|
Corticorelin
Corticorelin (INN, trade name Xerecept) is a diagnostic agent. It is a synthetic form of human corticotropin-releasing hormone (hCRH). Medical uses The corticorelin stimulation test helps to differentiate between the causes for adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-dependent hypercortisolism. It is used to distinguish a pituitary source of excessive ACTH secretion from a different source. * If corticorelin injection increases plasma levels of ACTH and cortisol, a diagnosis of Cushing's disease is achieved (ACTH of pituitary origin). * If corticorelin injection leads to little or no response in plasma levels of ACTH or cortisol, a diagnosis of ectopic ACTH syndrome is confirmed. Side effects The most common side effects (in 1% to 10% of patients) are transient dysosmia and dysgeusia (distortion of the sense of smell and taste), as well as a sensation of warmth. About 0.1 to 1% of patients experience hypersensitivity, hypotension (lowering of blood pressure), tachycardia (increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticotropin-releasing Hormone
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) (also known as corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) or corticoliberin; corticotropin may also be spelled corticotrophin) is a peptide hormone involved in stress responses. It is a releasing hormone that belongs to corticotropin-releasing factor family. In humans, it is encoded by the ''CRH'' gene. Its main function is the stimulation of the pituitary synthesis of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), as part of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis). Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is a 41-amino acid peptide derived from a 196-amino acid preprohormone. CRH is secreted by the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus in response to stress. Increased CRH production has been observed to be associated with Alzheimer's disease and major depression, and autosomal recessive hypothalamic corticotropin deficiency has multiple and potentially fatal metabolic consequences including hypoglycemia. In addition to being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
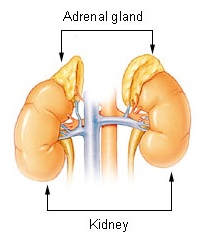
Pituitary Tumour
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.Pituitary Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version NIH National Cancer Institute Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial neoplasms and the estimated in the general population is approximately 17%. Non-invasive and non-secreting pituitary adenomas are considered to be [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetracosactide
Adrenocorticotropic hormone is used as a medication and as diagnostic agent in the ACTH stimulation test. The form that is purified from pig pituitary glands is known as corticotropin is a medication and naturally occurring polypeptide tropic hormone produced and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. The form that is made synthetically is tetracosactide, also known as synacthen, tetracosactrin and cosyntropin. It consists of the first 24 (of a total of 39) amino acids of ACTH and retains full function of the parent peptide. Tetracosactide stimulates the release of corticosteroids such as cortisol from the adrenal glands, and is used for the ACTH stimulation test to assess adrenal gland function. Medical uses Both corticotropin and tetracosactide have been used for diagnostic purposes to determine adrenocortical insufficiency, particularly in Addison's disease, via the ACTH stimulation test. However, as of 2015 the US label for corticotropin does not include diagnostic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metyrapone
Metyrapone, sold under the brand name Metopirone, is a medication which is used in the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency and occasionally in the treatment of Cushing's syndrome (hypercortisolism). Medical uses Metyrapone can be used in the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency. Metyrapone 30 mg/kg, maximum dose 3,000 mg, is administered at midnight usually with a snack. The plasma cortisol and 11-deoxycortisol are measured the next morning between 8:00 and 9:00 am. A plasma cortisol less than 220 nmol/L indicates adequate inhibition of 11β-hydroxylase. In patients with intact Hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis, CRH and ACTH levels rise as a response to the falling cortisol levels. This results in an increase of the steroid precursors in the pathway. Therefore, if 11-deoxycortisol levels do not rise and remain less than 7 µg/dL (202 nmol/L) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) rises, then it is highly suggestive of adrenal insufficiency. If neither 11- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexamethasone Suppression Test
The dexamethasone suppression test (DST) is used to assess adrenal gland function by measuring how cortisol levels change in response to oral doses or an injection of dexamethasone. It is typically used to diagnose Cushing's syndrome. The DST was historically used for diagnosing depression, but by 1988 it was considered to be "at best, severely limited in its clinical ability" for this purpose. Physiology Dexamethasone is an exogenous steroid that provides negative feedback to the pituitary gland to suppress the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Specifically, dexamethasone binds to glucocorticoid receptors in the anterior pituitary gland, which lie outside the blood–brain barrier, resulting in regulatory modulation. Test Procedures There are several types of DST procedures: # Overnight DST - An oral dose of dexamethasone is given between 11pm and midnight, and the cortisol level is measured at 8 - 9am the next morning # Two-day DST - This involves giving an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACTH Stimulation Test
The ACTH test (also called the cosyntropin, tetracosactide, or Synacthen test) is a medical test usually requested and interpreted by endocrinologists to assess the functioning of the adrenal glands' stress response by measuring the adrenal response to adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; corticotropin) or another corticotropic agent such as tetracosactide (cosyntropin, tetracosactrin; Synacthen) or alsactide (Synchrodyn). ACTH is a hormone produced in the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates the adrenal glands to release cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S), and aldosterone. During the test, a small amount of synthetic ACTH is injected, and the amount of cortisol (and sometimes aldosterone) that the adrenals produce in response is measured. This test may cause mild side effects in some individuals. This test is used to diagnose or exclude primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency, Addison's disease, and related conditions. In addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasopressin Analogue
Vasopressin analogues are chemicals similar in function but not necessarily similar in structure to vasopressin Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then ... (ADH), such as desmopressin. Desmopressin is administered as an oral spray to treat diseases where ADH is either not being produced in sufficient amounts, or vasopressin's receptors are not being stimulated by vasopressin. An example of desmopressin's use is for childhood bed-wetting, where it is believed that children's circadian rhythms are not synchronized with normal light-dark cycles, and consequentially the ADH surge normal children experience at night is not experienced in these children. Taking a desmopressin dose 30–45 minutes before sleeping results in concentrated urine production, and the urination reflex e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
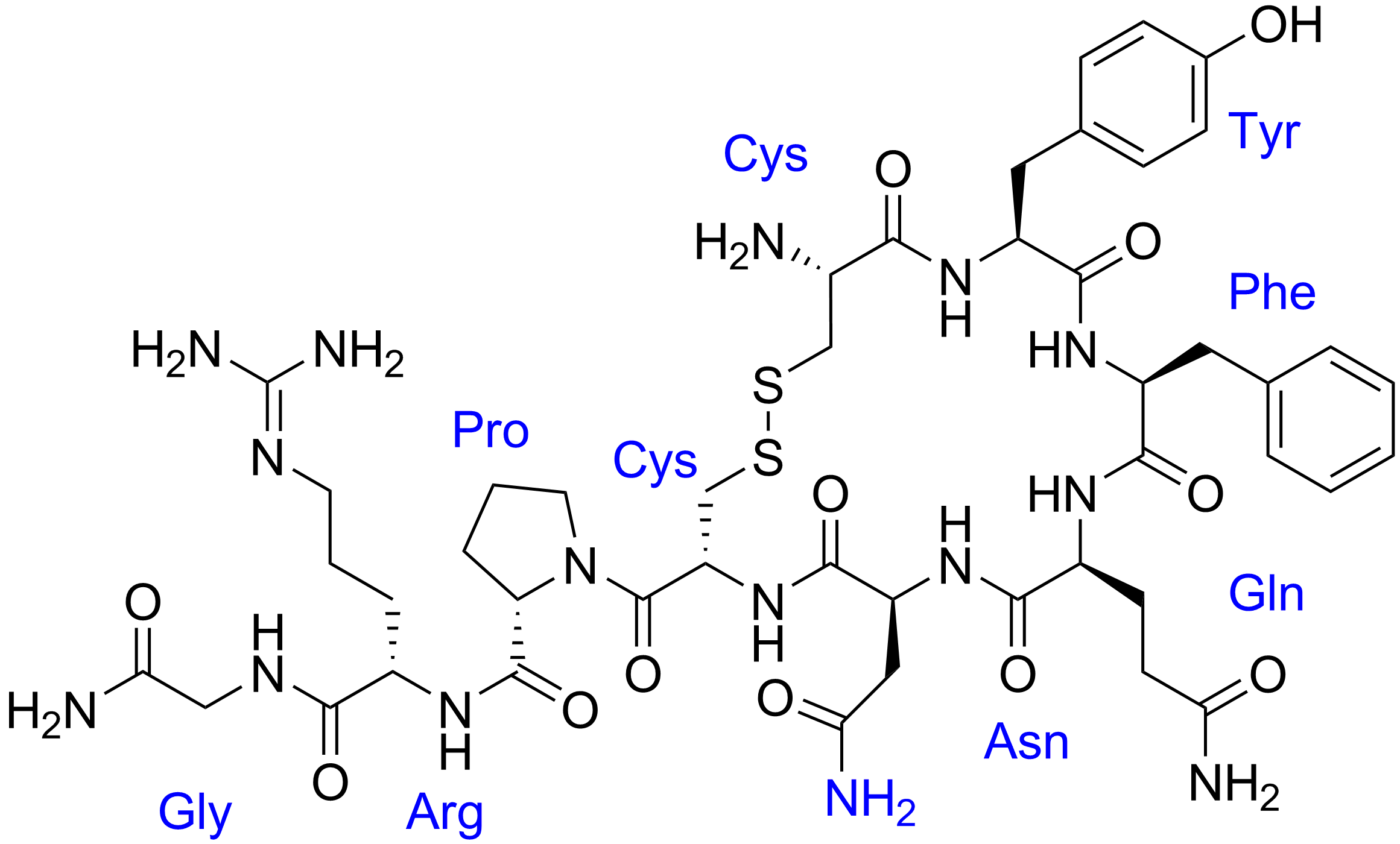
Vasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon terminating in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity ( hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure. A third function is possible. Some AVP may be released directly into the brain from the hypothalamus, and may play an important role in social behavior, sexual motivation and pair bonding, and maternal responses to stress. Vasopressin induces differentiation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |