|
Crystal Structure Prediction
Crystal structure prediction (CSP) is the calculation of the crystal structures of solids from first principles. Reliable methods of predicting the crystal structure of a compound, based only on its composition, has been a goal of the physical sciences since the 1950s. Computational methods employed include simulated annealing, evolutionary algorithms, distributed multipole analysis, random sampling, basin-hopping, data mining, density functional theory and molecular mechanics. History The crystal structures of simple ionic solids have long been rationalised in terms of Pauling's rules, first set out in 1929 by Linus Pauling. For metals and semiconductors one has different rules involving valence electron concentration. However, prediction and rationalization are rather different things. Most commonly, the term crystal structure prediction means a search for the minimum-energy arrangement of its constituent atoms (or, for molecular crystals, of its molecules) in space. The problem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in a material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of principal axes/edges, of the unit cell and angles between them are lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of a crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Chemical Physics
''The Journal of Chemical Physics'' is a scientific journal published by the American Institute of Physics that carries research papers on chemical physics."About the Journal" from the ''Journal of Chemical Physics'' website. Two volumes, each of 24 issues, are published annually. It was established in 1933 when '''' editors refused to publish theoretical works. The editors have been: *2019–present: Tim Lian *2008–2018: Marsha I. Lester *2007–2008: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulations to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry incorporated into computer programs to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. The importance of this subject stems from the fact that, with the exception of some relatively recent findings related to the hydrogen molecular ion (dihydrogen cation), achieving an accurate quantum mechanical depiction of chemical systems analytically, or in a closed form, is not feasible. The complexity inherent in the many-body problem exacerbates the challenge of providing detailed descriptions of quantum mechanical systems. While computational results normally complement information obtained by chemical experiments, it can occasionally predict unobserved chemical phenomena. Overview Computational chemistry differs from theoretical chemistry, which involves a mathematical description of chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming 2014 the International Year of Crystallography.UN announcement "International Year of Crystallography" iycr2014.org. 12 July 2012 Crystallography is a broad topic, and many of its subareas, such as X-ray crystallography, are themselves important scientific topics. Crystallography ranges from the fundamentals of crystal structure to the mathematics of Crystal system, crystal geometry, including those that are Aperiodic crystal, not periodic or quasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Chemical Theory And Computation
The ''Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal, established in 2005 by the American Chemical Society. The editor-in-chief is Laura Gagliardi (University of Chicago). Originally bimonthly, the journal switched to monthly in 2008. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 5.7. See also References External links * {{American Chemical Society Journals American Chemical Society academic journals Monthly journals English-language journals Academic journals established in 2005 Computational chemistry Quantum chemistry Theoretical chemistry Chemistry journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Free Energy
In thermodynamics, the thermodynamic free energy is one of the state functions of a thermodynamic system. The change in the free energy is the maximum amount of work that the system can perform in a process at constant temperature, and its sign indicates whether the process is thermodynamically favorable or forbidden. Since free energy usually contains potential energy, it is not absolute but depends on the choice of a zero point. Therefore, only relative free energy values, or changes in free energy, are physically meaningful. The free energy is the portion of any first-law energy that is available to perform thermodynamic work at constant temperature, ''i.e.'', work mediated by thermal energy. Free energy is subject to irreversible loss in the course of such work. Since first-law energy is always conserved, it is evident that free energy is an expendable, second-law kind of energy. Several free energy functions may be formulated based on system criteria. Free energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angewandte Chemie International Edition
''Angewandte Chemie'' (, meaning "Applied Chemistry") is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published by Wiley-VCH on behalf of the German Chemical Society (Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker). Publishing formats include feature-length reviews, short highlights, research communications, minireviews, essays, book reviews, meeting reviews, correspondences, corrections, and obituaries. This journal contains review articles covering all aspects of chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2023 impact factor of 16.1. Editions The journal appears in two editions with separate volume and page numbering: a German edition, ''Angewandte Chemie'', and a fully English-language edition, ''Angewandte Chemie International Edition''. The editions are identical in content with the exception of occasional reviews of German-language books or German translations of IUPAC recommendations. Publication history In 1887, Ferdinand Fischer established the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Energy
In chemistry, the lattice energy is the energy change (released) upon formation of one mole of a crystalline compound from its infinitely separated constituents, which are assumed to initially be in the gaseous state at 0 K. It is a measure of the cohesive forces that bind crystalline solids. The size of the lattice energy is connected to many other physical properties including solubility, hardness, and volatility. Since it generally cannot be measured directly, the lattice energy is usually deduced from experimental data via the Born–Haber cycle. Lattice energy and lattice enthalpy The concept of lattice energy was originally applied to the formation of compounds with structures like rocksalt ( NaCl) and sphalerite ( ZnS) where the ions occupy high-symmetry crystal lattice sites. In the case of NaCl, lattice energy is the energy change of the reaction: Na^+ (g) + Cl^- (g) -> NaCl (s) which amounts to −786 kJ/mol.David Arthur Johnson, ''Metals and Chemical Change' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acta Crystallographica B
''Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials'' publishes scientific articles on structural science. According to the journal: "Knowledge of the arrangements of atoms, including their temporal variations and dependencies on temperature and pressure, is often the key to understanding physical and chemical phenomena and is crucial for the design of new materials and supramolecular devices." It was formed in 1968 when the journal ''Acta Crystallographica'' was split into two parts and has been published for the International Union of Crystallography under the following titles: *''Acta Crystallographica. Section B: Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry'' () from its formation until the end of 1982. It was published in Denmark by Munksgaard and accepted articles in English, French, and German. *On the launch of ''Acta Crystallographica Section C'' in 1983, the title of Section B changed to ''Acta Crystallographica Section B: Struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
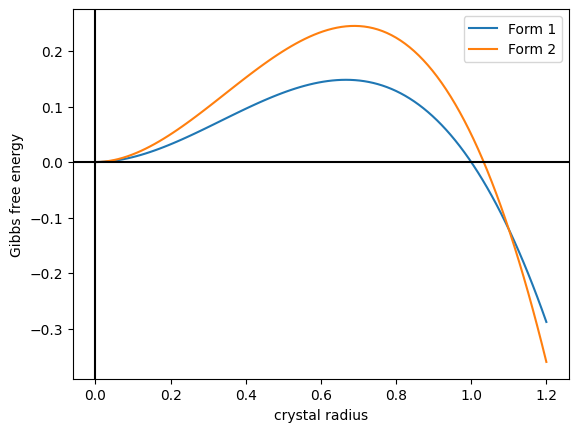
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In crystallography, polymorphism is the phenomenon where a compound or element can crystallize into more than one crystal structure. The preceding definition has evolved over many years and is still under discussion today. Discussion of the defining characteristics of polymorphism involves distinguishing among types of transitions and structural changes occurring in polymorphism versus those in other phenomena. Overview Phase transitions (phase changes) that help describe polymorphism include polymorphic transitions as well as melting and vaporization transitions. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." Additionally, Walter McCrone described the phases in polymorphic matter as "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." McCrone also def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored substances which are soluble or go into solution at some stage in their use. Dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compound, inorganic. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic chemistry, inorganic, organic chemistry, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. According to an April 2018 report by ''Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |