|
Cooper Bluffs
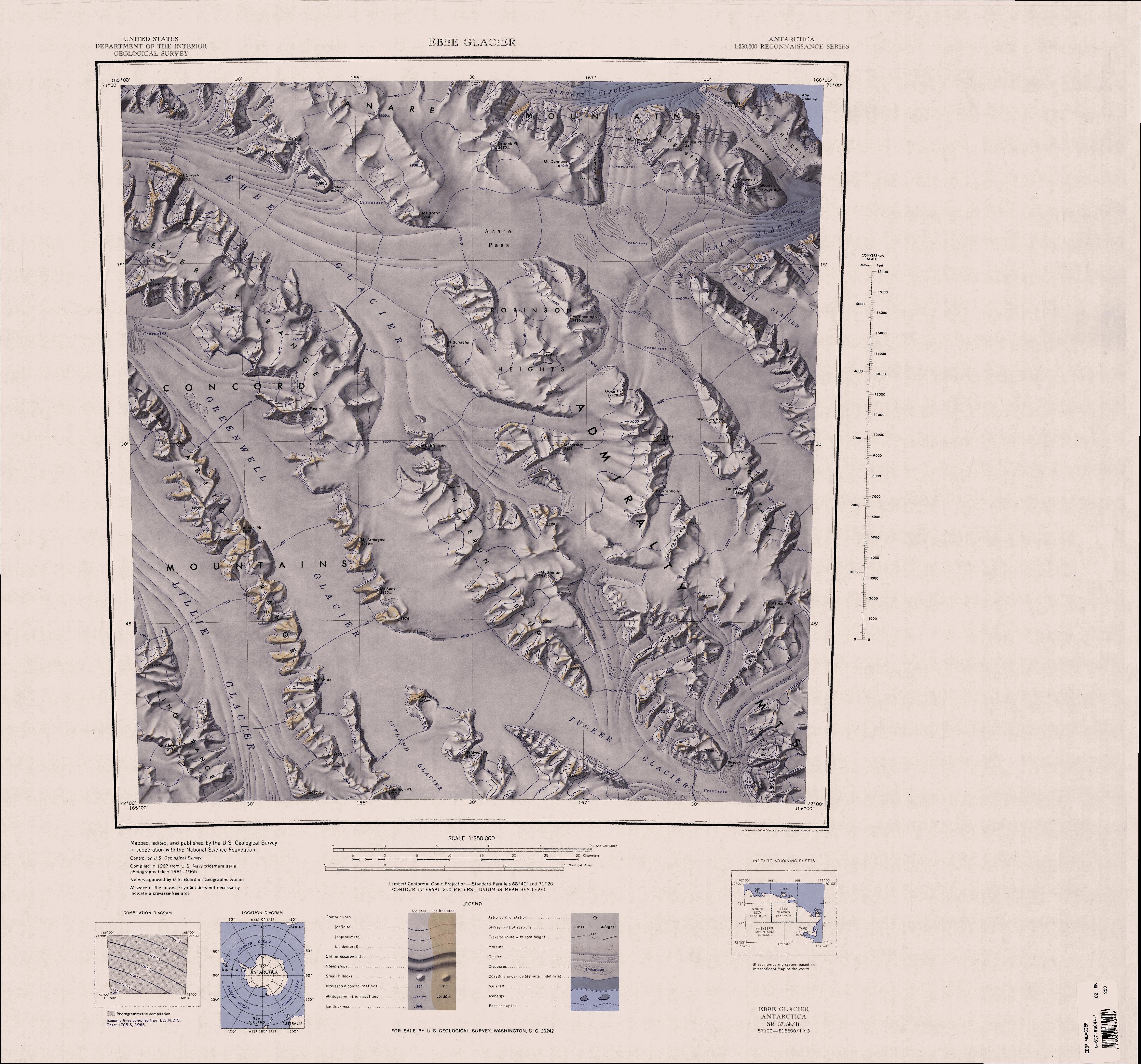
Zykov Glacier () is a valley glacier about long in the Anare Mountains of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It flows northwest and reaches the coast between Cape Williams and Cooper Bluffs. It was photographed by the Soviet Antarctic Expedition (SovAE) in 1958 and named for student navigator Ye. Zykov, who died in Antarctica, Feb. 3, 1957. Geology The underlying rock includes micaceous phyllite and micaceous schist; it was estimated by radioisotope dating ( potassium–argon) in 1964 to be 410 or 420 million years old. A separate study of metamorphic rocks recovered from near the glacier (1959–62) found evidence of thermal crystallisation.Scientific and Technical Aerospace Reports' 6 (5): 651 Location The Zykov Glacier forms in the Anare Mountains to the north of Mount Hemphill and west of McMahon Glacier. It flows northeast past the Cooper Spur and Cooper Bluffs to the east, and the Buell Peninsula to the west, to enter the Pacific Ocean to the east of Cape Williams. Feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier Morphology
Glacier morphology, or the form a glacier takes, is influenced by temperature, precipitation, topography, and other factors. The goal of glacial morphology is to gain a better understanding of glaciated landscapes and the way they are shaped. Types of glaciers can range from massive ice sheets, such as the Greenland ice sheet, to small cirque glaciers found perched on mountain tops. Glaciers can be grouped into two main categories: * Ice flow is constrained by the underlying bedrock topography * Ice flow is unrestricted by surrounding topography Unconstrained Glaciers Ice sheets and ice caps Ice sheets and ice caps cover the largest areas of land in comparison to other glaciers, and their ice is unconstrained by the underlying topography. They are the largest glacial ice formations and hold the vast majority of the world's fresh water. Ice sheets Ice sheets are the largest form of glacial formation. They are continent-sized ice masses that span areas over . They are dome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphic Rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and form 12% of the Earth's land surface. They are classified by their protolith, their chemical and mineral makeup, and their texture. They may be formed simply by being deeply buried beneath the Earth's surface, where they are subject to high temperatures and the great pressure of the rock layers above. They can also form from tectonic processes such as continental collisions, which cause horizontal pressure, friction, and dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on its hundredth anniversary, was "Earth Science in the Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buell Peninsula
The Buell Peninsula () is an ice-covered peninsula terminating in Cape Williams, located between the lower ends of Lillie Glacier, George Glacier and Zykov Glacier, at the northwest end of the Anare Mountains in Antarctica. The peninsula is long and at its greatest width. Exploration and naming The Buell Peninsula was photographed from United States Navy aircraft during Operation Highjump, 1946–47, and again in 1960–62. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) in 1962–63, and named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Lieutenant (later Lieutenant Commander) Kenneth R. Buell, a U.S. Navy navigator on aircraft with Squadron VX-6 in Antarctica in 1965–66 and 1966–67. Location The Buell Peninsula extends northward into the Pacific Ocean from the Anare Mountains between Zykov Glacier to the east, George Glacier to the southwest and the Lillie Glacier Tongue to the west. Features include Cape Williams in the north, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMahon Glacier
McMahon Glacier () is a glacier about long in the Anare Mountains of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It drains north between the Buskirk Bluffs and Gregory Bluffs into Nielsen Fjord. Name The McMahon Glacier was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia (ANCA) for F.P. McMahon, Logistics Officer with the Australian Antarctic Division, who led a number of expeditions to Macquarie Island and was second-in-charge of several expeditions to Antarctica. Location The McMahon Glacier forms in the Anare Mountains to the west of Tiger Peak and flows north past Buskirk Bluffs to the west and Gregory Bluffs to the east to enter the Nielsen Fjord, which leads to the Pacific Ocean. Cape North is at the west of the fjord's mouth, and the mouth of the Kirkby Glacier is at the east. Features Buskirk Bluffs . A sheer rock bluff on the west side of McMahon Glacier. Named by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expedition (ANARE) for Maj. H. Buskirk, United States Air Force, offic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Hemphill
The Anare Mountains () are a large group of mainly snow-covered peaks and ridges along the northern coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The group is bounded on the north and east by the Pacific Ocean, on the west by Lillie Glacier, and on the south by Ebbe Glacier and Dennistoun Glacier. They are north of the Concord Mountains and east of the Bowers Mountains. Exploration and naming Mountains in this area were first sighted by Captain James Clark Ross in 1841. They were photographed during United States Navy Operation Highjump (1946–1947) and were surveyed by United States Geological Survey (USGS) helicopter teams, 1962–63. The Anare Mountains were named by the northern party of the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1963–64, for the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE), 1962, under Phillip Law, which performed survey work along the coast. Location In the northwest the Anare Mountains extend along the Pacific coast to the east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C70192s1 Yule Bay
C7, C07 or C-7 may refer to: Vehicles (including military) * C-7 Caribou, a military transport aircraft * AEG C.VII, a World War I German armed reconnaissance aircraft * AGO C.VII, a World War I German reconnaissance aircraft * Albatros C.VII, a World War I German military reconnaissance aircraft * C-7, a United States Navy C class blimp and the first airship inflated with helium * Chevrolet Corvette (C7), the seventh generation of a sports car made by General Motors * Fokker C.VII, a 1928 Dutch reconnaissance seaplane * HMS ''C7'', a British Royal Navy C-class submarine * Sauber C7, a 1983 Group C prototype race car * USS ''Cincinnati'' (C-7), a United States Navy protected cruiser Science * Caldwell 7 (NGC 2403), a spiral galaxy in Camelopardalis Technology * Nokia C7-00, a touch screen mobile from Nokia * VIA C7, an IA-32 central processing unit by VIA Technologies * C7, an incandescent light bulb of the size typically used in nightlights and Christmas lighting usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
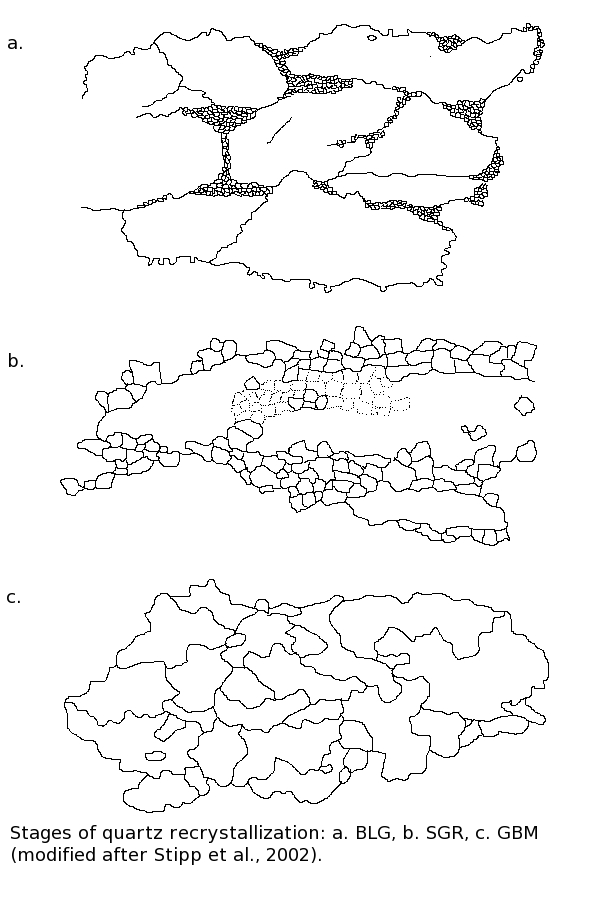
Dynamic Quartz Recrystallization
Quartz is the most abundant single mineral in the Earth's crust (although behind the feldspar group when taken collectively), and as such is present in a very large proportion of rocks both as primary crystals and as detrital grains in sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Dynamic recrystallization is a process of crystal regrowth under conditions of stress and elevated temperature, commonly applied in the fields of metallurgy and materials science. Dynamic quartz recrystallization happens in a relatively predictable way with relation to temperature, and given its abundance quartz recrystallization can be used to easily determine relative temperature profiles, for example in orogenic belts or near intrusions. Mechanisms of recrystallization Previous research has outlined several dislocation creep regimes present in experimental conditions. Two main mechanisms for altering grain boundaries have been defined. The first is the process by which quartz softens as temperature increases, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K–Ar Dating
Potassium–argon dating, abbreviated K–Ar dating, is a radiometric dating method used in geochronology and archaeology. It is based on the measurement of the product of the radioactive decay of an isotope of potassium (K) into argon (Ar). Potassium is a common element in many materials, such as feldspars, micas, clay minerals, tephra, and evaporites. In these materials, the decay product can escape the liquid (molten) rock but starts to accumulate when the rock solidifies (Recrystallization (geology), recrystallizes). The amount of argon sublimation that occurs is a function of the sample's purity, the composition of the mother material, and several other factors. These factors introduce error limits on the upper and lower bounds of dating so that the final determination of age is reliant on the environmental factors during formation, melting, and exposure to decreased pressure or open air. Time since recrystallization is calculated by measuring the ratio of the amount of accum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Antarctica
East Antarctica, also called Greater Antarctica, constitutes the majority (two-thirds) of the Antarctic continent, lying primarily in the Eastern Hemisphere south of the Indian Ocean, and separated from West Antarctica by the Transantarctic Mountains. It is generally greater in elevation than West Antarctica, and includes the Gamburtsev Mountain Range in the center. The geographic South Pole is located within East Antarctica. Apart from small areas of the coast, East Antarctica is permanently covered by ice and it has relatively low biodiversity, with only a small number of species of terrestrial plants, animals, algae, and lichens. The coasts are the breeding ground for various seabirds and penguins, and the leopard seal, Weddell seal, elephant seal, crabeater seal and Ross seal breed on the surrounding pack ice in summer. Location and description Almost completely covered in thick, permanent ice, East Antarctica comprises Coats Land, Queen Maud Land, Enderby Land, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |