|
Cophen Campaign
The Cophen campaign was conducted by Alexander the Great in the Kabul (Sanskrit: "Kubha") Valley between May 327 BCDodge 1890, p. 509 and March 326 BC.Dodge 1890, p. 540 It was conducted against the '' Aspasioi'', the ''Guraeans'', and the ''Assakenoi'' tribes in the Kunar valley of Afghanistan, and Panjkora ( Dir) and Swat valleys in what is now Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. The goal of the campaign was to secure the Macedonian line of communications so that the Macedonian army could proceed into India proper. Background It had been Alexander's purpose to conquer the whole of the Persian Empire which extended as far as Gandara.Dodge 1890, p. 510 A previous king of the Persian Achaemenid Empire, Darius the Great, had sent one of his generals, Skylax, to sail down the Indus. Following this expedition, Darius was able to conquer the surrounding Indian territory and receive tribute of 350 Euboic talents per annum.Smith 1914, p. 37 Relatively little is known about t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Campaign Of Alexander The Great
The Indian campaign of Alexander the Great began in 327BC and lasted until 325BC. After conquering the Achaemenid Persian Empire, the Macedonian army undertook an expedition into the Indus Valley of Northwestern Indian subcontinent. Within two years, Alexander expanded the Macedonian Empire, a kingdom closely linked to the broader Greek world, to include Gandhara and the Indus Valley of Punjab and Sindh (now in India and Pakistan), surpassing the earlier frontiers established by the Persian Achaemenid conquest. Following Macedon's absorption of Gandhara (a former Persian satrapy), including the city of Taxila, Alexander and his troops advanced into Punjab, where they were confronted by Porus, the regional Indian king. In 326 BC, Alexander defeated Porus and the Pauravas during the Battle of the Hydaspes,Fuller, p. 198 but that engagement was possibly the Macedonians' most costly battle. Alexander's continued eastward march was leading his army into a confrontation wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pella
Pella () is an ancient city located in Central Macedonia, Greece. It served as the capital of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. Currently, it is located 1 km outside the modern town of Pella (town), Pella. Pella was probably founded at the beginning of the 4th century BC by Archelaus I of Macedon, Archelaus I as the new capital of Macedon, supplanting Aegae (Macedonia), Aigai. The city was the birthplace of Philip II of Macedon, Philip II in 382 BC, and of Alexander the Great, his son, in 356 BC. Pella quickly became the largest and richest city in Macedonia and flourished particularly under the rule of Cassander and Antigonus II Gonatas, Antigonus II. In 168 BC the city was sacked by the Roman Republic, Romans during the Third Macedonian War and entered a long period of decline, its importance eclipsed by that of the nearby Thessaloniki, Thessalonica. Etymology The name is probably derived from the word ''pella'', (), "ston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile Delta, Nile River delta. Founded in 331 BC by Alexander the Great, Alexandria grew rapidly and became a major centre of Hellenic civilisation, eventually replacing Memphis, Egypt, Memphis, in present-day Greater Cairo, as Egypt's capital. Called the "Bride of the Mediterranean" and "Pearl of the Mediterranean Coast" internationally, Alexandria is a popular tourist destination and an important industrial centre due to its natural gas and petroleum, oil pipeline transport, pipelines from Suez. The city extends about along the northern coast of Egypt and is the largest city on the Mediterranean, the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second-largest in Egypt (after Cairo), the List of largest cities in the Arab world, fourth- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaza City
Gaza City, also called Gaza, is a city in the Gaza Strip, Palestine, and the capital of the Gaza Governorate. Located on the Mediterranean coast, southwest of Jerusalem, it was home to Port of Gaza, Palestine's only port. With a population of 590,481 people as of 2017, Gaza City was the most populous city in Palestine until the Gaza war caused most of the population to be displaced. Inhabited since at least the 15th century BC, Gaza City has been dominated by different peoples and empires throughout its history. The Philistines made it a part of their Philistia, pentapolis after the ancient Egyptians had ruled it for nearly 350 years. Under the Roman Empire, Gaza City experienced relative peace and its Port of Gaza, Mediterranean port flourished. In 635 AD, it became the first city in the Palestine (region), Palestine region to be conquered by the Rashidun army and quickly developed into a centre of Fiqh, Islamic law. However, by the time the Crusader states were established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Gaza (332 BCE)
The siege of Gaza, as part of the Wars of Alexander the Great, took place in October of 332 BC. Resulting in a victory for Macedon, it ended the 31st Dynasty of Egypt, which functioned as a satrapy under the Achaemenid Persian Empire. Alexander succeeded in breaching the walls of Gaza by utilizing the engines that he had employed earlier that year, during the siege of Tyre brought by Hephaestion. Following three unsuccessful assaults, the Macedonian army was able to storm and take the Gazan stronghold. Batis, the military commander of Gaza's fortress, expected to hold the city as well as the rest of Egypt in complete subjection until the raising of another army by Persian king Darius III; confronting Alexander at Gaza was crucial to denying the Macedonians a route into the Egyptian mainland. The fortress was located on an eminence, on the edge of a desert from which the surrounding area could be easily controlled, including the main road from Assyria to Egypt. The city, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyre, Lebanon
Tyre (; ; ; ; ) is a city in Lebanon, and one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. It was one of the earliest Phoenician metropolises and the legendary birthplace of Europa (consort of Zeus), Europa, her brothers Cadmus and Phoenix (son of Agenor), Phoenix, and Carthage's founder Dido (Elissa). The city has many ancient sites, including the Tyre Hippodrome, and was added as a whole to the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 1984. The historian Ernest Renan noted that "One can call Tyre a city of ruins, built out of ruins". Tyre is the fifth-largest city in Lebanon after Beirut, Tripoli, Lebanon, Tripoli, Sidon, and Baalbek. It is the capital of the Tyre District in the South Governorate. There were approximately 200,000 inhabitants in the Tyre urban area in 2016, including many refugees, as the city hosts three of the twelve Palestinian refugee camps in Lebanon: Burj el-Shamali, Burj El Shimali, El-Buss refugee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Tyre (332 BC)
The siege of Tyre was orchestrated by Alexander the Great in 332 BC during his campaigns against the Persians. At first, the Macedonian army was unable to capture the city of Tyre, which was a strategic coastal base on the Mediterranean Sea, through conventional means because it was on an island that was 1 kilometer off the coast of Modern day Lebanon (at the time Phoenicia) and had walls right up to the sea. Alexander responded to this problem by first blockading and besieging Tyre for seven months, and then by building a causeway and placing siege towers with catapults built on top at the end after his soldiers discovered that they could not extend it any further due to a steep drop under the surface of the water. This allowed him to breach the fortifications. It is said that Alexander was so enraged at the Tyrians' defence of their city and the loss of his men that he destroyed half the city. According to Arrian, 8,000 Tyrian civilians were massacred after the city fell. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Issus (Cilicia)
Issus (Latin; Phoenician: ''Sissu'') or Issos (, ''Issós'', or , ''Issoí'') was an ancient settlement on the strategic coastal plain straddling the small Pinarus river (a fast melt-water stream several metres wide) below the navigationally difficult inland mountains towering above to the east in the Turkish Province of Hatay, near the border with Syria. It can be identified with Kinet Höyük in the village of Yeşilköy near Dörtyol in Turkey's Hatay Province. Excavations on the mound occurred between 1992 and 2012 by Bilkent University. It is most notable for being the place of no fewer than three decisive ancient or medieval battles each called in their own era the Battle of Issus: # The Battle of Issus (333 BC) or the First Battle of Issus, in which Alexander the Great of Macedonia defeated Darius III of Persia # Battle of Issus (194) or the Second Battle of Issus, in which P. Cornelius Anullinus defeated Septimius Severus's rival Pescennius Niger # Battle of Issus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
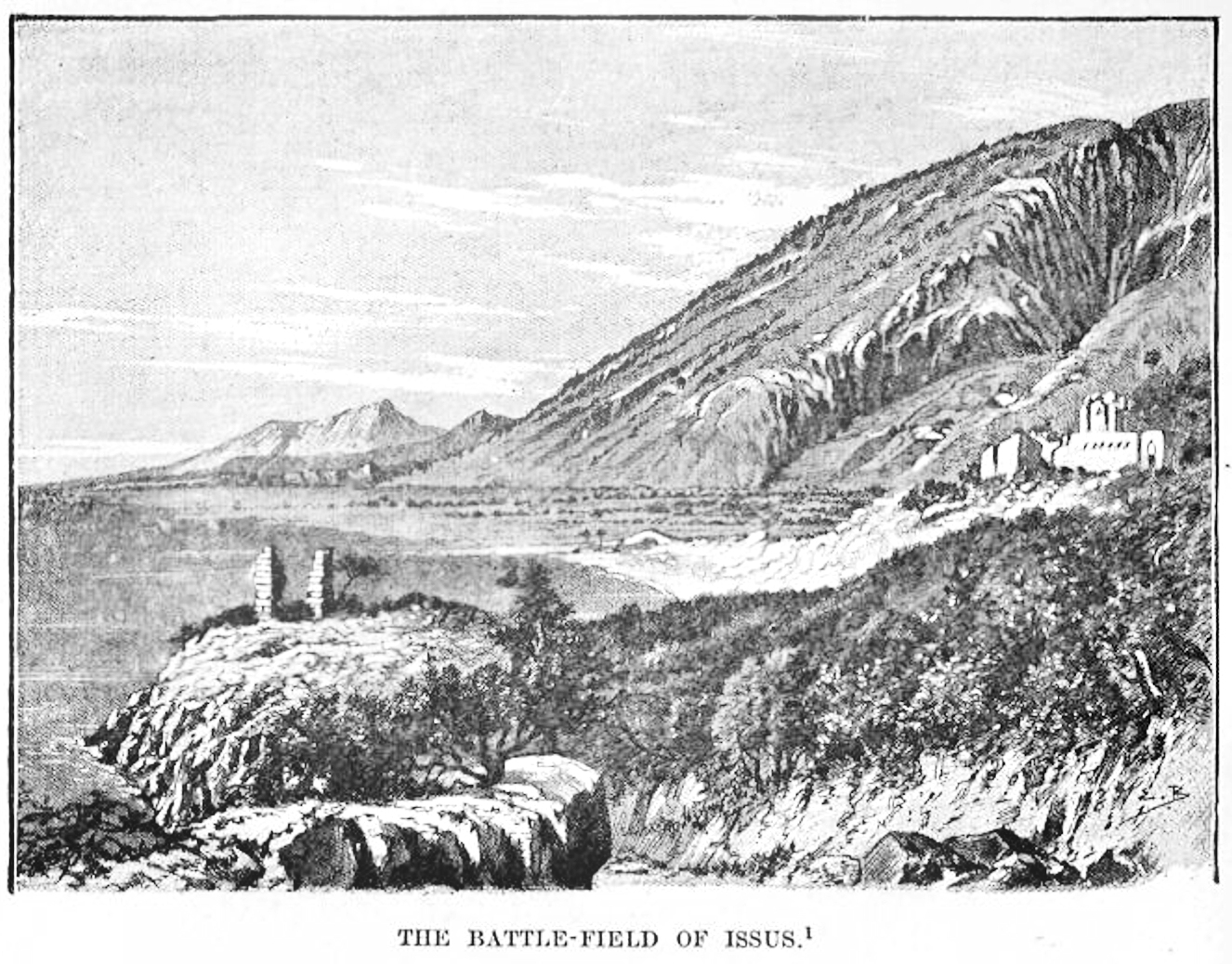
Battle Of Issus
The Battle of Issus (also Issos) occurred in southern Anatolia, on 5 November 333 BC between the League of Corinth, Hellenic League led by Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Empire, led by Darius III of Persia, Darius III. It was the second great battle of Alexander's conquest of Asia, and the first encounter between Darius III and Alexander the Great. The battle resulted in the Macedonian troops defeating the Persian forces. After the Hellenic League soundly defeated the Persian satraps of Asia Minor (led by Greek mercenary Memnon of Rhodes) at the Battle of the Granicus, Darius took personal command of his army. He gathered reinforcements and proceeded to lead his men in a surprise march behind the Hellenic advance, in order to cut off their line of supply. Alexander was forced to countermarch, and the stage was set for the battle near the mouth of the Pinarus River and the city of Issus (town), Issus. Location The battle took place south of the ancient city Issus (town) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miletus
Miletus (Ancient Greek: Μίλητος, Mílētos) was an influential ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in present day Turkey. Renowned in antiquity for its wealth, maritime power, and extensive network of colonies, Miletus was a major center of trade, culture, and innovation from the Bronze Age through the Roman period. The city played a foundational role in the development of early Greek philosophy and science, serving as the home of the Milesian school with thinkers such as Thales, Anaximander, and Anaximenes of Miletus, Anaximenes. Miletus's prosperity was closely linked to its strategic coastal location and the productivity of its surrounding rural hinterland, which supported thriving agriculture and facilitated wide-ranging commercial activity. The city established dozens of colonies around the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Black Sea, significantly shaping the Ancient Greece, Greek world’s expansion. Archae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Halicarnassus
The siege of Halicarnassus was fought between Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Persian Empire in 334 BC. Alexander, who had no navy, was constantly being threatened by the Persian navy. It continuously attempted to provoke an engagement with Alexander, who would not oblige them. Eventually, the Persian fleet sailed to Halicarnassus, in order to establish a new defense. Ada of Caria, the former queen of Halicarnassus, had been driven from her throne by her younger brother Pixodarus of Caria. When Pixodarus died, Persian King Darius had appointed Orontobates satrap of Caria, which included Halicarnassus in its jurisdiction. On the arrival of Alexander in 334 BC, Ada, who was in possession of the fortress of Alinda, surrendered the fortress to him. Orontobates and Memnon of Rhodes entrenched themselves in Halicarnassus. Alexander had sent spies to meet with dissidents inside the city, who had promised to open the gates and allow Alexander to enter. When his spies arrived, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Miletus
The siege of Miletus was Alexander the Great's first siege and naval encounter with the Achaemenid Empire. This siege was directed against Miletus, a city in southern Ionia, which is now located in the Aydın province of modern-day Turkey. During the battle, Parmenion's son Philotas would be key in preventing the Persian Navy from finding safe anchorage. It was captured by Parmenion's son, Nicanor in 334 BC. References External links Discussion on Livius.org Miletus Miletus Miletus (Ancient Greek: Μίλητος, Mílētos) was an influential ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in present day Turkey. Renowned in antiquity for its wealth, maritime power, and ex ... 334 BC Miletus {{Mil-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |