|
Affine Combination
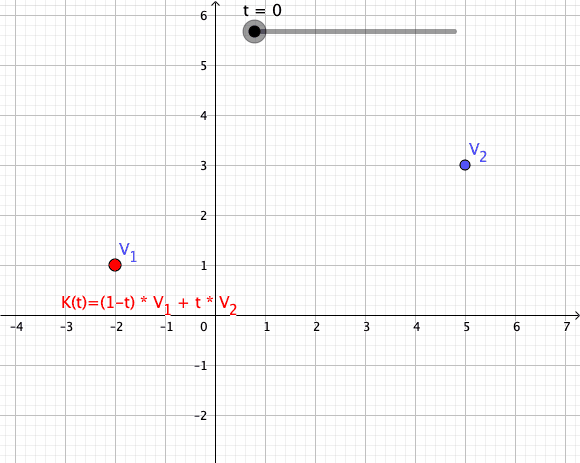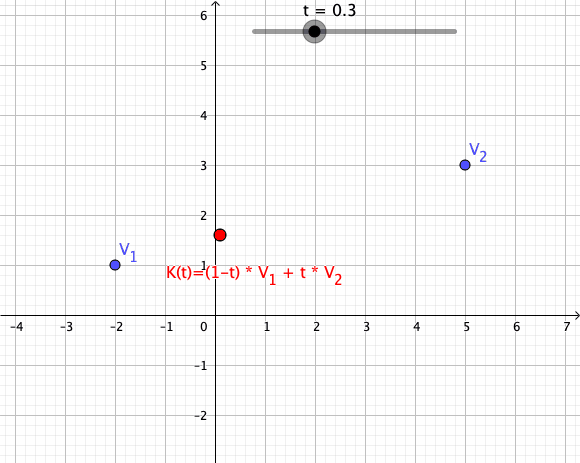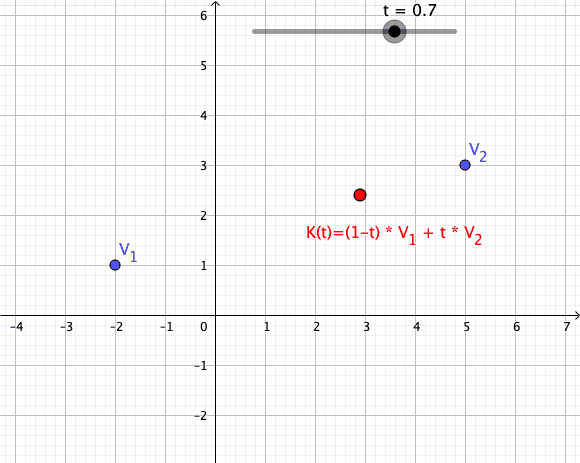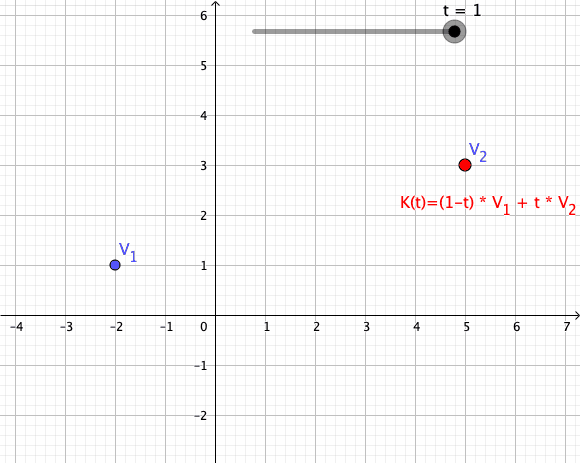
In mathematics, an affine combination of is a linear combination : \sum_^ = \alpha_ x_ + \alpha_ x_ + \cdots +\alpha_ x_, such that :\sum_^ =1. Here, can be elements ( vectors) of a vector space over a field , and the coefficients \alpha_ are elements of . The elements can also be points of a Euclidean space, and, more generally, of an affine space over a field . In this case the \alpha_ are elements of (or \mathbb R for a Euclidean space), and the affine combination is also a point. See for the definition in this case. This concept is fundamental in Euclidean geometry and affine geometry, because the set of all affine combinations of a set of points forms the smallest affine space containing the points, exactly as the linear combinations of a set of vectors form their linear span. The affine combinations commute with any affine transformation in the sense that : T\sum_^ = \sum_^. In particular, any affine combination of the fixed points of a given affine transform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Point (mathematics)
In mathematics, a fixed point (sometimes shortened to fixpoint), also known as an invariant point, is a value that does not change under a given transformation (mathematics), transformation. Specifically, for function (mathematics), functions, a fixed point is an element that is mapped to itself by the function. Any set of fixed points of a transformation is also an invariant set. Fixed point of a function Formally, is a fixed point of a function if belongs to both the domain of a function, domain and the codomain of , and . In particular, cannot have any fixed point if its domain is disjoint from its codomain. If is defined on the real numbers, it corresponds, in graphical terms, to a curve in the Euclidean plane, and each fixed-point corresponds to an intersection of the curve with the line , cf. picture. For example, if is defined on the real numbers by f(x) = x^2 - 3 x + 4, then 2 is a fixed point of , because . Not all functions have fixed points: for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Hull
In mathematics, the affine hull or affine span of a set ''S'' in Euclidean space R''n'' is the smallest affine set containing ''S'', or equivalently, the intersection of all affine sets containing ''S''. Here, an ''affine set'' may be defined as the translation of a vector subspace. The affine hull of ''S'' is what \operatorname S would be if the origin was moved to ''S''. The affine hull aff(''S'') of ''S'' is the set of all affine combinations of elements of ''S'', that is, :\operatorname (S)=\left\. Examples *The affine hull of the empty set is the empty set. *The affine hull of a singleton (a set made of one single element) is the singleton itself. *The affine hull of a set of two different points is the line through them. *The affine hull of a set of three points not on one line is the plane going through them. *The affine hull of a set of four points not in a plane in R''3'' is the entire space R''3''. Properties For any subsets S, T \subseteq X * \operatorname(\o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Geometry
In mathematics, affine geometry is what remains of Euclidean geometry when ignoring (mathematicians often say "forgetting") the metric notions of distance and angle. As the notion of '' parallel lines'' is one of the main properties that is independent of any metric, affine geometry is often considered as the study of parallel lines. Therefore, Playfair's axiom (Given a line and a point not on , there is exactly one line parallel to that passes through .) is fundamental in affine geometry. Comparisons of figures in affine geometry are made with affine transformations, which are mappings that preserve alignment of points and parallelism of lines. Affine geometry can be developed in two ways that are essentially equivalent. In synthetic geometry, an affine space is a set of ''points'' to which is associated a set of lines, which satisfy some axioms (such as Playfair's axiom). Affine geometry can also be developed on the basis of linear algebra. In this context an affine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Space
In mathematics, an affine space is a geometric structure that generalizes some of the properties of Euclidean spaces in such a way that these are independent of the concepts of distance and measure of angles, keeping only the properties related to parallelism and ratio of lengths for parallel line segments. Affine space is the setting for affine geometry. As in Euclidean space, the fundamental objects in an affine space are called '' points'', which can be thought of as locations in the space without any size or shape: zero-dimensional. Through any pair of points an infinite straight line can be drawn, a one-dimensional set of points; through any three points that are not collinear, a two-dimensional plane can be drawn; and, in general, through points in general position, a -dimensional flat or affine subspace can be drawn. Affine space is characterized by a notion of pairs of parallel lines that lie within the same plane but never meet each-other (non-parallel lines wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Combination
In mathematics, a linear combination or superposition is an Expression (mathematics), expression constructed from a Set (mathematics), set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results (e.g. a linear combination of ''x'' and ''y'' would be any expression of the form ''ax'' + ''by'', where ''a'' and ''b'' are constants). The concept of linear combinations is central to linear algebra and related fields of mathematics. Most of this article deals with linear combinations in the context of a vector space over a field (mathematics), field, with some generalizations given at the end of the article. Definition Let ''V'' be a vector space over the field ''K''. As usual, we call elements of ''V'' ''vector space, vectors'' and call elements of ''K'' ''scalar (mathematics), scalars''. If v1,...,v''n'' are vectors and ''a''1,...,''a''''n'' are scalars, then the ''linear combination of those vectors with those scalars as coefficients'' is :a_1 \mathbf v_1 + a_2 \mathbf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conical Combination
Given a finite number of vectors x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n in a real vector space, a conical combination, conical sum, or weighted sum''Convex Analysis and Minimization Algorithms'' by Jean-Baptiste Hiriart-Urruty, Claude Lemaréchal, 1993, pp. 101, 102/ref>''Mathematical Programming'', by Melvyn W. Jeter (1986) p. 68/ref> of these vectors is a vector of the form : \alpha_1x_1+\alpha_2x_2+\cdots+\alpha_nx_n where \alpha_i are non-negative real numbers. The name derives from the fact that the set of all conical sum of vectors defines a cone (possibly in a lower-dimensional subspace). Conical hull The set of all conical combinations for a given set ''S'' is called the conical hull of ''S'' and denoted ''cone''(''S'') or ''coni''(''S''). That is, :\operatorname (S)=\left\. By taking ''k'' = 0, it follows the zero vector ( origin) belongs to all conical hulls (since the summation becomes an empty sum). The conical hull of a set ''S'' is a convex set. In fact, it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Combination
In convex geometry and Vector space, vector algebra, a convex combination is a linear combination of point (geometry), points (which can be vector (geometric), vectors, scalar (mathematics), scalars, or more generally points in an affine space) where all coefficients are non-negative and sum to 1. In other words, the operation is equivalent to a standard weighted average, but whose weights are expressed as a percent of the total weight, instead of as a fraction of the ''count'' of the weights as in a standard weighted average. Formal definition More formally, given a finite number of points x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n in a real vector space, a convex combination of these points is a point of the form : \alpha_1x_1+\alpha_2x_2+\cdots+\alpha_nx_n where the real numbers \alpha_i satisfy \alpha_i\ge 0 and \alpha_1+\alpha_2+\cdots+\alpha_n=1. As a particular example, every convex combination of two points lies on the line segment between the points. A set is convex set, convex if it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Matrix
In mathematics, a stochastic matrix is a square matrix used to describe the transitions of a Markov chain. Each of its entries is a nonnegative real number representing a probability. It is also called a probability matrix, transition matrix, ''substitution matrix'', or Markov matrix. The stochastic matrix was first developed by Andrey Markov at the beginning of the 20th century, and has found use throughout a wide variety of scientific fields, including probability theory, statistics, mathematical finance and linear algebra, as well as computer science and population genetics. There are several different definitions and types of stochastic matrices: *A right stochastic matrix is a square matrix of nonnegative real numbers, with each row summing to 1 (so it is also called a row stochastic matrix). *A left stochastic matrix is a square matrix of nonnegative real numbers, with each column summing to 1 (so it is also called a column stochastic matrix). *A ''doubly stochastic matrix'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Transformation
In Euclidean geometry, an affine transformation or affinity (from the Latin, '' affinis'', "connected with") is a geometric transformation that preserves lines and parallelism, but not necessarily Euclidean distances and angles. More generally, an affine transformation is an automorphism of an affine space (Euclidean spaces are specific affine spaces), that is, a function which maps an affine space onto itself while preserving both the dimension of any affine subspaces (meaning that it sends points to points, lines to lines, planes to planes, and so on) and the ratios of the lengths of parallel line segments. Consequently, sets of parallel affine subspaces remain parallel after an affine transformation. An affine transformation does not necessarily preserve angles between lines or distances between points, though it does preserve ratios of distances between points lying on a straight line. If is the point set of an affine space, then every affine transformation on can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Combination
In mathematics, a linear combination or superposition is an Expression (mathematics), expression constructed from a Set (mathematics), set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results (e.g. a linear combination of ''x'' and ''y'' would be any expression of the form ''ax'' + ''by'', where ''a'' and ''b'' are constants). The concept of linear combinations is central to linear algebra and related fields of mathematics. Most of this article deals with linear combinations in the context of a vector space over a field (mathematics), field, with some generalizations given at the end of the article. Definition Let ''V'' be a vector space over the field ''K''. As usual, we call elements of ''V'' ''vector space, vectors'' and call elements of ''K'' ''scalar (mathematics), scalars''. If v1,...,v''n'' are vectors and ''a''1,...,''a''''n'' are scalars, then the ''linear combination of those vectors with those scalars as coefficients'' is :a_1 \mathbf v_1 + a_2 \mathbf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Span
In mathematics, the linear span (also called the linear hull or just span) of a set S of elements of a vector space V is the smallest linear subspace of V that contains S. It is the set of all finite linear combinations of the elements of , and the intersection of all linear subspaces that contain S. It is often denoted pp. 29-30, §§ 2.5, 2.8 or \langle S \rangle. For example, in geometry, two linearly independent vectors span a plane. To express that a vector space is a linear span of a subset , one commonly uses one of the following phrases: spans ; is a spanning set of ; is spanned or generated by ; is a generator set or a generating set of . Spans can be generalized to many mathematical structures, in which case, the smallest substructure containing S is generally called the substructure ''generated'' by S. Definition Given a vector space over a field , the span of a set of vectors (not necessarily finite) is defined to be the intersection of all subsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |