|
Cubic Miles
A cubic mile (abbreviation: cu mi or mi3) is an imperial and US customary (non- SI non-metric) unit of volume, used in the United States, Canada and the United Kingdom. It is defined as the volume of a cube with sides of length, giving a volume of . Conversions See also * Square mile * Orders of magnitude for a comparison with other volumes * * Cube (arithmetic) ** Cube root ** Cubic equation ** Cubic function In mathematics, a cubic function is a function of the form f(x)=ax^3+bx^2+cx+d, that is, a polynomial function of degree three. In many texts, the ''coefficients'' , , , and are supposed to be real numbers, and the function is considered as ... References {{United States Customary Units Units of volume Imperial units Customary units of measurement in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Units
The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units (also known as British Imperial or Exchequer Standards of 1826) is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments. The imperial system developed from earlier English units as did the Comparison of the imperial and US customary measurement systems, related but differing system of United States customary units, customary units of the United States. The imperial units replaced the Winchester measure, Winchester Standards, which were in effect from 1588 to 1825. The system came into official use across the British Empire in 1826. By the late 20th century, most nations of the former empire had metrication, officially adopted the metric system as their main system of measurement, but imperial units are still used alongside metric units in the United Kingdom and in some other parts of the former empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Kilometre
The cubic metre (in Commonwealth English and international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures) or cubic meter (in American English) is the unit of volume in the International System of Units (SI). Its symbol is m3. Bureau International de Poids et Mesures.Derived units expressed in terms of base units". 2014. Accessed 7 August 2014. It is the volume of a cube with edges one metre in length. An alternative name, which allowed a different usage with metric prefixes, was the stère, still sometimes used for dry measure (for instance, in reference to wood). Another alternative name, no longer widely used, was the kilolitre. Conversions : A cubic metre of pure water at the temperature of maximum density (3.983 °C) and standard atmospheric pressure (101.325 kPa) has a mass of , or one tonne. At 0 °C, the freezing point of water, a cubic metre of water has slightly less mass, 999.85 kilograms. A cubic metre is sometimes abbreviated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
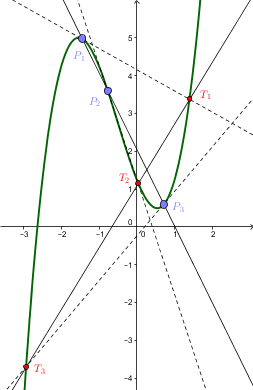
Cubic Function
In mathematics, a cubic function is a function of the form f(x)=ax^3+bx^2+cx+d, that is, a polynomial function of degree three. In many texts, the ''coefficients'' , , , and are supposed to be real numbers, and the function is considered as a real function that maps real numbers to real numbers or as a complex function that maps complex numbers to complex numbers. In other cases, the coefficients may be complex numbers, and the function is a complex function that has the set of the complex numbers as its codomain, even when the domain is restricted to the real numbers. Setting produces a cubic equation of the form :ax^3+bx^2+cx+d=0, whose solutions are called roots of the function. The derivative of a cubic function is a quadratic function. A cubic function with real coefficients has either one or three real roots ( which may not be distinct); all odd-degree polynomials with real coefficients have at least one real root. The graph of a cubic function always has a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Equation
In algebra, a cubic equation in one variable is an equation of the form ax^3+bx^2+cx+d=0 in which is not zero. The solutions of this equation are called roots of the cubic function defined by the left-hand side of the equation. If all of the coefficients , , , and of the cubic equation are real numbers, then it has at least one real root (this is true for all odd-degree polynomial functions). All of the roots of the cubic equation can be found by the following means: * algebraically: more precisely, they can be expressed by a ''cubic formula'' involving the four coefficients, the four basic arithmetic operations, square roots, and cube roots. (This is also true of quadratic (second-degree) and quartic (fourth-degree) equations, but not for higher-degree equations, by the Abel–Ruffini theorem.) * trigonometrically * numerical approximations of the roots can be found using root-finding algorithms such as Newton's method. The coefficients do not need to be real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cube Root
In mathematics, a cube root of a number is a number that has the given number as its third power; that is y^3=x. The number of cube roots of a number depends on the number system that is considered. Every real number has exactly one real cube root that is denoted \sqrt /math> and called the ''real cube root'' of or simply ''the cube root'' of in contexts where complex numbers are not considered. For example, the real cube roots of and are respectively and . The real cube root of an integer or of a rational number is generally not a rational number, neither a constructible number. Every nonzero real or complex number has exactly three cube roots that are complex numbers. If the number is real, one of the cube roots is real and the two other are nonreal complex conjugate numbers. Otherwise, the three cube roots are all nonreal. For example, the real cube root of is and the other cube roots of are -1+i\sqrt 3 and -1-i\sqrt 3. The three cube roots of are 3i, \tfrac-\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cube (arithmetic)
In arithmetic and algebra, the cube of a number is its third exponentiation, power, that is, the result of multiplying three instances of together. The cube of a number is denoted , using a superscript 3, for example . The cube Mathematical operation, operation can also be defined for any other expression (mathematics), mathematical expression, for example . The cube is also the number multiplied by its square (algebra), square: :. The ''cube function'' is the function (mathematics), function (often denoted ) that maps a number to its cube. It is an odd function, as :. The volume of a Cube (geometry), geometric cube is the cube of its side length, giving rise to the name. The Inverse function, inverse operation that consists of finding a number whose cube is is called extracting the cube root of . It determines the side of the cube of a given volume. It is also raised to the one-third power. The graph of a function, graph of the cube function is known as the cubic para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orders Of Magnitude (volume)
The table lists various objects and units by the order of magnitude of their volume. Sub-microscopic Microscopic Human measures Terrestrial Astronomical References {{DEFAULTSORT:Orders Of Magnitude (Volume) Volume Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch) ... * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Mile
The square mile (abbreviated as sq mi and sometimes as mi2)Rowlett, Russ (September 1, 2004) University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved February 22, 2012. is an imperial and US unit of measure for area. One square mile is equal to the area of a square with each side measuring a length of one mile. Equivalents One square mile is equal to: *4,014,489,600 square inches * * * * One square mile is also equivalent to: * * * Similarly named units Miles square Square miles should not be confused with miles square, a square region with each side having a length of the value given. For example, a region which is 20 miles square ( × ) has an area of ; a rectangle of measuring × also has an area of , but is not 20 miles square. Section In the United States Public Land Survey System The Public Land Survey System (PLSS) is the surveying method developed and used in the United States to plat, or divide, real property for sale and settling. Also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
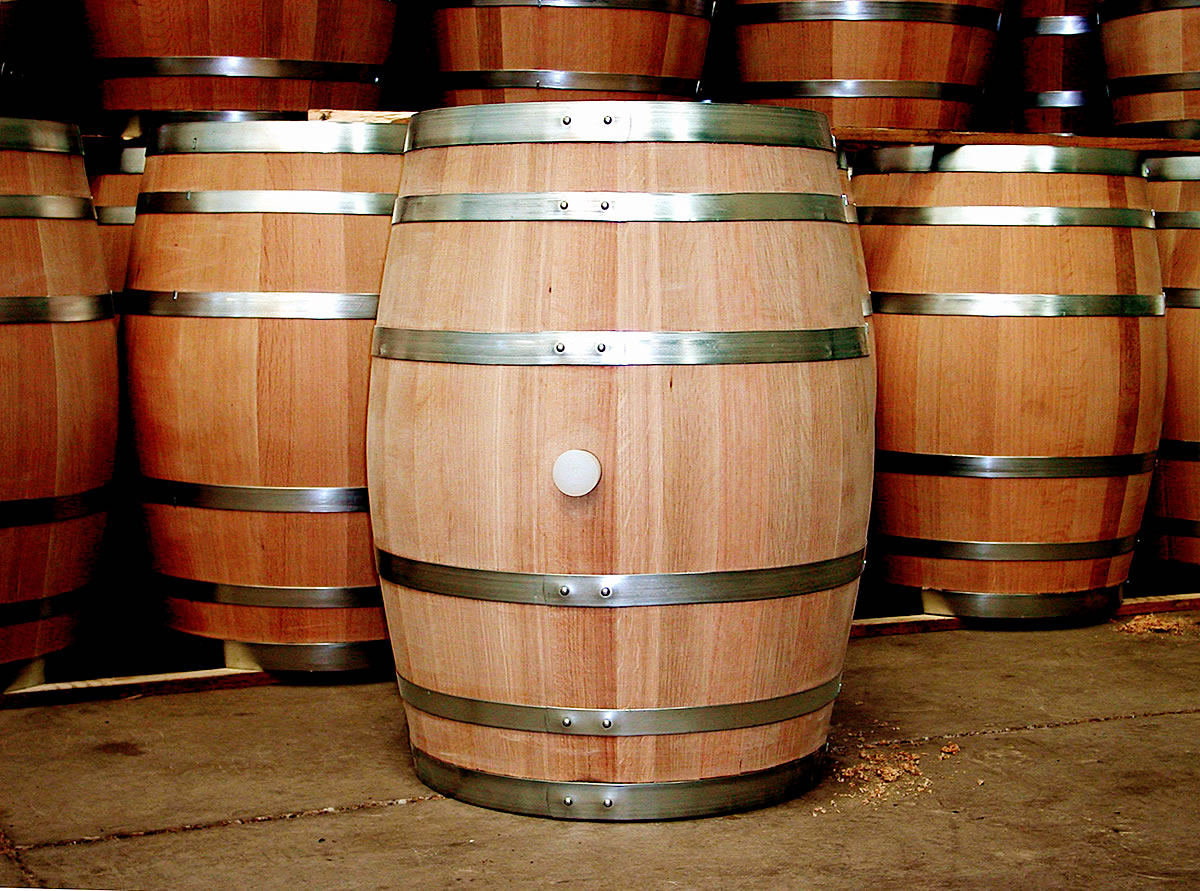
Barrel
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden stave (wood), staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, usually alcoholic beverages; a small barrel or cask is known as a keg. Barrels have a variety of uses, including storage of liquids such as water, oil, and alcohol. They are also employed to hold maturing beverages such as wine, Cognac (brandy), cognac, Armagnac (drink), armagnac, sherry, port wine, port, whiskey, beer, arrack, and sake. Other commodities once stored in wooden casks include gunpowder, Salt-cured meat, meat, fish, paint, honey, nails, and tallow. Modern wooden barrels for wine-making are made of English oak (''Quercus robur''), white Oak (wine), oak (''Quercus petraea''), American white oak (''Quercus alba''), more exotic is mizunara oak (''Quercus crispula''), and recently Oregon oak (''Quercus garryana'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bushel
A bushel (abbreviation: bsh. or bu.) is an Imperial unit, imperial and United States customary units, US customary unit of volume, based upon an earlier measure of dry capacity. The old bushel was used mostly for agriculture, agricultural products, such as wheat: in modern usage, the volume is nominal, with bushels denoting a mass defined differently for each commodity. The name "bushel" is also used to translate similar units in other measurement systems. Name The word "bushel" as originally used for a container itself, and later a unit of measurement. The name comes from the Old French ' and ', meaning "little box".. It may further derive from Old French ', thus meaning "little butt (unit), butt". History The bushel is an intermediate value between the pound (mass), pound and ton or tun (unit), tun that was introduced to England following the Norman Conquest of England, Norman Conquest. Norman England, Norman Weights and Measures Acts (UK), statutes made the London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallon
The gallon is a unit of volume in British imperial units and United States customary units. The imperial gallon (imp gal) is defined as , and is or was used in the United Kingdom and its former colonies, including Ireland, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, India, South Africa, Malaysia and some Caribbean countries, while the US gallon (US gal) is defined as , and is used in the United States and some Latin American and Caribbean countries. There are four gills in a pint, two pints in a quart, and four quarts (''quarter'' gallons) in a gallon, with the imperial gill being divided into five imperial fluid ounces and the US gill being divided into four US fluid ounces: this, and a slight difference in the sizes of the imperial fluid ounce and the US fluid ounce, give different sizes for the imperial gallon and US gallon. The IEEE standard symbol for both the imperial and US gallons is gal, not to be confused with the gal (symbol: Gal), a CGS unit of acceleration. Definitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acre-foot
The acre-foot is a non- SI unit of volume equal to about commonly used in the United States in reference to large-scale water resources, such as reservoirs, aqueducts, canals, sewer flow capacity, irrigation water, and river flows. An acre-foot equals approximately an eight-lane swimming pool, long, wide and deep. Definitions As the name suggests, an acre-foot is defined as the volume of one acre of surface area to a depth of one foot. Since an acre is defined as a chain by a furlong (i.e. ), an acre-foot is . There have been two definitions of the acre-foot (differing by about 0.0006%), using either the international foot (0.3048 m) or a U.S. survey foot (exactly meters since 1893). On December 31, 2022, the National Institute of Standards and Technology, the National Geodetic Survey, and the United States Department of Commerce deprecated use of the US survey foot and recommended conversion to either the meter or the international foot. Application As a rule of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |