|
Constitutional History Of Australia
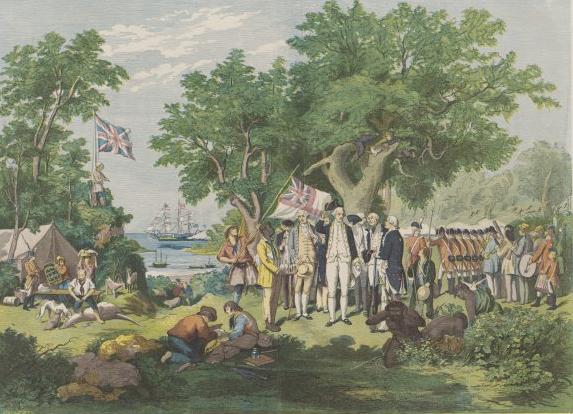
The Constitutional history of Australia is the history of Australia's foundational legal principles. Australia's legal origins as a nation state began in the colonial era, with the reception of English law and the lack of any regard to existing Indigenous legal structures. As the colonies expanded, Australia gradually began to achieve de facto independence. Over the years as a result the foundations of the Australian legal system gradually began to shift. This culminated in the Australia Act, an act formally ending legal ties with the UK. Settlement Prior to European settlement of Australia, Europeans had been to the land merely as explorers. The only exception was James Cook who in 1770 sailed up most of the east coast of Australia and then claimed the entire coastline he had just explored as British territory. No formal legal justification was made of the claim at the time, but in any event no regard was given to any potential Indigenous legal rights. Orders-in-Council were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia Act 1986
The ''Australia Act 1986'' is the short title of each of a pair of separate but related pieces of legislation: one an act of the Parliament of Australia, the other an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. In Australia they are referred to, respectively, as the ''Australia Act 1986'' (Cth) and the ''Australia Act 1986'' (UK). These nearly identical Acts were passed by the two parliaments, because of uncertainty as to whether the Commonwealth Parliament alone had the ultimate authority to do so. They were enacted using legislative powers conferred by enabling acts passed by the parliaments of every Australian state. The acts came into effect simultaneously, on 3 March 1986. According to the long title of the Australian act, its purpose was "to bring constitutional arrangements affecting the Commonwealth and the States into conformity with the status of the Commonwealth of Australia as a sovereign, independent and federal nation". The Australia Act (Cth and UK) elimin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians are people with familial heritage from, or recognised membership of, the various ethnic groups living within the territory of contemporary Australia prior to History of Australia (1788–1850), British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups, which include many ethnic groups: the Aboriginal Australians of the mainland and many islands, including Aboriginal Tasmanians, Tasmania, and the Torres Strait Islanders of the seas between Queensland and Papua New Guinea, located in Melanesia. 812,728 people Aboriginality, self-identified as being of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander origin in the 2021 Australian Census, representing 3.2% of the total population of Australia. Of these Indigenous Australians, 91.4% identified as Aboriginal, 4.2% identified as Torres Strait Islander, and 4.4% identified with both groups. The term Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples or the person's specific cultural group, is often preferred, though the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Australia and New South Wales to the west, south-west and south, respectively. To the east, Queensland is bordered by the Coral Sea and the Pacific Ocean; to the state's north is the Torres Strait, separating the Australian mainland from Papua New Guinea, and the Gulf of Carpentaria to the north-west. With an area of , Queensland is the world's List of country subdivisions by area, sixth-largest subnational entity; it List of countries and dependencies by area, is larger than all but 16 countries. Due to its size, Queensland's geographical features and climates are diverse, and include tropical rainforests, rivers, coral reefs, mountain ranges and white sandy beaches in its Tropical climate, tropical and Humid subtropical climate, sub-tropical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria, commonly abbreviated as Vic, is a States and territories of Australia, state in southeastern Australia. It is the second-smallest state (after Tasmania), with a land area of ; the second-most-populated state (after New South Wales), with a population of over 7 million; and the most densely populated state in Australia (30.6 per km2). Victoria's economy is the List of Australian states and territories by gross state product, second-largest among Australian states and is highly diversified, with service sectors predominating. Victoria is bordered by New South Wales to the north and South Australia to the west and is bounded by the Bass Strait to the south (with the exception of a small land border with Tasmania located along Boundary Islet), the Southern Ocean to the southwest, and the Tasman Sea (a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean) to the southeast. The state encompasses a range of climates and geographical features from its temperate climate, temperate coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letters Patent
Letters patent (plurale tantum, plural form for singular and plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, President (government title), president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, government-granted monopoly, monopoly, title or status to a person or corporation. Letters patent can be used for the creation of corporations, government offices, to grant city status or heraldry, coats of arms. Letters patent are issued for the appointment of representatives of the Crown, such as governors and governor-general, governors-general of Commonwealth realms, as well as appointing a Royal Commission. In the United Kingdom, they are also issued for the creation of peers of the realm. A particular form of letters patent has evolved into the modern intellectual property patent (referred to as a utility patent or design patent in United States patent law) granting exclusive rights in an invention or design. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Of New Zealand
The Colony of New Zealand was a colony of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom from 1841 to 1907. British authority was vested in a List of governors-general of New Zealand, governor. The colony had Capital of New Zealand, three successive capitals: Okiato (or Old Russell) in 1841; Auckland from 1841 to 1865; and Wellington from 1865. Following the New Zealand Constitution Act 1852, the colony became a Crown colony with its first elected parliament in 1853. Responsible self-government was established in 1856 with the governor being required to act on the advice of his Ministers in the New Zealand Government, ministers. In 1907, the colony became the Dominion of New Zealand within the British Empire. History Establishment Following the extension of the boundaries of New South Wales in January 1840 by Governor Gipps to include New Zealand, William Hobson left Sydney for New Zealand. The Treaty of Waitangi—between Māori chiefs and British repre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Sovereignty
A list of former and present British colonies, dependencies and dates when they severed legal ties with Britain: Losses * (1986) – severed legal ties (see: Constitution Act 1986) with Britain, but (see: Monarchy of New Zealand) retained Elizabeth II as head of state. * (1987) – post-coup end of dominion status accepted on 15 October. Elizabeth II remained traditional (though unofficial) Paramount Chief until 2012, when the informal links with the British monarchy have been terminated. * (2003) – court of final appeal transferred from the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council to the Supreme Court of New Zealand, which was created in 2004. Losses in sovereignty or other jurisdiction *The Thirteen Colonies declared independence from Great Britain on 4 July 1776. * (1922) – see Unilateral Declaration of Egyptian Independence. *, , the , , , and (1926) – Dominions at the time of the Balfour Declaration of 1926. *Weihai (1930) – fully restored to Republic of China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hobson
Captain William Hobson (26 September 1792 – 10 September 1842) was an Anglo-Irish officer in the British Royal Navy, who served as the first Governor of New Zealand. He was a co-author of the Treaty of Waitangi. Hobson was dispatched from London in July 1839, with instructions to take the constitutional steps needed to establish a British colony in New Zealand. He was sworn in as Lieutenant-Governor in Sydney (under George Gipps) and arrived in New Zealand on 29 January 1840. On 5 February 1840, Hobson met with Māori chiefs at Waitangi, and the following morning they signed a treaty by which the chiefs purportedly voluntarily transferred sovereignty to the British Crown in return for guarantees respecting their lands and possessions and their rights as British subjects. Three months later, Hobson proclaimed British sovereignty over the islands of New Zealand. He also selected the site for a new capital, which he named Auckland. In May 1841, New Zealand was constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Waitangi
The Treaty of Waitangi (), sometimes referred to as ''Te Tiriti'', is a document of central importance to the history of New Zealand, Constitution of New Zealand, its constitution, and its national mythos. It has played a major role in the treatment of the Māori people in New Zealand by successive governments and the wider population, something that has been especially prominent from the late 20th century. The treaty document is an agreement, not a treaty as recognised in international law. It was first signed on 6 February 1840 by Captain William Hobson as Administrative consul, consul for the British Crown and by Māori chiefs () from the North Island of New Zealand. The treaty's quasi-legal status satisfies the demands of biculturalism in contemporary New Zealand society. In general terms, it is interpreted today as having established a partnership between equals in a way the Crown likely did not intend it to in 1840. Specifically, the treaty is seen, first, as entitling M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
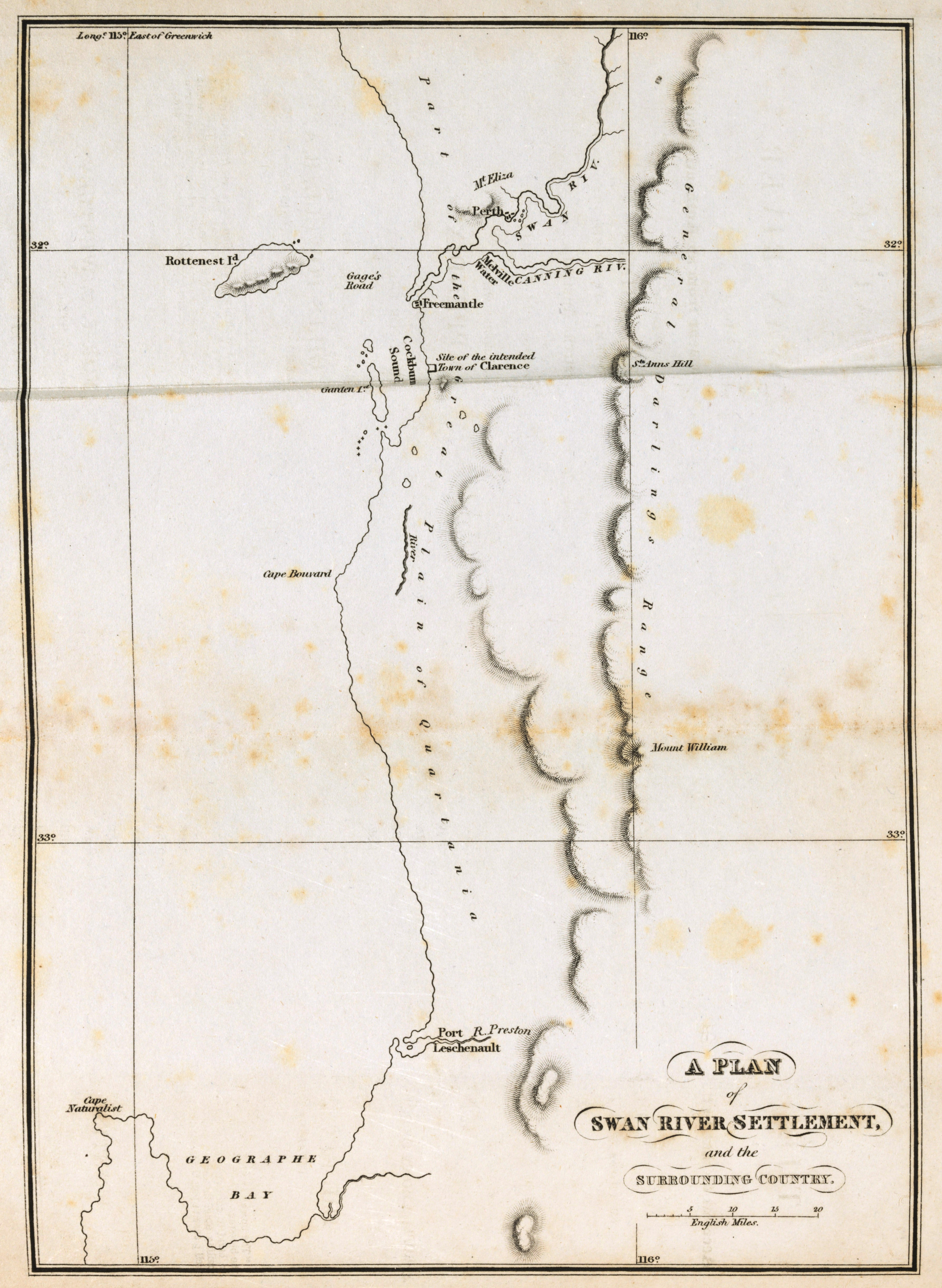
Swan River Colony
The Swan River Colony, also known as the Swan River Settlement, or just ''Swan River'', was a British colony established in 1829 on the Swan River, in Western Australia. This initial settlement place on the Swan River was soon named Perth, and it became the capital city of Western Australia. The name was a ''pars pro toto'' for Western Australia. On 6 February 1832, the colony was renamed the Colony of Western Australia, when the colony's founding lieutenant-governor, Captain James Stirling, belatedly received his commission. However, the name ''Swan River Colony'' remained in informal use for many years. European exploration The first recorded Europeans to sight land where the city of Perth is now located were Dutch sailors. Most likely the first visitor to the Swan River area was Frederick de Houtman on 19 July 1619, travelling on the ships and . His records indicate he first reached the Western Australian coast at latitude 32°20', which is approximately at Warn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Parliament House, Canberra
Old Parliament House, formerly known as the Provisional Parliament House, was the seat of the Parliament of Australia from 1927 to 1988. The building began operation on 9 May 1927 after Parliament's relocation from Melbourne to the new capital, Canberra. In 1988, the Commonwealth Parliament transferred to the new Parliament House on Capital Hill. Since 2009, Old Parliament House has become a museum about the building and Australian democracy more broadly, named the Museum of Australian Democracy at Old Parliament House (MoAD). It also serves as a venue for temporary exhibitions, lectures and concerts. Old Parliament House is, looking across Lake Burley Griffin, situated in front of Parliament House and in line with the Australian War Memorial. It was designed by John Smith Murdoch and a team of assistants from the Department of Works and Railways and was intended to be neither temporary nor permanent—only to be a "provisional" building that would serve the needs of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
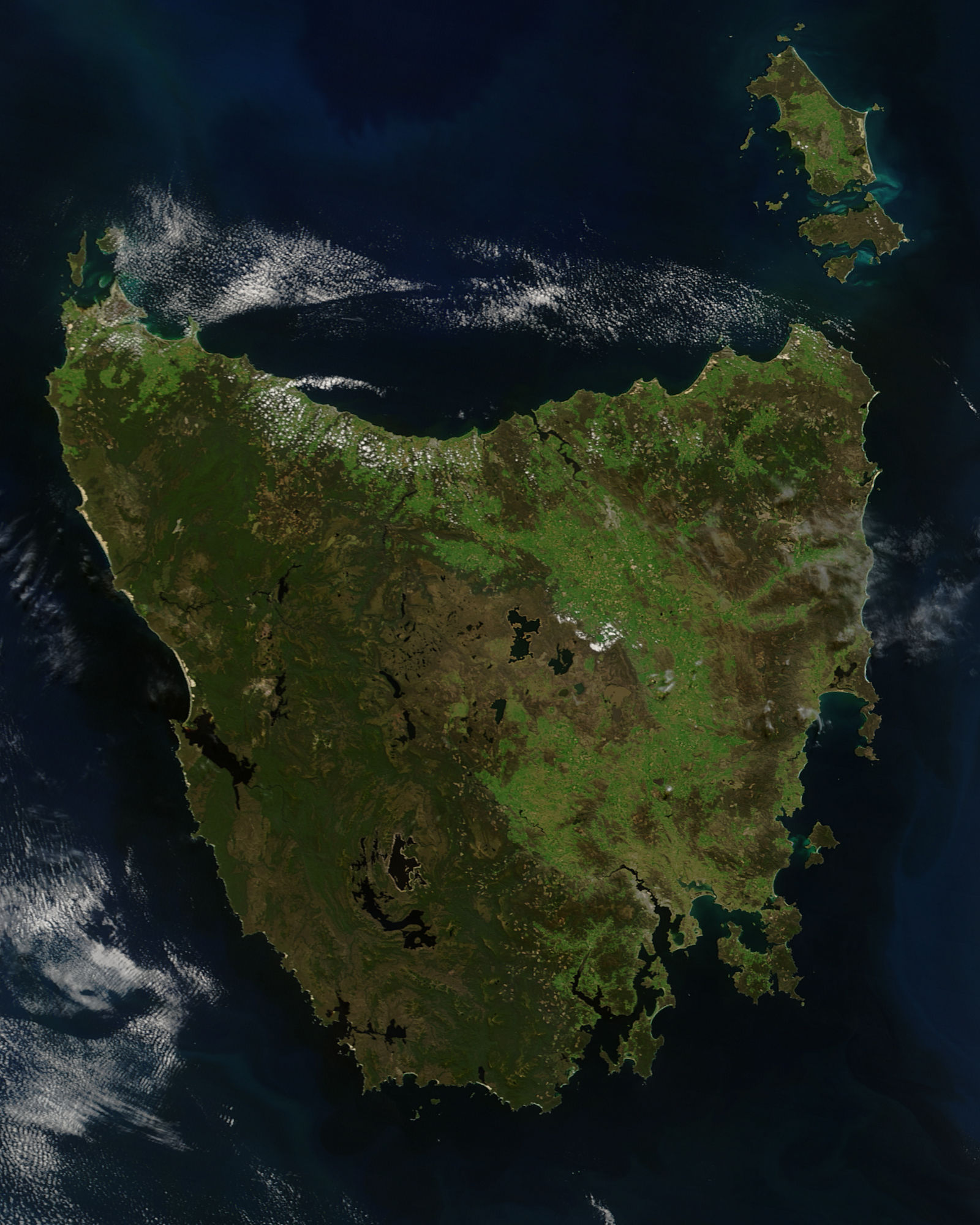
Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The state encompasses the main island of Tasmania, the List of islands by area#Islands, 26th-largest island in the world, and the List of islands of Tasmania, surrounding 1000 islands. It is Australia's smallest and least populous state, with 573,479 residents . The List of Australian capital cities, state capital and largest city is Hobart, with around 40% of the population living in the Greater Hobart area. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017. Tasmania is the most decentralised state in Australia, with the lowest proportion of its residents living within its capital city. Tasmania's main island was first inhabited by Aboriginal Australians, Aboriginal peoples, who today generally identify as Palawa or Pakana. It is believed that Abori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |