|
Convoy PQ 1
Convoy PQ 1 was the first of the Arctic Convoys of the Second World War to have the code prefix PQ, which was chosen from the initials of Commander Phillip Quellyn Roberts, an operations officer in the Admiralty. The Western Allies used the Arctic route to supply the Soviet Union after the beginning of Operation Barbarossa, the German invasion, which began on 22 June 1941. The convoy sailed from Hvalfjörður, Hvalfiord in Iceland on 29 September 1941 and arrived at Archangelsk on 11 October 1941. To protect return convoys and sweep for mines, a British naval force of ocean-going Halcyon-class minesweepers, which accompanied the convoy, that had the speed, armament and anti-submarine capacity similar to that of Flower-class corvettes, to be established at the Kola naval base. The fleet oiler , which had accompanied the first Arctic convoy, Operation Dervish (1941), Operation Dervish (21–31 August 1941), was at Kola to refuel ships for the return journey. Soviet destroyers at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Convoys
The Arctic convoys of World War II were oceangoing convoys which sailed from the United Kingdom, Iceland, and North America to northern ports in the Soviet Union – primarily Arkhangelsk (Archangel) and Murmansk in Russia. There were 78 convoys between August 1941 and May 1945, sailing via several seas of the Atlantic and Arctic oceans, with periods with no sailings during several months in 1942, and in the summers of 1943 and 1944. About 1,400 merchant ships delivered essential supplies to the Soviet Union under the Anglo-Soviet Agreement and US Lend-Lease program, escorted by ships of the Royal Navy, Royal Canadian Navy, and the U.S. Navy. Eighty-five merchant vessels and 16 Royal Navy warships (two cruisers, six destroyers, eight other escort ships) were lost. Nazi Germany's ''Kriegsmarine'' lost a number of vessels including one battleship, three destroyers, 30 U-boats, and many aircraft. The convoys demonstrated the Allies' commitment to helping the Soviet Union, prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyarny, Murmansk Oblast
Polyarny () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative center of the city of federal subject significance, closed administrative-territorial formation of Alexandrovsk, Murmansk Oblast, Alexandrovsk in Murmansk Oblast, Russia, situated on the outermost western side of the Kola Bay. Population: It was previously known as ''Alexandrovsk'' (until 15 March 1926), ''Alexandrovskoye'' (until 11 March 1931), ''Polyarnoye'' (until 19 September 1939). History It was founded in 1896 and named Alexandrovsk () in honor of Tsar Alexander III of Russia, Alexander III.Official website of PolyarnyHistory of Polyarny, p. 5 Other sources, however, state that the original name was Alexandrovsk-na-Murmane (), it was called so after Alexandra Feodorovna (Alix of Hesse), Alexandra Fyodorovna, wife of Emperor Nicholas II of Russia, Nicholas II, and did not become known as "Alexandrovsk" until later.Pospelov, p. 26 Town status was granted to it on 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Ocean - En
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway (Nordland, Troms, Finnmark, Svalbard and Jan Mayen), northernmost Sweden ( Västerbotten, Norrbotten and Lappland), northern Finland ( North Ostrobothnia, Kainuu and Lappi), Russia ( Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), the United States (Alaska), Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), and northern Iceland ( Grímsey and Kolbeinsey), along with the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas. Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost under the tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ecosystems. The cultures in the region and the Arctic indigenous peoples have adapted to its cold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Naval Intelligence Service
The German Naval Intelligence Service (German: ''Marinenachrichtendienst'' [MND]) was the naval intelligence department of the German Navy, Germany Navy and had a long history, going back to the naval aspirations of Wilhelm II, German Emperor, German emperor Wilhelm II in 1899. The department had various names throughout its existence. Between 1901 and 1919, the service was called the Nachrichten-Abteilung also known as N (English: Military intelligence department) and was the naval intelligence service of the Imperial German Navy. It focused its efforts on France, the United States and above all the United Kingdom, whose Royal Navy was Germany's principal rival for naval supremacy. Its activities had little practical impact on the course of the First World War and it was dissolved in 1919 after Germany's defeat in the war. After the war, saw the establishment of the observation service (B-Dienst) in 1918–1919. In spring 1925, the Naval Intelligence Division was disbanded and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official military branch, branches, along with the and the , of the , the German armed forces from 1935 to 1945. In violation of the Treaty of Versailles, the grew rapidly during German rearmament, German naval rearmament in the 1930s. The 1919 treaty had limited the size of the German navy and prohibited the building of submarines. ships were deployed to the waters around Spain during the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939) under the guise of enforcing non-intervention in the Spanish Civil War, non-intervention, but in reality supporting the Francoist Spain, Nationalists against the Second Spanish Republic, Spanish Republicans. In January 1939, Plan Z, a massive shipbuilding programme, was ordered, calling for surface naval parity with the United Kingdom, British Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-Dienst
The ''B-Dienst'' (, observation service), also called x''B-Dienst'', X-''B-Dienst'' and χ''B-Dienst'', was a Department of the German Naval Intelligence Service (, MND III) of the Oberkommando der Marine, OKM that dealt with the interception and recording, decoding and analysis of the enemy. In particular, it focused on British radio communications before and during World War II. B-Dienst worked on cryptanalysis and deciphering (decrypting) of enemy and neutral states' message traffic and security control of ''Kriegsmarine'' key processes and machinery. :"The ultimate goal of all evaluation was recognizing the opponent's goal by pro-active identification of data." B-Dienst was instrumental in moulding Wehrmacht operations during the Norwegian Campaign, Battles of Norway and Battle of France, France in spring 1940, primarily due to the cryptanalysis successes it had achieved against early and less secure British Naval ciphers. B-Dienst broke British Naval Combined Cypher No. 3 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless Telegraphy
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is the transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using electrical cable, cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies for transmitting telegraph signals without wires. In radiotelegraphy, information is transmitted by pulses of radio waves of two different lengths called "dots" and "dashes", which spell out text messages, usually in Morse code. In a manual system, the sending operator taps on a switch called a telegraph key which turns the transmitter on and off, producing the pulses of radio waves. At the radio receiver, receiver the pulses are audible in the receiver's speaker as beeps, which are translated back to text by an operator who knows Morse code. Radiotelegraphy was the first means of radio communication. The first practical radio transmitters and radio receiver, receivers invented in 1894–1895 by Guglielmo Marconi used radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial German Navy, Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, which banned Germany from having any air force. During the interwar period, German pilots were trained secretly in violation of the treaty at Lipetsk (air base), Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the Nazi Party and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the Luftwaffe's existence was publicly acknowledged and officially established on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through German rearmament and conscription would be announced on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a Luftwaffe detachment sent to aid Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalist for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
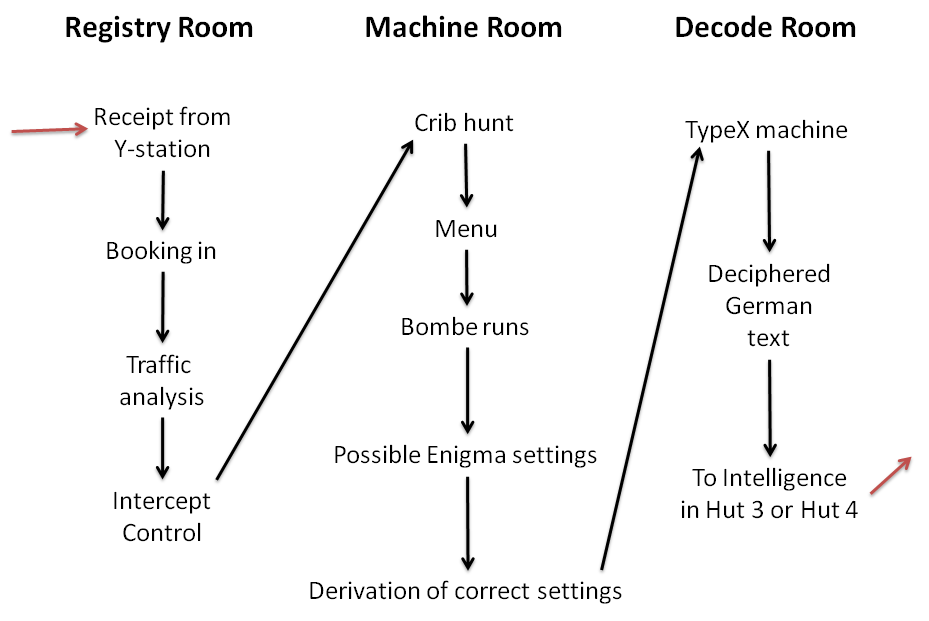
Y-stations
The "Y" service was a network of British signals intelligence collection sites, the Y-stations. The service was established during the First World War and used again during the Second World War. The sites were operated by a range of agencies including the British Army, Army, Royal Navy, Navy and Royal Air Force, RAF, and the Foreign Office (MI6 and MI5). The General Post Office and the Marconi Company provided some receiving stations, ashore and afloat. There were more than 600 receiving sets in use at Y-stations during the Second World War. Role The "Y" name derived from Wireless Interception (WI). The stations tended to be one of two types, for intercepting the signals and for identifying where they were coming from. Sometimes both functions were operated at the same site, with the direction finding (D/F) hut being a few hundred metres from the main interception building to minimise interference. The sites collected radio traffic which was then either analysed locally or, if e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enigma Machine
The Enigma machine is a cipher device developed and used in the early- to mid-20th century to protect commercial, diplomatic, and military communication. It was employed extensively by Nazi Germany during World War II, in all branches of the Wehrmacht, German military. The Enigma machine was considered so secure that it was used to encipher the most top-secret messages. The Enigma has an electromechanical Rotor machine, rotor mechanism that scrambles the 26 letters of the alphabet. In typical use, one person enters text on the Enigma's keyboard and another person writes down which of the 26 lights above the keyboard illuminated at each key press. If plaintext is entered, the illuminated letters are the ciphertext. Entering ciphertext transforms it back into readable plaintext. The rotor mechanism changes the electrical connections between the keys and the lights with each keypress. The security of the system depends on machine settings that were generally changed daily, based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic Analysis
Traffic analysis is the process of intercepting and examining messages in order to deduce information from patterns in communication. It can be performed even when the messages are encrypted. In general, the greater the number of messages observed, the greater information be inferred. Traffic analysis can be performed in the context of military intelligence, counter-intelligence, or pattern-of-life analysis, and is also a concern in computer security. Traffic analysis tasks may be supported by dedicated computer software programs. Advanced traffic analysis techniques which may include various forms of social network analysis. Traffic analysis has historically been a vital technique in cryptanalysis, especially when the attempted crack depends on successfully seeding a known-plaintext attack, which often requires an inspired guess based on how specific the operational context might likely influence what an adversary communicates, which may be sufficient to establish a short cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and Bletchley Park estate, estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes (Buckinghamshire), that became the principal centre of Allies of World War II, Allied World War II cryptography, code-breaking during the Second World War. During World War II, the estate housed the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS), which regularly penetrated the secret communications of the Axis Powers most importantly the German Enigma machine, Enigma and Lorenz cipher, Lorenz ciphers. The GC&CS team of codebreakers included John Tiltman, Dilwyn Knox, Alan Turing, Harry Golombek, Gordon Welchman, Conel Hugh O'Donel Alexander, Hugh Alexander, Donald Michie, W. T. Tutte, Bill Tutte and Stuart Milner-Barry. The team at Bletchley Park devised automatic machinery to help with decryption, culminating in the development of Colossus computer, Colossus, the world's first programmable digital electronic computer. Codebreaking operations at Bletchley Park ended in 1946 and al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |