|
Corannulene
Corannulene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C20 H10. The molecule consists of a cyclopentane ring fused with 5 benzene rings, so another name for it is irculene. It is of scientific interest because it is a geodesic polyarene and can be considered a fragment of buckminsterfullerene. Due to this connection and also its bowl shape, corannulene is also known as a buckybowl. Buckybowls are fragments of buckyballs. Corannulene exhibits a bowl-to-bowl inversion with an inversion barrier of 10.2 kcal/ mol (42.7 kJ/mol) at −64 °C. Synthesis Several synthetic routes exist to corannulene. Flash vacuum pyrolysis techniques generally have lower chemical yields than solution-chemistry syntheses, but offer routes to more derivatives. Corannulene was first isolated in 1966 by multistep organic synthesis. In 1971, the synthesis and properties of corannulane were reported. A flash vacuum pyrolysis method followed in 1991. One synthesis based on soluti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulene
A circulene is a macrocyclic arene in which a central polygon is surrounded and fused by benzenoids. Nomenclature within this class of molecules is based on the number of benzene rings surrounding the core, which is equivalent to the size of the central polygon. Examples which have been synthesized include irculene ( corannulene), irculene ( coronene), irculene, and 2irculene ( kekulene) These compounds belong to a larger class of geodesic polyarenes. Whereas irculene is bowl-shaped and irculene is planar, irculene has a unique saddle-shaped structure (compare to cones and partial cones in calixarenes). The helicenes are a conceptually related class of structures in which the array of benzene rings form an open helix rather than a closed ring. Quadrannulene ( irculene) The simple irculene compound itself has not been synthesized, but a derivative, tetrabenzo irculene, also called quadrannulene, has. irculenes The isolation of the irculene derivative 2,5,6,9,10,13, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon
A Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is any member of a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple fused aromatic rings. Most are produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter— by engine exhaust fumes, tobacco, incinerators, in roasted meats and cereals, or when biomass burns at lower temperatures as in forest fires. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings, and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are also found in fossil fuel deposits such as coal and in petroleum. Exposure to PAHs can lead to different types of cancer, to fetal development complications, and to cardiovascular issues. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are discussed as possible starting materials for abiotic syntheses of materials required by the earliest forms of life. Nomenclature and structure The terms polyaromatic hydrocarbon, or polynuclear aromatic hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
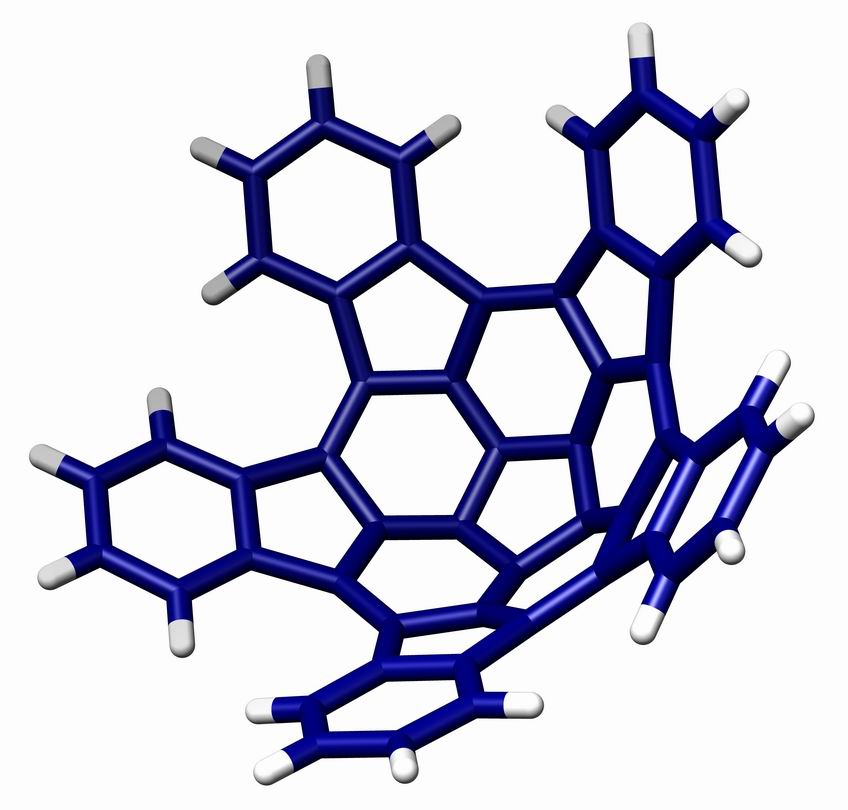
Geodesic Polyarene
A geodesic polyarene in organic chemistry is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with curved wikt:convex, convex or wiktionary:Concave, concave surfaces. Examples include fullerenes, Carbon nanotube, nanotubes, corannulenes, helicenes and sumanene. The molecular orbitals of the carbon atoms in these systems are to some extent pyramidalization, pyramidalized resulting a different pi electron density on either side of the molecule with consequences for reactivity. One member of this group of organic compounds, ''pentaindenocorannulene'' (depicted below), can be considered a large fullerene fragment. The experimentally obtained curvature and degree of pyramidalizion (12.6° for the carbons of the pentagon at the center ) are both actually larger than that of fullerene but according to its discoverers, the compound is relatively easy to synthesize starting from corannulene and a way is opened to produce larger such fragments by stitching. The crystal structure of pentaindenocorannul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoranthene
Fluoranthene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH). The molecule can be viewed as the fusion of naphthalene and benzene unit connected by a five-membered ring. The chemical formula is . Although samples are often pale yellow, the compound is colorless. It is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents.Karl Griesbaum, Arno Behr, Dieter Biedenkapp, Heinz-Werner Voges, Dorothea Garbe, Christian Paetz, Gerd Collin, Dieter Mayer, Hartmut Höke “Hydrocarbons” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. It is a member of the class of PAHs known as non-alternant PAHs because it has rings other than those with six carbon atoms. It is a structural isomer of the alternant PAH pyrene. It is not as thermodynamically stable as pyrene. Its name is derived from its fluorescence under UV light. Occurrence Traces of fluoranthene is found in many combustion products, along with other PAHs. It results from incomplete combustion. Fluoranthene was originally isola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions . Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive base (chemistry), base and alkali that decomposes lipids and proteins at ambient temperatures and at high concentrations may cause severe chemical burns. It is highly soluble in water, and readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide from the air. It forms a series of hydrates . The monohydrate crystallizes from water solutions between 12.3 and 61.8 °C. The commercially available "sodium hydroxide" is often this monohydrate, and published data may refer to it instead of the anhydrous compound. As one of the simplest hydroxides, sodium hydroxide is frequently used alongside neutral water and acidic hydrochloric acid to demonstrate the pH scale to chemistry students. Sodium hydroxide is used in many industries: in the making of wood pulp and paper, tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry
Organic may refer to: * Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity * Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ Chemistry * Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product of decay, or is composed of organic compounds * Organic compound, a compound that contains carbon ** Organic chemistry, chemistry involving organic compounds Farming, certification and products * Organic farming, agriculture conducted according to certain standards, especially the use of stated methods of fertilization and pest control * Organic certification, accreditation process for producers of organically-farmed products * Organic horticulture, the science and art of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, or ornamental plants by following the essential principles of organic agriculture * Organic products, "organics": ** Organic food, food produced from organic farming methods and often certified organic according to organic farming stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrocene
Ferrocene is an organometallic chemistry, organometallic compound with the formula . The molecule is a Cyclopentadienyl complex, complex consisting of two Cyclopentadienyl anion, cyclopentadienyl rings sandwiching a central iron atom. It is an orange solid with a camphor-like odor that Sublimation (phase transition), sublimes above room temperature, and is soluble in most organic solvents. It is remarkable for its stability: it is unaffected by air, water, strong bases, and can be heated to 400 °C without decomposition. In oxidizing conditions it can reversibly react with strong acids to form the ferrocenium cation . Ferrocene and the ferrocenium cation are sometimes abbreviated as Fc and respectively. The first reported synthesis of ferrocene was in 1951. Its unusual stability puzzled chemists, and required the development of new theory to explain its formation and bonding. The discovery of ferrocene and its many Structural analog, analogues, known as metallocenes, sparke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
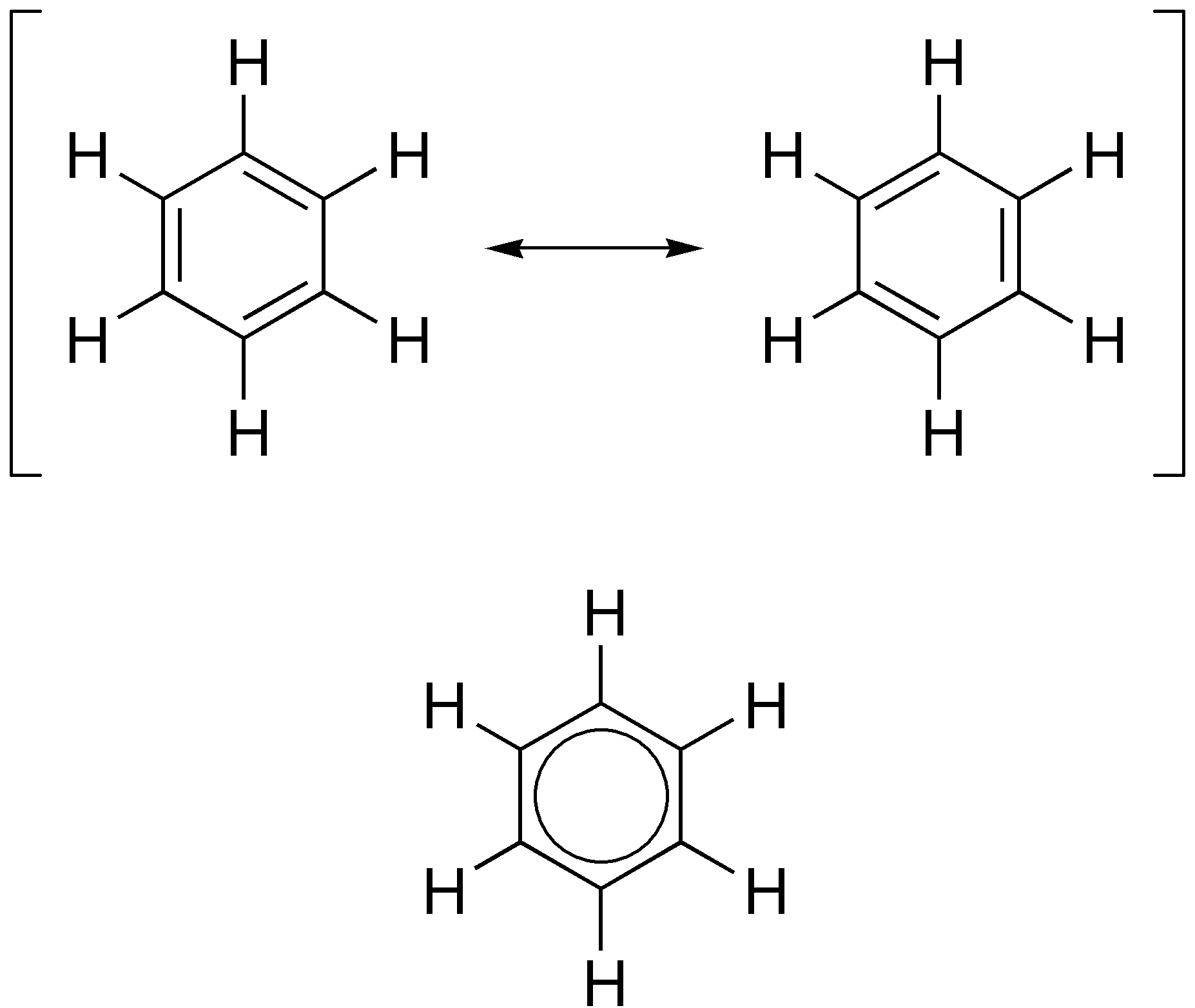
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds. Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double- bonded to one another. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Kekulé (see History section below). Each bond may be seen as a hybrid of a single bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
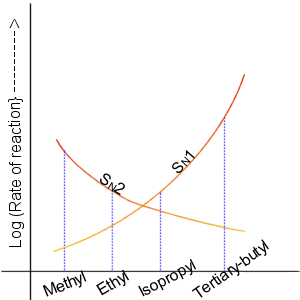
Nucleophilic Displacement
In chemistry, a nucleophilic substitution (SN) is a class of chemical reactions in which an electron-rich chemical species (known as a nucleophile) replaces a functional group within another electron-deficient molecule (known as the electrophile). The molecule that contains the electrophile and the leaving functional group is called the substrate. The most general form of the reaction may be given as the following: :\text\mathbf + \ce + \text\mathbf The electron pair (:) from the nucleophile (Nuc) attacks the substrate () and bonds with it. Simultaneously, the leaving group (LG) departs with an electron pair. The principal product in this case is . The nucleophile may be electrically neutral or negatively charged, whereas the substrate is typically neutral or positively charged. An example of nucleophilic substitution is the hydrolysis of an alkyl bromide, R-Br under basic conditions, where the attacking nucleophile is hydroxyl () and the leaving group is bromide (). :OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopentadienyl Complex
A cyclopentadienyl complex is a coordination complex of a metal and cyclopentadienyl groups (, abbreviated as Cp−). Cyclopentadienyl ligands almost invariably bind to metals as a pentahapto (''η''5-) bonding mode. The metal–cyclopentadienyl interaction is typically drawn as a single line from the metal center to the center of the Cp ring.Elschenbroich, C. "Organometallics" (2006) Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. Examples ''Bis''cyclopentadienyl complexes are called metallocenes. A famous example of this type of complex is ferrocene (FeCp2), which has many analogues for other metals, such as chromocene (CrCp2), cobaltocene (CoCp2), and nickelocene (NiCp2). When the Cp rings are mutually parallel the compound is known as a sandwich complex. This area of organometallic chemistry was first developed in the 1950s. Bent metallocenes are represented by compounds of the type Cp2Lx Some are catalysts for ethylene polymerization. Metallocenes are often thermally stable, and find use as ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |