|
Cx43
Gap junction alpha-1 protein (GJA1), also known as connexin 43 (Cx43), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GJA1'' gene on chromosome 6. As a connexin, GJA1 is a component of gap junctions, which allow for gap junction intercellular communication (GJIC) between cells to regulate cell death, proliferation, and differentiation. As a result of its function, GJA1 is implicated in many biological processes, including muscle contraction, embryonic development, inflammation, and spermatogenesis, as well as diseases, including oculodentodigital dysplasia (ODDD), heart malformations, and cancers. Structure GJA1 is a 43.0 kDa protein composed of 382 amino acids. GJA1 contains a long C-terminal tail, an N-terminal domain, and multiple transmembrane domains. The protein passes through the phospholipid bilayer four times, leaving its C- and N-terminals exposed to the cytoplasm. The C-terminal tail is composed of 50 amino acids and includes post-translational modification sites, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gap Junction
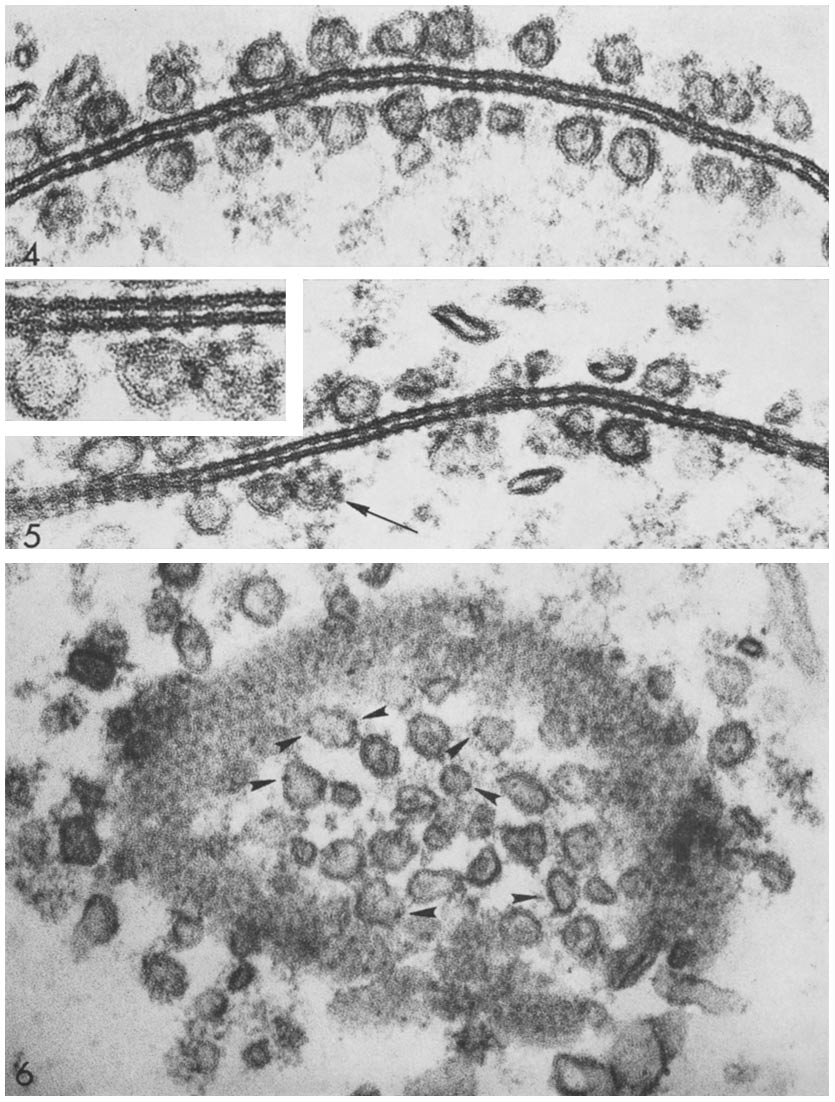
Gap junctions are membrane channels between adjacent cells that allow the direct exchange of cytoplasmic substances, such small molecules, substrates, and metabolites. Gap junctions were first described as ''close appositions'' alongside tight junctions, however, electron microscopy studies in 1967 led to gap junctions being named as such to be distinguished from tight junctions. They bridge a 2-4 nm gap between cell membranes. Gap junctions use protein complexes known as connexons, composed of connexin proteins to connect one cell to another. Gap junction proteins include the more than 26 types of connexin, as well as at least 12 non-connexin components that make up the gap junction complex or ''nexus,'' including the tight junction protein ZO-1—a protein that holds membrane content together and adds structural clarity to a cell, sodium channels, and aquaporin. More gap junction proteins have become known due to the development of next-generation sequencing. Connexins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connexin
Connexins (Cx)TC# 1.A.24, or gap junction proteins, are structurally related transmembrane proteins that assemble to form vertebrate gap junctions. An entirely different family of proteins, the innexins, forms gap junctions in invertebrates. Each gap junction is composed of two hemichannels, or connexons, which consist of homo- or heterohexameric arrays of connexins, and the connexon in one plasma membrane docks end-to-end with a connexon in the membrane of a closely opposed cell. The hemichannel is made of six connexin subunits, each of which consist of four transmembrane segments. Gap junctions are essential for many physiological processes, such as the coordinated depolarization of cardiac muscle, proper embryonic development, and the conducted response in microvasculature. Connexins also have non-channel dependant functions relating to cytoskeleton and cell migration. For these reasons, mutations in connexin-encoding genes can lead to functional and developmental abnormalitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Ribosome Entry Site
An internal ribosome entry site, abbreviated IRES, is an RNA element that allows for translation initiation in a cap-independent manner, as part of the greater process of protein synthesis. Initiation of eukaryotic translation nearly always occurs at and is dependent on the 5' cap of mRNA molecules, where the translation initiation complex forms and ribosomes engage the mRNA. IRES elements, however, allow ribosomes to engage the mRNA and begin translation independently of the 5' cap. History IRES sequences were first discovered in 1988 in the poliovirus (PV) and encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) RNA genomes in the laboratories of Nahum Sonenberg and Eckard Wimmer, respectively. They are described as distinct regions of RNA molecules that are able to recruit the eukaryotic ribosome to the mRNA. This process is also known as cap-independent translation. It has been shown that IRES elements have a distinct secondary or even tertiary structure, but similar structural features at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of Transcription (biology), transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and the ribosome creates the protein utilizing amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA). This process is known as Translation (biology), translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of geneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Prime Untranslated Region
The 5′ untranslated region (also known as 5′ UTR, leader sequence, transcript leader, or leader RNA) is the region of a messenger RNA (mRNA) that is directly upstream from the initiation codon. This region is important for the regulation of translation of a transcript by differing mechanisms in viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Despite its name, the 5′ UTR, or a portion of it is sometimes translated into a protein product. This product may involve in regulation of transcription, and translation of the main coding sequence of the mRNA, such as the sex-lethal gene in '' Drosophila''. Regulatory elements within 5′ UTRs have also been linked to mRNA export. In many organisms, however, the 5′ UTR is completely untranslated, instead forming a complex secondary structure to regulate translation. General structure Length The 5′ UTR begins at the transcription start site and ends one nucleotide (nt) before the initiation sequence (usually AUG) of the coding region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-regulatory Element
''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology. CREs are found in the vicinity of the genes that they regulate. CREs typically regulate gene transcription by binding to transcription factors. A single transcription factor may bind to many CREs, and hence control the expression of many genes ( pleiotropy). The Latin prefix ''cis'' means "on this side", i.e. on the same molecule of DNA as the gene(s) to be transcribed. CRMs are stretches of DNA, usually 100–1000 DNA base pairs in length, where a number of transcription factors can bind and regulate expression of nearby genes and regulate their transcription rates. They are labeled as ''cis'' because they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions from sub-disciplines and related fields, see Glossary of cell biology, Glossary of genetics, Glossary of evolutionary biology, Glossary of ecology, Glossary of environmental science and Glossary of scientific naming, or any of the organism-specific glossaries in :Glossaries of biology. A B C D E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. It is composed of three main components: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules, and these are all capable of rapid growth and or disassembly depending on the cell's requirements. Cytoskeleton can perform many functions. Its primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, and through association with extracellular connective tissue and other cells it stabilizes entire tissues. The cytoskeleton can also contract, thereby deforming the cell and the cell's environment and allowing cells to migrate. Moreover, it is involved in many cell signaling pathways and in the uptake of extracellular material ( endocytosis), the segregation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are Gene expression, expressed in the desired Cell (biology), cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are approximately 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-translational Modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biology), translate mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then change to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signal transduction, signalling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C-terminus, C- or N-terminus, N- termini. They can expand the chemical set of the 22 proteinogenic amino acid, amino acids by changing an existing functional group or adding a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is highly effective for controlling the enzyme activity and is the most common change after translation. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |