|
Gadiformes
Gadiformes , also called the Anacanthini, are an order of ray-finned fish that include the cod, hakes, pollock, haddock, burbot, rocklings and moras, many of which are food fish of major commercial value. They are mostly marine fish found throughout the world and the vast majority are found in temperate or colder regions (tropical species are typically deep-water) while a few species may enter brackish estuaries. Pacific tomcods, one of the two species that makes up the genus ''Microgadus'', are able to enter freshwater, but there is no evidence that they breed there. Some populations of landlocked Atlantic tomcod on the other hand, complete their entire life cycle in freshwater. Yet only one species, the burbot (''Lota lota''), is a true freshwater fish. Common characteristics include the positioning of the pelvic fins (if present), below or in front of the pectoral fins. Gadiformes are physoclists, which means their swim bladders do not have a pneumatic duct. The fins ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haddock
The haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus'') is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the Family (biology), family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the Monotypy, monotypic genus ''Melanogrammus''. It is found in the North Atlantic Ocean and associated seas, where it is an important species for fisheries, especially in northern Europe, where it is marketed fresh, frozen and Smoked fish, smoked; smoked varieties include the Finnan haddie and the Arbroath smokie. Other smoked versions include long boneless, the fileted side of larger haddock smoked in oak chips with the skin left on the fillet. Description The haddock has the elongated, tapering body shape typical of members of the cod family. It has a relatively small mouth which does not extend to below the eye; with the lower profile of the face being straight and the upper profile slightly rounded, this gives its snout a characteristic wedge-shaped profile. The upper jaw projects beyond the lower more so than in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylephoridae
''Stylephorus chordatus'', the tube-eye or thread-tail, is a deep-sea ray-finned fish, the only species in the genus ''Stylephorus'' and family Stylephoridae. It is found in deep subtropical and tropical oceans around the world, living at depths during the day and making nightly vertical migrations to feed on plankton. It is an extremely elongated fish; although its body grows only to long, its pair of tail fin rays triple its length to about . Its eyes are tubular in shape, resembling a pair of binoculars. It has a tubular mouth through which it sucks seawater by enlarging its oral cavity to about 40 times its original size. It then expels the water through the gills, leaving behind the copepods on which it feeds. The phylogenetic position of the tube-eye has been controversial. It has been historically placed amongst Lampriformes, but a study involving mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences analysis suggested ''Stylephorus'' is instead a close relative of the order Gadiform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codlet
Codlets are a family, Bregmacerotidae, of cod-like fishes, containing the single genus ''Bregmaceros'' found in tropical and subtropical waters throughout the world. They are very small fishes and even the largest, ''B. lanceolatus'', reaches only in length. Etymology Their scientific name is from Greek language, Greek ''bregma'' meaning the top of the head, and ''keras'' meaning "horn"; this refers to their occipital ray (a spine emerging from the top of the head). Fossil record Fossils of ''Bregmaceros'' are found from the Eocene to the Quaternary (age range: from 37.2 to 0.0 million years ago.). They are known from various localities in Europe, North America and South America. A potential extinct relative, ''Bregmacerina'', is known from the Early Miocene of Russia, where it inhabited the Paratethys. It shares close similarities to ''Bregmaceros'' in the reduction of the first dorsal fin, but differs in other aspects. It remains uncertain whether it is an actual member o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray-finned Fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of skin supported by radially extended thin bony spines called '' lepidotrichia'', as opposed to the bulkier, fleshy lobed fins of the sister clade Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). Resembling folding fans, the actinopterygian fins can easily change shape and wetted area, providing superior thrust-to-weight ratios per movement compared to sarcopterygian and chondrichthyian fins. The fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the articulation between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). The vast majority of actinopterygians are teleosts. By species count, they dominate the subphylum Vertebrata, and constitute nearly 99% of the over 30,000 extant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moridae
The Moridae are a family of cod-like fishes, known as codlings, hakelings, and moras. Morids are marine fishes found throughout the world, and may be found at depths to , although most prefer shallower waters. In appearance, they greatly resemble the typical cods, from which can only be distinguished by their skeletal features and the structure of the swim bladder. They grow up to long (red codling The red codling or hoka (''Pseudophycis bachus'') is a morid cod of the genus ''Pseudophycis'', restricted to New Zealand, from the surface to 700 m. A closely related species, ''Pseudophycis barbata'', is found in Australia. It reaches lengths u ..., ''Pseudophycis bachus''). The earliest fossil member of the group is '' Eophycis'' from the Early Oligocene of Europe. References * Euteleostei families {{Gadiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotidae
The Lotidae are a family of cod-like fishes commonly known as lings or rocklings. They are found in the Arctic, Atlantic, and Pacific Oceans. Except for a few species of '' Gaidropsarus'', all are restricted to the Northern Hemisphere. All species are marine, except for the burbot, ''Lota lota'', found in rivers and lakes in northern Europe, Siberia Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ..., and North America. They are important commercial and game fish species. References Euteleostei families Taxa named by Charles Lucien Bonaparte {{Gadiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microgadus Proximus
''Microgadus proximus'', also commonly known as Pacific tomcod, is a type of cod fish found in North American coastal waters from the southeastern Bering Sea to central California California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an .... This species can reach a length of . Their diet of the Pacific tomcod includes anchovies, shrimp, worms, and other small marine invertebrates. Pacific tomcod are occasionally taken by recreational anglers. This is usually incidental to fishing for other species of fish as they are relatively small in size. References Pacific tomcod Fish of the Pacific Ocean Western North American coastal fauna Pacific tomcod {{Gadiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microgadus
''Microgadus'', the tomcods, is a genus of cods. Species There are currently two recognized species in this genus: * '' Microgadus proximus'' ( Girard, 1854) (Pacific tomcod) * '' Microgadus tomcod'' ( Walbaum, 1792) (Atlantic tomcod) References Gadidae Marine fish genera Taxa named by Theodore Gill {{Gadiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
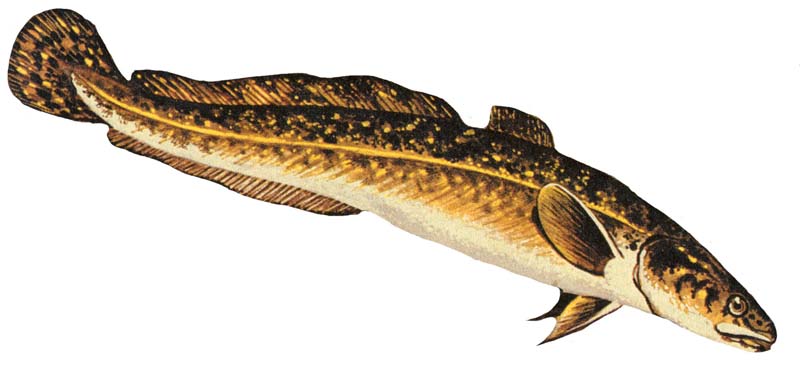
Burbot
The burbot (''Lota lota''), also known as bubbot, mariah, loche, cusk, freshwater cod, freshwater ling, freshwater cusk, the lawyer, coney-fish, lingcod, or eelpout, is a species of coldwater ray-finned fish native to the subarctic regions of the Northern hemisphere. It is the only member of the genus ''Lota'', and is the only freshwater species of the order Gadiformes. The species is closely related to marine fish such as the common ling and cusk, all of which belong to the family Lotidae (rocklings). Etymology The name burbot comes from the Latin word ''barba'', meaning beard, referring to its single chin whisker, or barbel. Its generic and specific names, ''Lota lota'', comes from the old French ''lotte'' fish, which is also named "barbot" in Old French. Description With an appearance like a cross between a catfish and an eel, the burbot has a serpent-like body, but is easily distinguished by a single barbel on the chin. The body is elongated and laterally compress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hake
Hake is the common name for fish in the Merlucciidae family of the northern and southern oceans and the Phycidae family of the northern oceans. Hake is a commercially important fish in the same taxonomic order, Gadiformes, as cod and haddock. Description Hakes are medium-to-large fish averaging from in weight, with specimens as large as . The fish can grow up to in length with a lifespan of as long as 14 years. Hake may be found in the Atlantic Ocean and Pacific Ocean in waters from deep. The fish stay in deep water during the day and come to shallower depths during the night. An undiscerning predator, hake feed on prey found near or on the bottom of the sea. Male and female hake are very similar in appearance. After spawning, the hake eggs float on the surface of the sea where the larvae develop. After a certain period of time, the baby hake then migrate to the bottom of the sea, preferring depths of less than . ''Merlucciidae'' A total of 13 hake species are know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physoclist
Physoclisti are, collectively, fishes that lack a connection between the gas bladder and the alimentary canal, with the bladder serving only as a buoyancy organ. Addition and removal of the gases from the gas bladder in such physoclistous fishes occurs through specialised structures called the gas gland and ovale respectively. The pneumatic duct that connects the gut and gas bladder is present in the embryos of these fish but it is lost during development. This anatomical state (the physoclistous condition) is believed to be evolutionarily derived from the ancestral physostomous state. Some fishes, such as eels, are anatomically physostomous, but their gas bladders function similar to those of physoclists. See also * Physostome Physostomes are fishes that have a pneumatic duct connecting the gas bladder to the alimentary canal. This allows the gas bladder to be filled or emptied via the mouth. This not only allows the fish to fill their bladder by gulping air, but al ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eschmeyer's Catalog Of Fishes
Catalog of Fishes is a comprehensive on-line database and reference work on the scientific names of fish species and genera. It is global in its scope and is hosted by the California Academy of Sciences. It has been compiled and is continuously updated by the curator emeritus of the CAS fish collection, William N. Eschmeyer. The taxonomy maintained by the Catalog of Fishes is considered authoritative and it is used as a baseline reference for instance by the broader global fish database FishBase, which involves cross-references to the Catalog's information for all accepted taxa. the searchable catalogue contains entries for about 58,300 fish species names, about 33,400 of which are currently accepted (valid), and for some 10,600 genera (5,100 valid). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |