard "Dick" Horace Battin (March 3, 1925 – February 8, 2014) was an American engineer, applied mathematician and educator who led the design of the Apollo guidance computer during the Apollo missions during the 1960s.
Battin was born on Ma ...
, Ramon Alonso,
and Hugh Blair-Smith.
The flight hardware was fabricated by Raytheon
Raytheon Technologies Corporation is an American multinational aerospace and defense conglomerate headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. It is one of the largest aerospace and defense manufacturers in the world by revenue and market capitaliz ...
, whose Herb Thaler was also on the architectural team.
Logic hardware
Following the use of integrated circuit (IC) chips in theInterplanetary Monitoring Platform Interplanetary Monitoring Platform was a program managed by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, as part of the Explorers program, with the primary objectives of investigation of interplanetary plasma and the interplanetary ...
(IMP) in 1963, IC technology was later adopted for the AGC. The Apollo flight computer was the first computer to use silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
IC chips.
While the Block I version used 4,100 ICs, each containing a single three-input NOR gate
The NOR gate is a digital logic gate that implements logical NOR - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output (1) results if both the inputs to the gate are LOW (0); if one or both input is HIGH (1), a LOW output (0 ...
, the later Block II version (used in the crewed flights) used about 2,800 ICs, mostly dual three-input NOR gates and smaller numbers of expanders and sense amplifiers. The ICs, from Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. Founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument, it became a pioneer in the manufacturing of transistors and of int ...
, were implemented using resistor–transistor logic Resistor–transistor logic (RTL) (sometimes also transistor–resistor logic (TRL)) is a class of digital circuits built using resistors as the input network and bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) as switching devices. RTL is the earliest class of ...
(RTL) in a flat-pack. They were connected via wire wrap
Wire wrap is an electronic component assembly technique that was invented to wire telephone crossbar switches, and later adapted to construct electronic circuit boards. Electronic components mounted on an insulating board are interconnected by l ...
, and the wiring was then embedded in cast epoxy
Epoxy is the family of basic components or Curing (chemistry), cured end products of epoxy resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide functional ...
plastic.
The use of a single type of IC (the dual NOR3) throughout the AGC avoided problems that plagued another early IC computer design, the Minuteman II guidance computer
Guidance may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Guidance'' (album), by American instrumental rock band Russian Circles
* ''Guidance'' (film), a Canadian comedy film released in 2014
* ''Guidance'' (web series), a 2015–2017 American web series
* "G ...
, which used a mix of diode–transistor logic
Diode–transistor logic (DTL) is a class of digital circuits that is the direct ancestor of transistor–transistor logic. It is called so because the logic gating function (e.g., AND) is performed by a diode network and the amplifying functio ...
and diode logic
Diode logic (DL), or diode-resistor logic (DRL), is the construction of Boolean logic gates from diodes. Diode logic was used extensively in the construction of early computers, where semiconductor diodes could replace bulky and costly active v ...
gates. NOR gates are universal logic gates from which any other gate can be made, though at the cost of using more gates.
Memory
The computer had 2048 words of erasablemagnetic-core memory
Magnetic-core memory was the predominant form of random-access computer memory for 20 years between about 1955 and 1975.
Such memory is often just called core memory, or, informally, core.
Core memory uses toroids (rings) of a hard magneti ...
and 36,864 words of read-only core rope memory
Core rope memory is a form of read-only memory (ROM) for computers, first used in the 1960s by early NASA Mars space probes and then in the Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) and programmed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Ins ...
. Both had cycle times of 11.72 microseconds. The memory word length was 16 bits: 15 bits of data and one odd-parity bit
A parity bit, or check bit, is a bit added to a string of binary code. Parity bits are a simple form of error detecting code. Parity bits are generally applied to the smallest units of a communication protocol, typically 8-bit octets (bytes) ...
. The CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, an ...
-internal 16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two mos ...
word format was 14 bits of data, one overflow bit, and one sign bit
In computer science, the sign bit is a bit in a signed number representation that indicates the sign of a number. Although only signed numeric data types have a sign bit, it is invariably located in the most significant bit position, so the te ...
(ones' complement
The ones' complement of a binary number is the value obtained by inverting all the bits in the binary representation of the number (swapping 0s and 1s). The name "ones' complement" (''note this is possessive of the plural "ones", not of a sin ...
representation).
DSKY interface
Theuser interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine f ...
to the AGC was the ''DSKY'', standing for ''display and keyboard'' and usually pronounced ''"DIS-kee".'' It has an array of indicator lights, numeric displays, and a calculator
An electronic calculator is typically a portable electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics.
The first solid-state electronic calculator was created in the early 1960s. Pocket-size ...
-style keyboard. Commands were entered numerically, as two-digit numbers: Verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual descr ...
, and Noun
A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for:
* Organism, Living creatures (including people ...
. ''Verb'' described the type of action to be performed and ''Noun'' specified which data were affected by the action specified by the Verb command.
Each digit was displayed via a green (specified as 530 nm) high-voltage electroluminescent
Electroluminescence (EL) is an optical and electrical phenomenon, in which a material emits light in response to the passage of an electric current or to a strong electric field. This is distinct from black body light emission resulting fro ...
seven-segment display
A seven-segment display is a form of electronic display device for displaying decimal numerals that is an alternative to the more complex dot matrix displays.
Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic ...
; these were driven by electromechanical relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated swit ...
s, limiting the update rate. Three five-digit signed numbers could also be displayed in octal
The octal numeral system, or oct for short, is the radix, base-8 number system, and uses the Numerical digit, digits 0 to 7. This is to say that 10octal represents eight and 100octal represents sixty-four. However, English, like most languages, ...
or decimal, and were typically used to display vectors such as space craft attitude
Attitude may refer to:
Philosophy and psychology
* Attitude (psychology), an individual's predisposed state of mind regarding a value
* Metaphysics of presence
* Propositional attitude, a relational mental state connecting a person to a prop ...
or a required velocity change (delta-V
Delta-''v'' (more known as " change in velocity"), symbolized as ∆''v'' and pronounced ''delta-vee'', as used in spacecraft flight dynamics, is a measure of the impulse per unit of spacecraft mass that is needed to perform a maneuver such ...
). Although data was stored internally in metric units
Metric units are units based on the metre, gram or second and decimal (power of ten) multiples or sub-multiples of these. The most widely used examples are the units of the International System of Units (SI). By extension they include units of ...
, they were displayed as United States customary units
United States customary units form a system of Units of measurement, measurement units commonly used in the United States and Territories of the United States, U.S. territories since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States cust ...
. This calculator-style interface was the first of its kind.
The command module has two DSKYs connected to its AGC: one located on the main instrument panel and a second located in the lower equipment bay near a sextant
A sextant is a doubly reflecting navigation instrument that measures the angular distance between two visible objects. The primary use of a sextant is to measure the angle between an astronomical object and the horizon for the purposes of cel ...
used for aligning the inertial guidance
An inertial navigation system (INS) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors ( accelerometers), rotation sensors (gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity (d ...
platform. The lunar module had a single DSKY for its AGC. A flight director attitude indicator (FDAI), controlled by the AGC, was located above the DSKY on the commander's console and on the LM.
Timing
The AGC timing reference came from a 2.048 MHzcrystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macr ...
clock
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and t ...
. The clock was divided by two to produce a four-phase 1.024 MHz clock which the AGC used to perform internal operations. The 1.024 MHz clock was also divided by two to produce a 512 kHz signal called the ''master frequency''; this signal was used to synchronize external Apollo spacecraft systems.
The master frequency was further divided through a '' scaler'', first by five using a ring counter to produce a 102.4 kHz signal. This was then divided by two through 17 successive stages called F1 (51.2 kHz) through F17 (0.78125 Hz). The F10 stage (100 Hz) was fed back into the AGC to increment the real-time clock
A real-time clock (RTC) is an electronic device (most often in the form of an integrated circuit) that measures the passage of time.
Although the term often refers to the devices in personal computers, servers and embedded systems, RTCs are ...
and other involuntary counters using Pinc (discussed below). The F17 stage was used to intermittently run the AGC when it was operating in the ''standby'' mode.
Central registers
The AGC had four 16-bitregister
Register or registration may refer to:
Arts entertainment, and media Music
* Register (music), the relative "height" or range of a note, melody, part, instrument, etc.
* ''Register'', a 2017 album by Travis Miller
* Registration (organ), the ...
s for general computational use, called the ''central registers'':
* A: The accumulator, for general computation
* Z: The program counter
The program counter (PC), commonly called the instruction pointer (IP) in Intel x86 and Itanium microprocessors, and sometimes called the instruction address register (IAR), the instruction counter, or just part of the instruction sequencer, is ...
– the address of the next instruction to be executed
* Q: The remainder from the DV instruction, and the return address
In postal mail, a return address is an explicit inclusion of the address of the person sending the message. It provides the recipient (and sometimes authorized intermediaries) with a means to determine how to respond to the sender of the message i ...
after TC instructions
* LP: The lower product after MP instructions
There were also four locations in core memory, at addresses 20–23, dubbed ''editing locations'' because whatever was stored there would emerge shifted or rotated by one bit position, except for one that shifted right seven bit positions, to extract one of the seven-bit interpretive op. codes that were packed two to a word. This was common to Block I and Block II AGCs.
Other registers


 The AGC had additional registers that were used internally in the course of operation:
* S: 12-bit memory address register, the lower portion of the memory address
* Bank/Fbank: 4-bit ROM bank register, to select the 1
The AGC had additional registers that were used internally in the course of operation:
* S: 12-bit memory address register, the lower portion of the memory address
* Bank/Fbank: 4-bit ROM bank register, to select the 1 kiloword
In computing, a word is the natural unit of data used by a particular processor design. A word is a fixed-sized datum handled as a unit by the instruction set or the hardware of the processor. The number of bits or digits in a word (the ''word ...
ROM bank when addressing in the fixed-switchable mode
*Ebank: 3-bit RAM bank register, to select the 256-word RAM bank when addressing in the erasable-switchable mode
* Sbank (super-bank): 1-bit extension to Fbank, required because the last 4 kilowords of the 36-kiloword ROM was not reachable using Fbank alone
*SQ: 4-bit sequence register; the current instruction
*G: 16-bit memory buffer register, to hold data words moving to and from memory
*X: The 'x' input to the ''adder'' (the adder was used to perform all 1's complement
The ones' complement of a binary number is the value obtained by inverting all the bits in the binary representation of the number (swapping 0s and 1s). The name "ones' complement" (''note this is possessive of the plural "ones", not of a sin ...
arithmetic) or the increment to the program counter (Z register)
* Y: The other ('y') input to the adder
*U: Not really a register, but the output of the adder (the one's complement
The ones' complement of a binary number is the value obtained by inverting all the bits in the binary representation of the number (swapping 0s and 1s). The name "ones' complement" (''note this is possessive of the plural "ones", not of a sin ...
sum of the contents of registers X and Y)
*B: General-purpose buffer register, also used to pre-fetch the next instruction. At the start of the next instruction, the upper bits of B (containing the next op. code) were copied to SQ, and the lower bits (the address) were copied to S.
*C: Not a separate register, but the one's complement of the B register
* IN: Four 16-bit input registers
* OUT: Five 16-bit output registers
Instruction set
The instruction format used 3 bits foropcode
In computing, an opcode (abbreviated from operation code, also known as instruction machine code, instruction code, instruction syllable, instruction parcel or opstring) is the portion of a machine language instruction that specifies the opera ...
, and 12 bits for address. Block I had 11 instructions: TC, CCS, INDEX, XCH, CS, TS, AD, and MASK (basic), and SU, MP, and DV (extra). The first eight, called ''basic instructions'', were directly accessed by the 3-bit op. code. The final three were denoted as ''extracode instructions'' because they were accessed by performing a special type of TC instruction (called EXTEND) immediately before the instruction.
The Block I AGC instructions consisted of the following:
;TC (transfer control): An unconditional branch to the address specified by the instruction. The return address was automatically stored in the Q register, so the TC instruction could be used for subroutine calls.
;CCS (count, compare, and skip): A complex conditional branch instruction. The A register was loaded with data retrieved from the address specified by the instruction. (Because the AGC uses ones' complement
The ones' complement of a binary number is the value obtained by inverting all the bits in the binary representation of the number (swapping 0s and 1s). The name "ones' complement" (''note this is possessive of the plural "ones", not of a sin ...
notation, there are two representations of zero. When all bits are set to zero, this is called ''plus zero''. If all bits are set to one, this is called ''minus zero''.) The ''diminished absolute value'' (DABS) of the data was then computed and stored in the A register. If the number was greater than zero, the DABS decrements the value by 1; if the number was negative, it is complemented before the decrement is applied—this is the absolute value. ''Diminished'' means "decremented but not below zero". Therefore, when the AGC performs the DABS function, positive numbers will head toward plus zero, and so will negative numbers but first revealing their negativity via the four-way skip below. The final step in CCS is a four-way skip, depending upon the data in register A before the DABS. If register A was greater than 0, CCS skips to the first instruction immediately after CCS. If register A contained plus zero, CCS skips to the second instruction after CCS. Less than zero causes a skip to the third instruction after CCS, and minus zero skips to the fourth instruction after CCS. The primary purpose of the count was to allow an ordinary loop, controlled by a positive counter, to end in a CCS and a TC to the beginning of the loop, equivalent to an IBM 360
The IBM System/360 (S/360) is a family of mainframe computer systems that was announced by IBM on April 7, 1964, and delivered between 1965 and 1978. It was the first family of computers designed to cover both commercial and scientific applica ...
's BCT. The absolute value function was deemed important enough to be built into this instruction; when used for only this purpose, the sequence after the CCS was TC *+2, TC *+2, AD ONE. A curious side effect was the creation and use of ''CCS-holes'' when the value being tested was known to be never positive, which occurred more often than one might suppose. That left two whole words unoccupied, and a special committee was responsible for assigning data constants to these holes.
;INDEX: Add the data retrieved at the address specified by the instruction to the next instruction. INDEX can be used to add or subtract an index value to the base address
In computing, a base address is an address serving as a reference point ("base") for other addresses. Related addresses can be accessed using an ''addressing scheme''.
Under the ''relative addressing'' scheme, to obtain an absolute address
In ...
specified by the operand of the instruction that follows INDEX. This method is used to implement arrays and table look-ups; since the addition was done on both whole words, it was also used to modify the op. code in a following (extracode) instruction, and on rare occasions both functions at once.
;RESUME: A special instance of INDEX (INDEX 25). This is the instruction used to return from interrupts. It causes execution to resume at the interrupted location.
;XCH (exchange): Exchange the contents of memory with the contents of the A register. If the specified memory address is in fixed (read-only) memory, the memory contents are not affected, and this instruction simply loads register A. If it is in erasable memory, overflow "correction" is achieved by storing the leftmost of the 16 bits in A as the sign bit in memory, but there is no exceptional behavior like that of TS.
;CS (clear and subtract): Load register A with the one's complement of the data referenced by the specified memory address.
;TS (transfer to storage): Store register A at the specified memory address. TS also detects, and corrects for, overflows in such a way as to propagate a carry for multi-precision add/subtract. If the result has no overflow (leftmost 2 bits of A the same), nothing special happens; if there is overflow (those 2 bits differ), the leftmost one goes the memory as the sign bit, register A is changed to +1 or −1 accordingly, and control skips to the second instruction following the TS. Whenever overflow is a possible but abnormal event, the TS was followed by a TC to the no-overflow logic; when it is a normal possibility (as in multi-precision add/subtract), the TS is followed by CAF ZERO (CAF = XCH to fixed memory) to complete the formation of the carry (+1, 0, or −1) into the next higher-precision word. Angles were kept in single precision
Single-precision floating-point format (sometimes called FP32 or float32) is a computer number format, usually occupying 32 bits in computer memory; it represents a wide dynamic range of numeric values by using a floating radix point.
A floati ...
, distances and velocities in double precision
Double-precision floating-point format (sometimes called FP64 or float64) is a floating-point number format, usually occupying 64 bits in computer memory; it represents a wide dynamic range of numeric values by using a floating radix point.
F ...
, and elapsed time in triple precision.
;AD (add): Add the contents of memory to register A and store the result in A. The 2 leftmost bits of A may be different (overflow state) before and/or after the AD. The fact that overflow is a state rather than an event forgives limited extents of overflow when adding more than two numbers, as long as none of the intermediate totals exceed twice the capacity of a word.
;MASK: Perform a bit-wise (boolean) ''and'' of memory with register A and store the result in register A.
;MP (multiply): Multiply the contents of register A by the data at the referenced memory address and store the high-order product in register A and the low-order product in register LP. The parts of the product agree in sign.
;DV (divide): Divide the contents of register A by the data at the referenced memory address. Store the quotient in register A and the absolute value of the remainder in register Q. Unlike modern machines, fixed-point numbers were treated as fractions (notional decimal point just to right of the sign bit), so you could produce garbage if the divisor was not larger than the dividend; there was no protection against that situation. In the Block II AGC, a double-precision dividend started in A and L (the Block II LP), and the correctly signed remainder was delivered in L. That considerably simplified the subroutine for double precision division.
;SU (subtract): Subtract (one's complement) the data at the referenced memory address from the contents of register A and store the result in A.
Instructions were implemented in groups of 12 steps, called ''timing pulses''. The timing pulses were named TP1 through TP12. Each set of 12 timing pulses was called an instruction ''subsequence''. Simple instructions, such as TC, executed in a single subsequence of 12 pulses. More complex instructions required several subsequences. The multiply instruction (MP) used 8 subsequences: an initial one called MP0, followed by an MP1 subsequence which was repeated 6 times, and then terminated by an MP3 subsequence. This was reduced to 3 subsequences in Block II.
Each timing pulse in a subsequence could trigger up to 5 ''control pulses''. The control pulses were the signals which did the actual work of the instruction, such as reading the contents of a register onto the bus, or writing data from the bus into a register.
Memory
 Block I AGC memory was organized into 1 kiloword banks. The lowest bank (bank 0) was erasable memory (RAM). All banks above bank 0 were fixed memory (ROM). Each AGC instruction had a 12-bit address field. The lower bits (1-10) addressed the memory inside each bank. Bits 11 and 12 selected the bank: 00 selected the erasable memory bank; 01 selected the lowest bank (bank 1) of fixed memory; 10 selected the next one (bank 2); and 11 selected the ''Bank'' register that could be used to select any bank above 2. Banks 1 and 2 were called ''fixed-fixed'' memory, because they were always available, regardless of the contents of the Bank register. Banks 3 and above were called ''fixed-switchable'' because the selected bank was determined by the bank register.
The Block I AGC initially had 12 kilowords of fixed memory, but this was later increased to 24 kilowords. Block II had 36 kilowords of fixed memory and 2 kilowords of erasable memory.
The AGC transferred data to and from memory through the G register in a process called the ''memory cycle''. The memory cycle took 12 timing pulses (11.72 μs). The cycle began at timing pulse 1 (TP1) when the AGC loaded the memory address to be fetched into the S register. The memory hardware retrieved the data word from memory at the address specified by the S register. Words from erasable memory were deposited into the G register by timing pulse 6 (TP6); words from fixed memory were available by timing pulse 7. The retrieved memory word was then available in the G register for AGC access during timing pulses 7 through 10. After timing pulse 10, the data in the G register was written back to memory.
The AGC memory cycle occurred continuously during AGC operation. Instructions needing memory data had to access it during timing pulses 7–10. If the AGC changed the memory word in the G register, the changed word was written back to memory after timing pulse 10. In this way, data words cycled continuously from memory to the G register and then back again to memory.
The lower 15 bits of each memory word held AGC instructions or data, with each word being protected by a 16th odd parity bit. This bit was set to 1 or 0 by a parity generator circuit so a count of the 1s in each memory word would always produce an odd number. A parity checking circuit tested the parity bit during each memory cycle; if the bit didn't match the expected value, the memory word was assumed to be corrupted and a ''parity alarm'' panel light was illuminated.
Block I AGC memory was organized into 1 kiloword banks. The lowest bank (bank 0) was erasable memory (RAM). All banks above bank 0 were fixed memory (ROM). Each AGC instruction had a 12-bit address field. The lower bits (1-10) addressed the memory inside each bank. Bits 11 and 12 selected the bank: 00 selected the erasable memory bank; 01 selected the lowest bank (bank 1) of fixed memory; 10 selected the next one (bank 2); and 11 selected the ''Bank'' register that could be used to select any bank above 2. Banks 1 and 2 were called ''fixed-fixed'' memory, because they were always available, regardless of the contents of the Bank register. Banks 3 and above were called ''fixed-switchable'' because the selected bank was determined by the bank register.
The Block I AGC initially had 12 kilowords of fixed memory, but this was later increased to 24 kilowords. Block II had 36 kilowords of fixed memory and 2 kilowords of erasable memory.
The AGC transferred data to and from memory through the G register in a process called the ''memory cycle''. The memory cycle took 12 timing pulses (11.72 μs). The cycle began at timing pulse 1 (TP1) when the AGC loaded the memory address to be fetched into the S register. The memory hardware retrieved the data word from memory at the address specified by the S register. Words from erasable memory were deposited into the G register by timing pulse 6 (TP6); words from fixed memory were available by timing pulse 7. The retrieved memory word was then available in the G register for AGC access during timing pulses 7 through 10. After timing pulse 10, the data in the G register was written back to memory.
The AGC memory cycle occurred continuously during AGC operation. Instructions needing memory data had to access it during timing pulses 7–10. If the AGC changed the memory word in the G register, the changed word was written back to memory after timing pulse 10. In this way, data words cycled continuously from memory to the G register and then back again to memory.
The lower 15 bits of each memory word held AGC instructions or data, with each word being protected by a 16th odd parity bit. This bit was set to 1 or 0 by a parity generator circuit so a count of the 1s in each memory word would always produce an odd number. A parity checking circuit tested the parity bit during each memory cycle; if the bit didn't match the expected value, the memory word was assumed to be corrupted and a ''parity alarm'' panel light was illuminated.
Interrupts and involuntary counters
The AGC had five vectoredinterrupt
In digital computers, an interrupt (sometimes referred to as a trap) is a request for the processor to ''interrupt'' currently executing code (when permitted), so that the event can be processed in a timely manner. If the request is accepted ...
s:
* ''Dsrupt'' was triggered at regular intervals to update the user display (DSKY).
* ''Erupt'' was generated by various hardware failures or alarms.
* ''Keyrupt'' signaled a key press from the user's keyboard.
* ''T3Rrupt'' was generated at regular intervals from a hardware timer to update the AGC's real-time clock
A real-time clock (RTC) is an electronic device (most often in the form of an integrated circuit) that measures the passage of time.
Although the term often refers to the devices in personal computers, servers and embedded systems, RTCs are ...
.
* ''Uprupt'' was generated each time a 16-bit word of uplink data was loaded into the AGC.
The AGC responded to each interrupt by temporarily suspending the current program, executing a short interrupt service routine, and then resuming the interrupted program.
The AGC also had 20 involuntary counters. These were memory locations which functioned as up/down counters, or shift registers. The counters would increment, decrement, or shift in response to internal inputs. The increment (''Pinc''), decrement (''Minc''), or shift (''Shinc'') was handled by one subsequence of microinstructions inserted between any two regular instructions.
Interrupts could be triggered when the counters overflowed. The T3rupt and Dsrupt interrupts were produced when their counters, driven by a 100 Hz hardware clock, overflowed after executing many Pinc subsequences. The Uprupt interrupt was triggered after its counter, executing the Shinc subsequence, had shifted 16 bits of uplink data into the AGC.
Standby mode
The AGC had a power-saving mode controlled by a ''standby allowed'' switch. This mode turned off the AGC power, except for the 2.048 MHz clock and the scaler. The F17 signal from the scaler turned the AGC power and the AGC back on at 1.28 second intervals. In this mode, the AGC performed essential functions, checked the standby allowed switch, and, if still enabled, turned off the power and went back to sleep until the next F17 signal. In the standby mode, the AGC slept most of the time; therefore it was not awake to perform the Pinc instruction needed to update the AGC's real time clock at 10 ms intervals. To compensate, one of the functions performed by the AGC each time it awoke in the standby mode was to update the real time clock by 1.28 seconds. The standby mode was designed to reduce power by 5 to 10 W (from 70 W) during midcourse flight when the AGC was not needed. However, in practice, the AGC was left on during all phases of the mission and this feature was never used.Data buses
The AGC had a 16-bit read bus and a 16-bit write bus. Data from central registers (A, Q, Z, or LP), or other internal registers could be gated onto the read bus with a control signal. The read bus connected to the write bus through a non-inverting buffer, so any data appearing on the read bus also appeared on the write bus. Other control signals could copy write bus data back into the registers. Data transfers worked like this: To move the address of the next instruction from the B register to the S register, an RB (read B) control signal was issued; this caused the address to move from register B to the read bus, and then to the write bus. A WS (write S) control signal moved the address from the write bus into the S register. Several registers could be read onto the read bus simultaneously. When this occurred, data from each register was inclusive-''OR''ed onto the bus. This inclusive-''OR'' feature was used to implement the Mask instruction, which was a logical ''AND'' operation. Because the AGC had no native ability to do a logical ''AND'', but could do a logical ''OR'' through the bus and could complement (invert) data through the C register,De Morgan's theorem
In propositional logic
Propositional calculus is a branch of logic. It is also called propositional logic, statement logic, sentential calculus, sentential logic, or sometimes zeroth-order logic. It deals with propositions (which can be t ...
was used to implement the equivalent of a logical ''AND''. This was accomplished by inverting both operands, performing a logical ''OR'' through the bus, and then inverting the result.
Software
 AGC software was written in AGC assembly language and stored on
AGC software was written in AGC assembly language and stored on rope memory
Core rope memory is a form of read-only memory (ROM) for computers, first used in the 1960s by early NASA Mars space probes and then in the Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) and programmed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Inst ...
. The bulk of the software was on read-only rope memory and thus could not be changed in operation, but some key parts of the software were stored in standard read-write magnetic-core memory
Magnetic-core memory was the predominant form of random-access computer memory for 20 years between about 1955 and 1975.
Such memory is often just called core memory, or, informally, core.
Core memory uses toroids (rings) of a hard magneti ...
and could be overwritten by the astronauts using the DSKY interface, as was done on Apollo 14
Apollo 14 (January 31, 1971February 9, 1971) was the eighth crewed mission in the United States Apollo program, the third to land on the Moon, and the first to land in the lunar highlands. It was the last of the " H missions", landings at s ...
.
A simple real-time operating system
A real-time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system (OS) for real-time applications that processes data and events that have critically defined time constraints. An RTOS is distinct from a time-sharing operating system, such as Unix, which ...
designed by J. Halcombe Laning consisting of the 'Exec', a batch job-scheduling using cooperative multi-tasking, and an interrupt
In digital computers, an interrupt (sometimes referred to as a trap) is a request for the processor to ''interrupt'' currently executing code (when permitted), so that the event can be processed in a timely manner. If the request is accepted ...
-driven pre-emptive scheduler called the 'Waitlist' which scheduled timer-driven 'tasks', controlled the computer. Tasks were short threads of execution which could reschedule themselves for re-execution on the Waitlist, or could kick off a longer operation by starting a 'job' with the Exec. Calculations were carried out using the metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the definition of the Intern ...
, but display readouts were in units of feet, feet per second, and nautical miles – units that the Apollo astronauts were accustomed to.
The AGC had a sophisticated software interpreter, developed by the MIT Instrumentation Laboratory
Draper Laboratory is an American non-profit research and development organization, headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts; its official name is The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory, Inc (sometimes abbreviated as CSDL). The laboratory specialize ...
, that implemented a virtual machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization/ emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve specialized har ...
with more complex and capable pseudo-instructions than the native AGC. These instructions simplified the navigational programs. Interpreted code, which featured double precision trigonometric
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. ...
, scalar and vector arithmetic (16 and 24-bit), even an MXV (matrix × vector) instruction, could be mixed with native AGC code. While the execution time of the pseudo-instructions was increased (due to the need to interpret these instructions at runtime) the interpreter provided many more instructions than AGC natively supported and the memory requirements were much lower than in the case of adding these instructions to the AGC native language which would require additional memory built into the computer (at that time the memory capacity was very expensive). The average pseudo-instruction required about 24 ms to execute. The assembler, named ''YUL'' for an early prototype ''Christmas Computer'', enforced proper transitions between native and interpreted code.
A set of interrupt-driven user interface routines called 'Pinball' provided keyboard and display services for the jobs and tasks running on the AGC. A set of user-accessible routines were provided to let the astronauts display the contents of various memory locations in octal
The octal numeral system, or oct for short, is the radix, base-8 number system, and uses the Numerical digit, digits 0 to 7. This is to say that 10octal represents eight and 100octal represents sixty-four. However, English, like most languages, ...
or decimal in groups of 1, 2, or 3 registers at a time. 'Monitor' routines were provided so the operator could initiate a task to periodically redisplay the contents of certain memory locations. Jobs could be initiated.
The design principles developed for the AGC by MIT Instrumentation Laboratory
Draper Laboratory is an American non-profit research and development organization, headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts; its official name is The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory, Inc (sometimes abbreviated as CSDL). The laboratory specialize ...
, directed in late 1960s by Charles Draper, became foundational to software engineering
Software engineering is a systematic engineering approach to software development.
A software engineer is a person who applies the principles of software engineering to design, develop, maintain, test, and evaluate computer software. The term ' ...
—particularly for the design of more reliable systems that relied on asynchronous software, priority scheduling
Prioritization is an action that arranges items or activities in order of importance.
Priority may refer specifically to:
Law
* Priority or right of way on the road, see Traffic § Priority (right of way)
** Priority signs, a traffic sign th ...
, testing, and human-in-the-loop decision capability.NASA Press Releas"NASA Honors Apollo Engineer"
(September 03, 2003) When the design requirements for the AGC were defined, necessary software and programming techniques did not exist so they had to be designed from scratch. Many of the trajectory and guidance algorithms used were based on earlier work by
Richard Battin
Richard "Dick" Horace Battin (March 3, 1925 – February 8, 2014) was an American engineer, applied mathematician and educator who led the design of the Apollo guidance computer during the Apollo missions during the 1960s.
Battin was born on Ma ...
. The first command module flight was controlled by a software package called CORONA whose development was led by Alex Kosmala. Software for lunar missions consisted of COLOSSUS for the command module, whose development was led by Frederic Martin, and LUMINARY on the lunar module led by George Cherry. Details of these programs were implemented by a team under the direction of Margaret Hamilton Margaret Hamilton may refer to:
* Margaret Hamilton (nurse) (1840–1922), American nurse in the Civil War
* Maggie Hamilton (1867–1952), Scottish artist
* Margaret Hamilton (educator) (1871–1969), American educator
* Margaret Hamilton (actre ...
. Hamilton was very interested in how the astronauts would interact with the software and predicted the types of errors that could occur due to human error. In total, software development on the project comprised 1400 person-years
A man-hour (sometimes referred to as person-hour) is the amount of work performed by the average worker in one hour. It is used for estimation of the total amount of uninterrupted labor required to perform a task. For example, researching and wr ...
of effort, with a peak workforce of 350 people. In 2016, Hamilton received the Presidential Medal of Freedom
The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest civilian award of the United States, along with the Congressional Gold Medal. It is an award bestowed by the president of the United States to recognize people who have made "an especially merit ...
for her role in creating the flight software.
The Apollo Guidance Computer software influenced the design of Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operation ...
, Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
and early fly-by-wire fighter aircraft systems.NASA Office of Logic Desig"About Margaret Hamilton"
(Last Revised: February 03, 2010)By ''A.J.S. Rayl'
/ref> The Apollo Guidance computer has been called "The fourth astronaut" for its role in helping the three astronauts who relied on it
Neil Armstrong
Neil Alden Armstrong (August 5, 1930 – August 25, 2012) was an American astronaut and aeronautical engineer who became the first person to walk on the Moon in 1969. He was also a naval aviator, test pilot, and university professor.
...
, Buzz Aldrin
Buzz Aldrin (; born Edwin Eugene Aldrin Jr.; January 20, 1930) is an American former astronaut, engineer and fighter pilot. He made three spacewalks as pilot of the 1966 Gemini 12 mission. As the Lunar Module ''Eagle'' pilot on the 1969 ...
and Michael Collins.
Block II
A Block II version of the AGC was designed in 1966. It retained the basic Block I architecture, but increased erasable memory from 1 to 2 kilowords. Fixed memory was expanded from 24 to 36 kilowords. Instructions were expanded from 11 to 34 and I/O channels were implemented to replace the I/O registers on Block I. The Block II version is the one that actually flew to the moon. Block I was used during the uncrewedApollo 4
Apollo 4 (November 9, 1967), also known as SA-501, was the uncrewed first test flight of the Saturn V launch vehicle, the rocket that eventually took astronauts to the Moon. The space vehicle was assembled in the Vehicle Assembly Buildi ...
and 6 flights, and was on board the ill-fated Apollo 1
Apollo 1, initially designated AS-204, was intended to be the first crewed mission of the Apollo program, the American undertaking to land the first man on the Moon. It was planned to launch on February 21, 1967, as the first low Earth orbita ...
.
The decision to expand the memory and instruction set for Block II, but to retain the Block I's restrictive three-bit op. code and 12-bit address had interesting design consequences. Various tricks were employed to squeeze in additional instructions, such as having special memory addresses which, when referenced, would implement a certain function. For instance, an INDEX to address 25 triggered the RESUME instruction to return from an interrupt. Likewise, INDEX 17 performed an INHINT instruction (inhibit interrupts), while INDEX 16 reenabled them (RELINT). Other instructions were implemented by preceding them with a special version of TC called EXTEND. The address spaces were extended by employing the Bank (fixed) and Ebank (erasable) registers, so the only memory of either type that could be addressed at any given time was the current bank, plus the small amount of fixed-fixed memory and the erasable memory. In addition, the bank register could address a maximum of 32 kilowords, so an Sbank (super-bank) register was required to access the last 4 kilowords. All across-bank subroutine calls had to be initiated from fixed-fixed memory through special functions to restore the original bank during the return: essentially a system of far pointer
In a segmented architecture computer, a far pointer is a pointer which includes a segment selector, making it possible to point to addresses outside of the default segment.
Comparison and arithmetic on far pointers is problematic: there can be s ...
s.
The Block II AGC also has the EDRUPT instruction (the name is a contraction of ''Ed's Interrupt'', after Ed Smally
Ed, ed or ED may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ed'' (film), a 1996 film starring Matt LeBlanc
* Ed (''Fullmetal Alchemist'') or Edward Elric, a character in ''Fullmetal Alchemist'' media
* ''Ed'' (TV series), a TV series that ran fro ...
, the programmer who requested it). This instruction does not generate an interrupt, rather it performs two actions that are common to interrupt processing. The first action, inhibits further interrupts (and requires a RESUME instruction to enable them again). In the second action, the ZRUPT register is loaded with the current value of the program counter (Z). It was only used once in the Apollo software, for setting up the DAP cycle termination sequence in the Digital Autopilot of the lunar module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed ...
. It is believed to be responsible for problems emulating the LEM AGC Luminary software
A celestial body, as the sun or moon or an object that gives light; or, a person of eminence or brilliant achievement. From Old French ''luminarie'' or late Latin ''luminarium'', from Latin ''lumen'', ''lumin-'' "light".
Luminary may also refer t ...
.
1201 and 1202 program alarms
 PGNCS generated unanticipated warnings during Apollo 11's lunar descent, with the AGC showing a ''1202 alarm'' ("Executive overflow - NO CORE SETS"), and then a ''1201 alarm'' ("Executive overflow - NO VAC AREAS"). The response of the AGC to either alarm was a soft restart. The cause was a rapid, steady stream of spurious cycle steals from the rendezvous radar (tracking the orbiting command module), intentionally left on standby during the descent in case it was needed for an abort.
During this part of the approach, the processor would normally be almost 85% loaded. The extra 6,400 cycle steals per second added the equivalent of 13% load, leaving just enough time for all scheduled tasks to run to completion. Five minutes into the descent, Buzz Aldrin gave the computer the command ''1668'', which instructed it to periodically calculate and display DELTAH (the difference between altitude sensed by the radar and the computed altitude).More specifically, verb 16 instructs the AGC to print the ''noun'' (in this case, 68, DELTAH) approximately twice per second. Had Aldrin known this, a simple ''0668'' (calculate and display DELTAH, once) would have only added approximately 5% load to the system, and would have only done so once, when ENTER was pressed. The ''1668'' added another 10% to the processor workload, causing executive overflow and a ''1202'' alarm. After being given the "GO" from Houston, Aldrin entered ''1668'' again and another ''1202'' alarm occurred. When reporting the second alarm, Aldrin added the comment "It appears to come up when we have a ''1668'' up". The AGC software had been designed with priority scheduling, and automatically recovered, deleting lower priority tasks including the ''1668'' display task, to complete its critical guidance and control tasks. Guidance controller Steve Bales and his support team that included Jack Garman issued several "GO" calls and the landing was successful. For his role, Bales received the US
PGNCS generated unanticipated warnings during Apollo 11's lunar descent, with the AGC showing a ''1202 alarm'' ("Executive overflow - NO CORE SETS"), and then a ''1201 alarm'' ("Executive overflow - NO VAC AREAS"). The response of the AGC to either alarm was a soft restart. The cause was a rapid, steady stream of spurious cycle steals from the rendezvous radar (tracking the orbiting command module), intentionally left on standby during the descent in case it was needed for an abort.
During this part of the approach, the processor would normally be almost 85% loaded. The extra 6,400 cycle steals per second added the equivalent of 13% load, leaving just enough time for all scheduled tasks to run to completion. Five minutes into the descent, Buzz Aldrin gave the computer the command ''1668'', which instructed it to periodically calculate and display DELTAH (the difference between altitude sensed by the radar and the computed altitude).More specifically, verb 16 instructs the AGC to print the ''noun'' (in this case, 68, DELTAH) approximately twice per second. Had Aldrin known this, a simple ''0668'' (calculate and display DELTAH, once) would have only added approximately 5% load to the system, and would have only done so once, when ENTER was pressed. The ''1668'' added another 10% to the processor workload, causing executive overflow and a ''1202'' alarm. After being given the "GO" from Houston, Aldrin entered ''1668'' again and another ''1202'' alarm occurred. When reporting the second alarm, Aldrin added the comment "It appears to come up when we have a ''1668'' up". The AGC software had been designed with priority scheduling, and automatically recovered, deleting lower priority tasks including the ''1668'' display task, to complete its critical guidance and control tasks. Guidance controller Steve Bales and his support team that included Jack Garman issued several "GO" calls and the landing was successful. For his role, Bales received the US Presidential Medal of Freedom
The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest civilian award of the United States, along with the Congressional Gold Medal. It is an award bestowed by the president of the United States to recognize people who have made "an especially merit ...
on behalf of the entire control center team and the three Apollo astronauts.
The problem was not a programming error in the AGC, nor was it pilot error. It was a peripheral hardware design bug that had already been known and documented by Apollo 5 engineers. However, because the problem had only occurred once during testing, they concluded that it was safer to fly with the existing hardware that they had already tested, than to fly with a newer but largely untested radar system. In the actual hardware, the position of the rendezvous radar was encoded with synchro
A synchro (also known as selsyn and by other brand names) is, in effect, a transformer whose primary-to-secondary coupling may be varied by physically changing the relative orientation of the two windings. Synchros are often used for measurin ...
s excited by a different source of 800 Hz AC than the one used by the computer as a timing reference. The two 800 Hz sources were frequency locked but not phase locked, and the small random phase variations made it appear as though the antenna was rapidly "dithering" in position, even though it was completely stationary. These phantom movements generated the rapid series of cycle steals.
J. Halcombe Laning's software and computer design saved the Apollo 11 landing mission. Had it not been for Laning's design, the landing would have been aborted for lack of a stable guidance computer.
Applications outside Apollo
 The AGC formed the basis of an experimental fly-by-wire (FBW) system installed into an
The AGC formed the basis of an experimental fly-by-wire (FBW) system installed into an F-8 Crusader
The Vought F-8 Crusader (originally F8U) is a single-engine, supersonic, carrier-based air superiority jet aircraft built by Vought for the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps (replacing the Vought F7U Cutlass), and for the Fr ...
to demonstrate the practicality of computer driven FBW. The AGC used in the first phase of the program was replaced with another machine in the second phase, and research done on the program led to the development of fly-by-wire systems for the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
. The AGC also led, albeit indirectly, to the development of fly-by-wire systems for the generation of fighters that were being developed at the time.
The AGC was also used for the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
's Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle
A deep-submergence rescue vehicle (DSRV) is a type of deep-submergence vehicle used for rescue of downed submarines and clandestine missions. While DSRV is the term most often used by the United States Navy, other nations have different desig ...
.
Source code release
In 2003, an effort was started by Ron Burkey to recover the source code that powered the AGC and build an emulator able to run it, the VirtualAGC. Part of the large amount of source code rescued as a result of this effort was uploaded by a formerNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedi ...
intern to GitHub
GitHub, Inc. () is an Internet hosting service for software development and version control using Git. It provides the distributed version control of Git plus access control, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, co ...
on July 7, 2016, attracting significant media attention. The original Apollo 11 Guidance Computer source code was originally made accessible in 2003 by thVirtual AGC Project
and
MIT Museum
The MIT Museum, founded in 1971, is located at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It hosts collections of holography, technology-related artworks, artificial intelligence, architecture, robotics, maritime histor ...
. It was transcribed and digitalized from the original hard-copy source code listings that were made in the 60s. In mid 2016, former NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedi ...
intern, Chris Garry, uploaded the AGC Source code onto GitHub
GitHub, Inc. () is an Internet hosting service for software development and version control using Git. It provides the distributed version control of Git plus access control, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, co ...
.
See also
*Apollo PGNCS
The Apollo primary guidance, navigation, and control system (PGNCS, pronounced ''pings'') was a self-contained inertial guidance system that allowed Apollo spacecraft to carry out their missions when communications with Earth were interrupted, ...
- the Apollo Primary Guidance and Navigation System
* AP-101 (IBM S/360-derived) computers used in the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
* Gemini Guidance Computer
* History of computer hardware
The history of computing hardware covers the developments from early simple devices to aid calculation to modern day computers. Before the 20th century, most calculations were done by humans.
The first aids to computation were purely mechanic ...
Notes
References
Sources
*External links
;Documentation on the AGC and its development''AGC4 Memo #9, Block II Instructions''
– The infamous memo that served as de facto official documentation of the instruction set
– By James Tomayko (Chapter 2, Part 5, ''The Apollo guidance computer: Hardware'')
''Computers Take Flight''
– By James Tomayko
''The Apollo Guidance Computer - A Users View''
(
PDF
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. ...
) – By David Scott, Apollo mission astronaut''Lunar Module Attitude Controller Assembly Input Processing''
(
PDF
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. ...
) – By José Portillo Lugo, History of TechnologyThe MIT AGC Project
– With comprehensive document archive
for Lunar Module guidance computer. (nb. 622 Mb)
for Command Module guidance computer. (nb. 83 Mb)
National Air and Space Museum's AGC Block I
an
Dsky
– An AGC system programmer discusses some obscure details of the development of AGC, including specifics of Ed's Interrupt ;Documentation of AGC hardware design, and particularly the use of the new integrated circuits in place of transistors
;Documentation of AGC software operation
Delco Electronics, Apollo 15
- Manual for CSM and LEM AGC software used on the Apollo 15 mission, including detailed user interface procedures, explanation of many underlying algorithms and limited hardware information. Note that this document has over 500 pages and is over 150 megabytes in size.
for Command Module code (Comanche054) and Lunar Module code (Luminary099) as text.
GitHub Complete Source Code
Original Apollo 11 Guidance Computer (AGC) source code for the command and lunar modules. ;Some AGC-based projects and simulators
AGC Replica
– John Pultorak's successful project to build a hardware replica of the Block I AGC in his basement. Mirror site
AGC Replica
– Ronald Burkey's AGC simulator, plus source and binary code recovery for the Colossus (CSM) and Luminary (LEM) SW.
– A web-based AGC simulator based on Virtual AGC.
Eagle Lander 3D
Shareware Lunar Lander Simulator with a working AGC and DSKY (Windows only).
AGC restarted 45 years later
Feature Stories
Weaving the way to the Moon
(BBC News)
(Wall Street Journal)
''Computer for Apollo'' video
{{CPU technologies Guidance computers Apollo program hardware Computer-related introductions in 1966 Assembly language software Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1975 disestablishments Spacecraft navigation instruments