|
County Carlow
County Carlow ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county located in the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region of Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Carlow is the List of Irish counties by area, second smallest and the List of Irish counties by population, third least populous of Ireland's 32 traditional counties. Carlow County Council is the governing Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority. The county is named after the town of Carlow, which lies on the River Barrow and is both the county town and largest settlement, with over 40% of the county's population. Much of the remainder of the population also reside within the Barrow valley, in towns such as Leighlinbridge, Bagenalstown, Graiguenamanagh, Tinnahinch, Borris, County Carlow, Borris and St. Mullins, St Mullins. Carlow shares a border with County Kildare, Kildare and County Laois, Laois to the north, County Kilkenny, Kilkenny to the west, County Wicklow, Wicklow to the east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
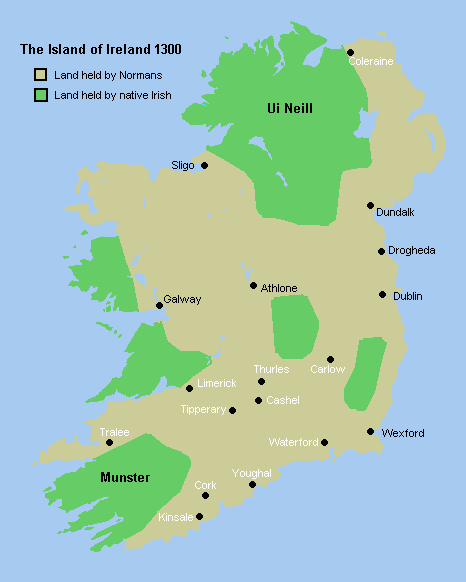
Counties Of Ireland
The counties of Ireland (Irish language, Irish: ) are historic administrative divisions of the island. They began as Normans in Ireland, Norman structures, and as the powers exercised by the Cambro-Norman barons and the Old English (Ireland), Old English nobility waned over time, new offices of political control came to be established at a county level. The number of counties varied depending on the time period, however thirty-two is the traditionally accepted and used number. Upon the partition of Ireland in 1921, six of the traditional counties became part of Northern Ireland. In Northern Ireland, Counties of Northern Ireland, counties ceased to be used for local government in 1973; Local government in Northern Ireland, districts are instead used. In the Republic of Ireland, some counties have been split resulting in the creation of new counties: there are currently 26 counties, 3 cities and 2 cities and counties that demarcate areas of local government in the Republic of Ire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Ireland
There are four provinces of Ireland: Connacht, Leinster, Munster and Ulster. The Irish language, Irish word for this territorial division, , meaning "fifth part", suggests that there were once five, and at times Kingdom of Meath, Meath has been considered to be the fifth province. In the medieval period, however, there were often more than five. The number of provinces and their delimitation fluctuated until 1610, when they were permanently set by the English administration of James VI and I, James I. The provinces of Ireland no longer serve administrative or political purposes but function as historical and cultural entities. Etymology In modern Irish language, Irish, the word for province is (pl. ). The modern Irish term derives from the Old Irish (pl. ) which literally meant "a fifth". This term appears in 8th-century law texts such as and in the legendary tales of the Ulster Cycle where it refers to the five kingdoms of the "Pentarchy". MacNeill enumerates the five earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graiguenamanagh
Graiguenamanagh or Graignamanagh () is a town on the River Barrow in County Kilkenny, Ireland. Part of the settlement, known as Tinnahinch, is on the County Carlow side of the river, and Carlow County Council refers to the whole village as "Graiguenamanagh-Tinnahinch". Also combined for census purposes, as of the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census, Graiguenamanagh-Tinnahinch had a population of 1,506 people. The town is in a townland and Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish of the same name. Graiguenamanagh is located at the foot of Brandon Hill and is home to Duiske Abbey, the largest of the thirty-four mediaeval Cistercian abbeys in Ireland. History Ecclesiastical sites Evidence of ancient settlement in the area include an ecclesiastical enclosure and holy well sites in the townlands of Graiguenamanagh and Tinnahinch. St. Caelán reputedly founded a monastery at Tinnahinch during the 6th or 7th century. Also located in the area are the ruined remains of the early Christ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagenalstown
Bagenalstown ( ), officially named Muine Bheag (), is a small town on the River Barrow in County Carlow, Ireland. History and name In the eight century, Saint Lappan reputedly founded a monastic school outside Bagenalstown in the townland of Donore. He is the patron saint of Bagenalstown. The town grew within the townland of Moneybeg, from Irish ''Muine Bheag'' or ''Muinebheag'' (meaning "small thicket"). In the 18th century there was a small hamlet there. Walter Bagenal decided to build a town on the site, to be named "New Versailles" and modelled after Versailles in France.Mayse, Shirley. ''Our Caswell Relatives''. University of Wisconsin, 1975. p.343 However, shortly after building began, the coach route from Dublin, which had passed the location, was changed so it crossed the River Barrow a few kilometres away, at Leighlinbridge, instead. Bagenal abandoned his plans, having built only a courthouse. It was not until the arrival of the railway in 1846 that the settleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leighlinbridge
Leighlinbridge (; ) is a small town on the River Barrow in County Carlow, Ireland. It is 11 km south of Carlow town, on the R705 road. The N9 national primary route once passed through the village, but was by-passed in the 1980s. It covers the townlands of Leighlin (east bank of the river) and Ballyknockan (west bank). The village features narrow winding streets, grey limestone malthouses and castle ruins overlooking a 14th-century bridge across the River Barrow. Leighlinbridge has won the National Tidy Towns Competition, has come first in the Barrow Awards, been an overall national winner in Ireland's Green Town 2000, and represented Ireland in the European "Entente Florale" competition in 2001. Places of interest Leighlinbridge Castle, also called Black Castle, was one of Ireland's earliest Norman castles. A 50 ft tall broken castle tower and bawn wall are all that can be seen today. The Arboretum Garden Centre is a located a kilometre east of the village at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Town
In Great Britain and Ireland, a county town is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county, and the place where public representatives are elected to parliament. Following the establishment of county councils in England in 1889, the headquarters of the new councils were usually established in the county town of each county; however, the concept of a county town pre-dates these councils. The concept of a county town is ill-defined and unofficial. Some counties in Great Britain have their administrative bodies housed elsewhere. For example, Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster is the county town of Lancashire, but the county council is in Preston, Lancashire, Preston. Owing to the creation of Unitary authorities of England, unitary authorities, some county towns in Great Britain are administratively separate from the county. For example, Nottingham is separated from the rest of Nottinghamshire, and Brighton and Hove is separate from East Sussex. On a ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Barrow
The Barrow () is a river in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is one of The Three Sisters (Ireland), The Three Sisters; the other two being the River Suir and the River Nore. The Barrow is the longest of the three rivers and, at 192 km (120 mi), the second-longest river in Ireland, behind the River Shannon. The catchment area of the River Barrow is 3,067 km2 before the River Nore joins it a little over 20 km before its mouth.South Eastern River Basin District Management System. Page 38 The river's long term average flow rate, again before it is joined by River Nore, is 37.4 cubic metres per second. At the merger with the River Nore, its catchment area is ca. 5,500 km2 and its discharge over 80&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Leinster
Mount Leinster (, ) is a mountain in the Republic of Ireland. It straddles the border between Counties Carlow and Wexford, in the province of Leinster. It is the fifth-highest mountain in Leinster after Lugnaquilla , Mullaghcleevaun , Tonelagee , and Cloghernagh , and the highest of the Blackstairs Mountains. A 2RN transmission site tops the peak with a mast height of . Summit access The mountain is most often climbed from the Nine Stones, a landmark point at the foot of Mount Leinster, about 8 miles east of Borris. From Borris there is a road to a visitor car park on the mountain. From there the steep 2RN access road leads to the summit. This road is closed to normal traffic and 2RN have now fenced off the transmitter mast from public access to prevent vandalism. The Nine Stones and the car park lie on the saddle between Mount Leinster and the nearby Slievebawn (''Sliabh Bán''; ; ). There are in fact ten stones. They are arranged in a line and the largest is about h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eircode
A postal address in Ireland is a place of Delivery (commerce), delivery defined by Irish Standard (IS) EN 14142-1:2011 ("Postal services. Address databases") and serviced by the universal service provider, . Its addressing guides comply with the guidelines of the Universal Postal Union (UPU), the United Nations-affiliated body responsible for promoting standards in the postal industry, across the world. In Ireland, 35% of premises (over 600,000) have non-unique addresses due to an absence of house numbers or names. Before the introduction of a national postcode system (Eircode) in 2015, this required postal workers to remember which family names corresponded to which house in smaller towns, and many townlands. , An Post encourages customers to use Eircode because it ensures that their post person can pinpoint the exact location. Ireland was the last country in the OECD to create a postcode system. In July 2015 all 2.2 million residential and business addresses in Ireland r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Numbers In The Republic Of Ireland
Numbers on the Irish telephone numbering plan are regulated and assigned to operators by ComReg. Overview Telephone numbers in Ireland are part of an open numbering plan that allows variations in number length. The Irish format is similar to systems used in many parts of Europe, notably the Netherlands, Sweden, Germany, Belgium and France, where geographical numbers are organised using a logic of large regional prefixes, which are then further subdivided into smaller regions. It differs from UK numbering, which originated as alphanumeric codes based on town names. Irish Mobile and non–geographic numbers are fixed length and do not support local dialling. The trunk prefix 0 is used to access numbers outside the local area and for all mobile calls. This is followed by an area code, referred to as a National Dialling Code (NDC), the first digit of which indicates the geographical area or type of service (e.g. mobile). Calls made from mobile phones and some VoIP systems always ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Standard Time
Ireland uses Irish Standard Time (IST, UTC+01:00; ) in the summer months and Greenwich Mean Time ( UTC+00:00; ) in the winter period. Roughly two-thirds of the Republic is located west of the 7.5°W meridian. Thus the local mean time in most of Ireland is closer to UTC-01:00 time than to GMT. The Standard Time Act 1968 legally established that "the time for general purposes in the State (to be known as standard time) shall be one hour in advance of Greenwich mean time throughout the year". This act was amended by the Standard Time (Amendment) Act 1971, which legally established Greenwich Mean Time as a winter time period. Ireland therefore operates one hour behind its statutory standard time during the winter period, and reverts to standard time in the summer months. This definition contrasts with the practice of other states in the European Union, which operate one hour ahead of their standard time during the summer period, but produces the same result. The net effect is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western European Time
Western European Time (WET, UTC+00:00) is a time zone covering parts of western Europe and consists of countries using UTC+00:00 (also known as Greenwich Mean Time, abbreviated GMT). It is one of the three standard time zones in the European Union along with Central European Time and Eastern European Time. The following Western European countries and regions use UTC+00:00 in winter months: *Portugal, since 1912 with pauses (except Azores, UTC−01:00) *United Kingdom and Crown Dependencies, since 1847 in England, Scotland, Wales, the Channel Islands, and the Isle of Man, and since 1916 in Northern Ireland, with pauses *Ireland, since 1916, except between 1968 and 1971 *Canary Islands, since 1946 (rest of Spain is CET, UTC+01:00) *Faroe Islands, since 1908 * North Eastern Greenland ( Danmarkshavn and surrounding area) *Iceland, since 1968, without summer time changes All the above countries except Iceland implement daylight saving time in summer (from the last Sunday in March ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |