ACTH Stimulation Test on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ACTH test (also called the cosyntropin, tetracosactide, or Synacthen test) is a
 Measuring a morning, fasting ACTH level helps assess for the etiology of adrenal insufficiency.
;Interpretation for primary adrenal insufficiency and Addison's disease
ACTH will be high – usually well above upper limits of reference range.
;Interpretation for secondary adrenal insufficiency
ACTH will be low – usually below 35, but most people with secondary fall within the range limit. This is inappropriately normal for the low cortisol level.
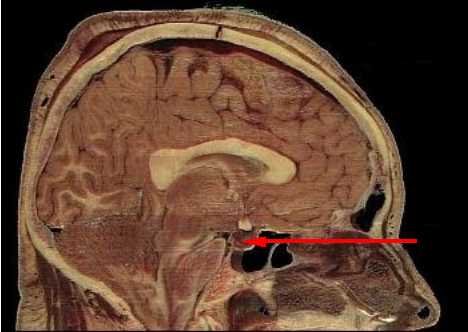
In some cases, the actual cause of low ACTH is from low CRH in the hypothalamus. It is possible to have separate ACTH and CRH impairment such as can happen in a head injury.
Measuring a morning, fasting ACTH level helps assess for the etiology of adrenal insufficiency.
;Interpretation for primary adrenal insufficiency and Addison's disease
ACTH will be high – usually well above upper limits of reference range.
;Interpretation for secondary adrenal insufficiency
ACTH will be low – usually below 35, but most people with secondary fall within the range limit. This is inappropriately normal for the low cortisol level.
In some cases, the actual cause of low ACTH is from low CRH in the hypothalamus. It is possible to have separate ACTH and CRH impairment such as can happen in a head injury.
ACTH stimulation test
– Procedures/Diagnostic tests Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center
medical test
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic ...
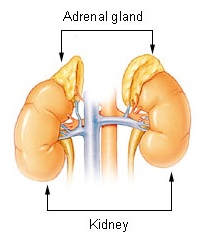
usually requested and interpreted by endocrinologists to assess the functioning of the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer adrenal corte ...
s' stress response by measuring the adrenal response to adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; corticotropin) or another corticotropic agent such as tetracosactide (cosyntropin, tetracosactrin; Synacthen) or alsactide (Synchrodyn). ACTH is a hormone produced in the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates the adrenal glands to release cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S), and aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
.
During the test, a small amount of synthetic ACTH is injected, and the amount of cortisol (and sometimes aldosterone) that the adrenals produce in response is measured. This test may cause mild side effects in some individuals.
This test is used to diagnose or exclude primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency, Addison's disease, and related conditions. In addition to quantifying adrenal insufficiency, the test can distinguish whether the cause is adrenal (low cortisol and aldosterone production) or pituitary (low ACTH production). The insulin tolerance test is recognized as the gold standard assay of adrenal insufficiency, but due to the cumbersome requirement for a two-hour test and the risks of seizures or myocardial infarction, the ACTH stimulation test is commonly used as an easier, safer, though not as accurate, alternative. The test is extremely sensitive (97% at 95% specificity) to primary adrenal insufficiency, but less so to secondary adrenal insufficiency (57–61% at 95% specificity); while secondary adrenal insufficiency may thus be dismissed by some interpreters on the basis of the test, additional testing may be called for if the probability of secondary adrenal insufficiency is particularly high.
Adrenal insufficiency is a potentially life-threatening condition. Treatment should be initiated as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed, or sooner if the patient presents in apparent adrenal crisis.
Versions of the test
This test can be given as a ''low-dose short test'', a ''conventional-dose short test'', or as a ''prolonged-stimulation test''. In the low-dose short test, 1 μg of an ACTH drug is injected into the patient. In the conventional-dose short test, 250 μg of drug are injected. Both of these short tests last for about an hour and provide the same information. Studies have shown the cortisol response of the adrenals is the same for the low-dose and conventional-dose tests. The prolonged-stimulation test, which is also called a ''long conventional-dose test'', can last up to 48 hours. This form of the test can differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary adrenal insufficiency. This form of the test is rarely performed because earlier testing of cortisol and ACTH levels in association with the short test may provide all the necessary information.Preparation
The test should not be given if on glucocorticoids or adrenal extract supplement, as these will affect test results. Stress and recently administered radioisotope scans can artificially increase levels and may invalidate test results. Spironolactone, contraceptives, licorice,estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
, androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
(including DHEA) and progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the ma ...
therapy may also affect both aldosterone and cortisol stimulation test results. To stimulate aldosterone, consumption of salt should be reduced to a minimum, and foods high in sodium avoided for 24 hours prior to testing. Women should ideally undergo testing during the first week of their menstrual cycle as aldosterone (and occasionally cortisol) may be falsely elevated in the luteal cycle secondary to progesterone inhibition, leading to a compensatory rise in aldosterone levels.
Administration
Traditionally, cortisol and ACTH levels (separate lavender top tube) are drawn at baseline (time = 0). Next, synthetic ACTH or another corticotropic agent is injected IM or IV, depending on the agent. Approximately 20 mL of heparinized venous blood is collected at 30 and 60 minutes after the synthetic ACTH injection to measure cortisol levels. ACTH samples are kept on ice and sent immediately to the laboratory, whereas cortisol does not need to be kept on ice.Potential side effects
Commonly reported reactions are nausea, anxious sweating, dizziness, itchy skin, redness and or swelling of injection site, palpitations (a fast or fluttering heart beat), and facial flushing (may also include arms and torso), but should disappear within a few hours. Rarely seen, but serious side effects include rash, fainting, headache, blurred vision, severe swelling, severe dizziness, trouble breathing, irregular heartbeat.Interpretation of results

Cosyntropin stimulation testing
In healthy individuals, the cortisol level should increase above 18–20 μg/dl within 60 minutes on a 250 mcg cosyntropin stimulation test. ;Interpretation for primary adrenal insufficiency, Addison's disease In Addison's disease, both the cortisol andaldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
levels are low, and the cortisol will not rise during the cosyntropin stimulation test
;Interpretation for secondary adrenal insufficiency
In secondary adrenal insufficiency, due to exogenous steroid administration suppressing pituitary production of ACTH or due to primary pituitary disorder causing insufficient ACTH production, the adrenal glands will atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
over time and cortisol production will fall and patients will fail stimulation testing. Early in the development of secondary adrenal insufficiency, the adrenals may not have atrophied and can still stimulate, resulting in a normal cosyntropin stimulation test.
If secondary adrenal insufficiency is diagnosed, the insulin tolerance test (ITT) or the CRH (corticotropin-releasing hormone
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) (also known as corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) or corticoliberin; corticotropin may also be spelled corticotrophin) is a peptide hormone involved in stress responses. It is a releasing hormone that b ...
) stimulation test can be used to distinguish between a hypothalamic (tertiary) and pituitary (secondary) cause but is rarely used in clinical practice.
ACTH plasma test plus cortisol stimulation
 Measuring a morning, fasting ACTH level helps assess for the etiology of adrenal insufficiency.
;Interpretation for primary adrenal insufficiency and Addison's disease
ACTH will be high – usually well above upper limits of reference range.
;Interpretation for secondary adrenal insufficiency
ACTH will be low – usually below 35, but most people with secondary fall within the range limit. This is inappropriately normal for the low cortisol level.
In some cases, the actual cause of low ACTH is from low CRH in the hypothalamus. It is possible to have separate ACTH and CRH impairment such as can happen in a head injury.
Measuring a morning, fasting ACTH level helps assess for the etiology of adrenal insufficiency.
;Interpretation for primary adrenal insufficiency and Addison's disease
ACTH will be high – usually well above upper limits of reference range.
;Interpretation for secondary adrenal insufficiency
ACTH will be low – usually below 35, but most people with secondary fall within the range limit. This is inappropriately normal for the low cortisol level.
In some cases, the actual cause of low ACTH is from low CRH in the hypothalamus. It is possible to have separate ACTH and CRH impairment such as can happen in a head injury.
Aldosterone stimulation
The ACTH stimulation test is occasionally used to test adrenal production of aldosterone at the same time as cortisol to also help in determining if primary (hyperreninemic) or secondary (hyporeninemic) hypoaldosteronism is present. Human ACTH has a slight stimulatory effect on aldosterone, but the amount of synthetic ACTH given in the stimulation is equivalent to more than a whole days production of natural ACTH, so the aldosterone response can be easily measured in blood serum. Same as cortisol, aldosterone should double from a respectable base value (around 20 ng/dl, must fast salt 24 hours and sit upright for blood draw) in a healthy individual. ;Interpretation for primary aldosterone deficiency The aldosterone response in the ACTH stimulation test is blunted or absent in patients with primary adrenal insufficiency including Addison's disease. The base value is usually in the mid-teens or less and rise to less than double the base value thus indicating primary hypoaldosteronism (sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
low, potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
and renin enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
will be high) and is an indicator of primary adrenal insufficiency or Addison's disease.
;Interpretation for secondary aldosterone deficiency
Aldosterone response of several factors from a low base value. This factoring indicates secondary hypoaldosteronism (sodium low, potassium and renin enzyme will be low). Usually doubling to quadrupling from a low base aldosterone value is what is seen in secondary adrenal insufficiency. Decoupling of aldosterone in the ACTH stimulation test is possible (i.e. 2 ng/dl stimming to 20). A result of doubling or more of aldosterone may help in tandem with a cortisol stimulation that doubled or more confirm a diagnosis of secondary adrenal insufficiency. In rare cases, an aldosterone stimulation which did not double, but with the presence of low potassium, low renin and low ACTH indicates atrophy of aldosterone production from the prolonged lack of renin.
Similar to the cortisol stimulation in ACTH deficiency, the test interpreter may lack knowledge of how to properly interpret for secondary hypoaldosteronism and think a result of aldosterone doubling or more from a low base value is good.
Future perspectives
Recent data showed that Synacthen test results can be used to predict future recovery of HPA axis function in patients with reversible causes of Adrenal Insufficiency.Other hormones and chemicals that will rise in the ACTH stimulation test
*Progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the ma ...
– precursor to cortisol and aldosterone
* 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone – a progestogen steroid hormone related to progesterone
* Luteinizing hormone – a pituitary hormone that stimulates sex hormone production
* DHEA and DHEA-S – androgen hormones produced in the adrenal glands
Simple diagnostic chart
Veterinary medicine
The test is also used to diagnose hypoadrenocorticism in dogs and sometimes cats.See also
* Dexamethasone suppression test * Insulin tolerance test, another test used to identify sub-types of adrenal insufficiency * Metyrapone, a drug used in the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency * Triple bolus test * Renin, enzyme that converts angiotensinogen 1 to angiotensin 2, a precursor to aldosterone * Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system * HPA axis, explains the connections of the hypothalamus, pituitary and adrenal glands * Hypopituitarism * Pituitary adenoma * Adrenal adenoma * CorticorelinReferences
External links
ACTH stimulation test
– Procedures/Diagnostic tests Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center
National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in 1887 and is part of the United States Department of Health and Human Service ...
.
{{Endocrine system procedures
Blood tests
Endocrine procedures
Hormones of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis
Dynamic endocrine function tests