|
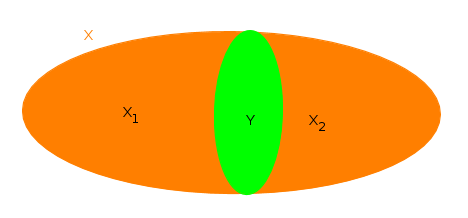
Convex Set
In geometry, a set of points is convex if it contains every line segment between two points in the set. For example, a solid cube (geometry), cube is a convex set, but anything that is hollow or has an indent, for example, a crescent shape, is not convex. The boundary (topology), boundary of a convex set in the plane is always a convex curve. The intersection of all the convex sets that contain a given subset of Euclidean space is called the convex hull of . It is the smallest convex set containing . A convex function is a real-valued function defined on an interval (mathematics), interval with the property that its epigraph (mathematics), epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of a function, graph of the function) is a convex set. Convex minimization is a subfield of mathematical optimization, optimization that studies the problem of minimizing convex functions over convex sets. The branch of mathematics devoted to the study of properties of convex sets and convex f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Polygon Illustration1
Convex or convexity may refer to: Science and technology * Convex lens, in optics Mathematics * Convex set, containing the whole line segment that joins points ** Convex polygon, a polygon which encloses a convex set of points ** Convex polytope, a polytope with a convex set of points ** Convex metric space, a generalization of the convexity notion in abstract metric spaces * Convex function, when the line segment between any two points on the graph of the function lies above or on the graph * Convex conjugate, of a function * Convexity (algebraic geometry), a restrictive technical condition for algebraic varieties originally introduced to analyze Kontsevich Moduli space, moduli spaces Economics and finance * Convexity (finance), second derivatives in financial modeling generally * Convexity in economics * Bond convexity, a measure of the sensitivity of the duration of a bond to changes in interest rates * Convex preferences, an individual's ordering of various outcomes Other use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Space
Euclidean space is the fundamental space of geometry, intended to represent physical space. Originally, in Euclid's ''Elements'', it was the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, but in modern mathematics there are ''Euclidean spaces'' of any positive integer dimension ''n'', which are called Euclidean ''n''-spaces when one wants to specify their dimension. For ''n'' equal to one or two, they are commonly called respectively Euclidean lines and Euclidean planes. The qualifier "Euclidean" is used to distinguish Euclidean spaces from other spaces that were later considered in physics and modern mathematics. Ancient Greek geometers introduced Euclidean space for modeling the physical space. Their work was collected by the ancient Greek mathematician Euclid in his ''Elements'', with the great innovation of '' proving'' all properties of the space as theorems, by starting from a few fundamental properties, called '' postulates'', which either were considered as evid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connected Space
In topology and related branches of mathematics, a connected space is a topological space that cannot be represented as the union (set theory), union of two or more disjoint set, disjoint Empty set, non-empty open (topology), open subsets. Connectedness is one of the principal topological properties that distinguish topological spaces. A subset of a topological space X is a if it is a connected space when viewed as a Subspace topology, subspace of X. Some related but stronger conditions are #Path connectedness, path connected, Simply connected space, simply connected, and N-connected space, n-connected. Another related notion is Locally connected space, locally connected, which neither implies nor follows from connectedness. Formal definition A topological space X is said to be if it is the union of two disjoint non-empty open sets. Otherwise, X is said to be connected. A subset of a topological space is said to be connected if it is connected under its subspace topology. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Path-connected
In topology and related branches of mathematics, a connected space is a topological space that cannot be represented as the union of two or more disjoint non-empty open subsets. Connectedness is one of the principal topological properties that distinguish topological spaces. A subset of a topological space X is a if it is a connected space when viewed as a subspace of X. Some related but stronger conditions are path connected, simply connected, and n-connected. Another related notion is locally connected, which neither implies nor follows from connectedness. Formal definition A topological space X is said to be if it is the union of two disjoint non-empty open sets. Otherwise, X is said to be connected. A subset of a topological space is said to be connected if it is connected under its subspace topology. Some authors exclude the empty set (with its unique topology) as a connected space, but this article does not follow that practice. For a topological space X the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Vector Space
In mathematics, a topological vector space (also called a linear topological space and commonly abbreviated TVS or t.v.s.) is one of the basic structures investigated in functional analysis. A topological vector space is a vector space that is also a topological space with the property that the vector space operations (vector addition and scalar multiplication) are also continuous functions. Such a topology is called a and every topological vector space has a uniform topological structure, allowing a notion of uniform convergence and completeness. Some authors also require that the space is a Hausdorff space (although this article does not). One of the most widely studied categories of TVSs are locally convex topological vector spaces. This article focuses on TVSs that are not necessarily locally convex. Other well-known examples of TVSs include Banach spaces, Hilbert spaces and Sobolev spaces. Many topological vector spaces are spaces of functions, or linear operators ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form a + bi, where and are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number is called the , and is called the . The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols \mathbb C or . Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world. Complex numbers allow solutions to all polynomial equations, even those that have no solutions in real numbers. More precisely, the fundamental theorem of algebra asserts that every non-constant polynomial equation with real or complex coefficie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Transformation
In Euclidean geometry, an affine transformation or affinity (from the Latin, '' affinis'', "connected with") is a geometric transformation that preserves lines and parallelism, but not necessarily Euclidean distances and angles. More generally, an affine transformation is an automorphism of an affine space (Euclidean spaces are specific affine spaces), that is, a function which maps an affine space onto itself while preserving both the dimension of any affine subspaces (meaning that it sends points to points, lines to lines, planes to planes, and so on) and the ratios of the lengths of parallel line segments. Consequently, sets of parallel affine subspaces remain parallel after an affine transformation. An affine transformation does not necessarily preserve angles between lines or distances between points, though it does preserve ratios of distances between points lying on a straight line. If is the point set of an affine space, then every affine transformation on can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Combination
In mathematics, an affine combination of is a linear combination : \sum_^ = \alpha_ x_ + \alpha_ x_ + \cdots +\alpha_ x_, such that :\sum_^ =1. Here, can be elements ( vectors) of a vector space over a field , and the coefficients \alpha_ are elements of . The elements can also be points of a Euclidean space, and, more generally, of an affine space over a field . In this case the \alpha_ are elements of (or \mathbb R for a Euclidean space), and the affine combination is also a point. See for the definition in this case. This concept is fundamental in Euclidean geometry and affine geometry, because the set of all affine combinations of a set of points forms the smallest affine space containing the points, exactly as the linear combinations of a set of vectors form their linear span. The affine combinations commute with any affine transformation in the sense that : T\sum_^ = \sum_^. In particular, any affine combination of the fixed points of a given affine transform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subset
In mathematics, a Set (mathematics), set ''A'' is a subset of a set ''B'' if all Element (mathematics), elements of ''A'' are also elements of ''B''; ''B'' is then a superset of ''A''. It is possible for ''A'' and ''B'' to be equal; if they are unequal, then ''A'' is a proper subset of ''B''. The relationship of one set being a subset of another is called inclusion (or sometimes containment). ''A'' is a subset of ''B'' may also be expressed as ''B'' includes (or contains) ''A'' or ''A'' is included (or contained) in ''B''. A ''k''-subset is a subset with ''k'' elements. When quantified, A \subseteq B is represented as \forall x \left(x \in A \Rightarrow x \in B\right). One can prove the statement A \subseteq B by applying a proof technique known as the element argument:Let sets ''A'' and ''B'' be given. To prove that A \subseteq B, # suppose that ''a'' is a particular but arbitrarily chosen element of A # show that ''a'' is an element of ''B''. The validity of this technique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordered Field
In mathematics, an ordered field is a field together with a total ordering of its elements that is compatible with the field operations. Basic examples of ordered fields are the rational numbers and the real numbers, both with their standard orderings. Every subfield of an ordered field is also an ordered field in the inherited order. Every ordered field contains an ordered subfield that is isomorphic to the rational numbers. Every Dedekind-complete ordered field is isomorphic to the reals. Squares are necessarily non-negative in an ordered field. This implies that the complex numbers cannot be ordered since the square of the imaginary unit ''i'' is (which is negative in any ordered field). Finite fields cannot be ordered. Historically, the axiomatization of an ordered field was abstracted gradually from the real numbers, by mathematicians including David Hilbert, Otto Hölder and Hans Hahn. This grew eventually into the Artin–Schreier theory of ordered fields and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Space
In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set (mathematics), set whose elements, often called vector (mathematics and physics), ''vectors'', can be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called scalar (mathematics), ''scalars''. The operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication must satisfy certain requirements, called ''vector axioms''. Real vector spaces and complex vector spaces are kinds of vector spaces based on different kinds of scalars: real numbers and complex numbers. Scalars can also be, more generally, elements of any field (mathematics), field. Vector spaces generalize Euclidean vectors, which allow modeling of Physical quantity, physical quantities (such as forces and velocity) that have not only a Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude, but also a Orientation (geometry), direction. The concept of vector spaces is fundamental for linear algebra, together with the concept of matrix (mathematics), matrices, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Supergraph
Convex or convexity may refer to: Science and technology * Convex lens, in optics Mathematics * Convex set, containing the whole line segment that joins points ** Convex polygon, a polygon which encloses a convex set of points ** Convex polytope, a polytope with a convex set of points ** Convex metric space, a generalization of the convexity notion in abstract metric spaces * Convex function, when the line segment between any two points on the graph of the function lies above or on the graph * Convex conjugate, of a function * Convexity (algebraic geometry), a restrictive technical condition for algebraic varieties originally introduced to analyze Kontsevich moduli spaces Economics and finance * Convexity (finance), second derivatives in financial modeling generally * Convexity in economics * Bond convexity, a measure of the sensitivity of the duration of a bond to changes in interest rates * Convex preferences In economics, convex preferences are an individual's orderi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |