|
Congener (chemistry)
In chemistry, congeners are chemical substances "related to each other by origin, structure, or function". Common origin and structure Any significant quantity of a polyhalogenated compound is by default a blend of multiple molecule types because each molecule forms independently, and chlorine and bromine do not strongly select which site(s) they bond to. *Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are a family of 209 congeners. * Polybrominated biphenyls and polychlorinated diphenyl ethers are also families of 209 congeners. Similarly polychlorinated dibenzodioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans, polychlorinated terphenyls, polychlorinated naphthalene, polychloro phenoxy phenol, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) ( pentabromodiphenyl ether, octabromodiphenyl ether, decabromodiphenyl ether), etc. are also groups of congeners. Common origin * Congener (alcohol), substances other than alcohol (desirable or undesirable) also produced during fermentation. *Congeners of olei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Structure
A chemical structure of a molecule is a spatial arrangement of its atoms and their chemical bonds. Its determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules (e.g., diatomic oxygen or nitrogen) to very complex ones (e.g., such as protein or DNA). Background Theories of chemical structure were first developed by August Kekulé, Archibald Scott Couper, and Aleksandr Butlerov, among others, from about 1858. These theories were first to state that chemical compounds are not a ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
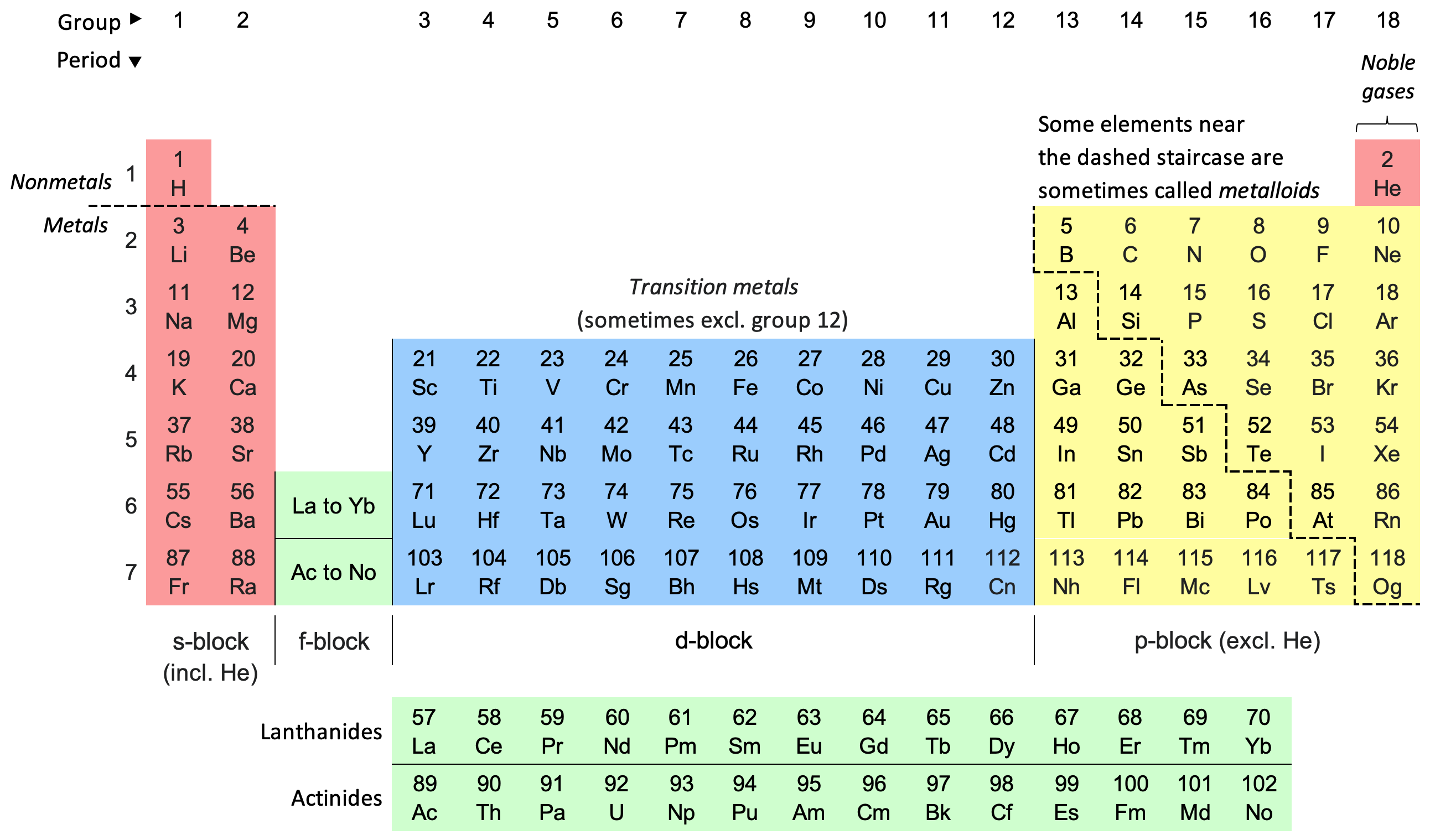
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Tetrachloride
Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide () and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4", as a phonetic representation of the symbols of its molecular formula (). Properties and structure is a dense, colourless liquid, although crude samples may be yellow or even red-brown. It is one of the rare transition metal halides that is a liquid at room temperature, being another example. This property reflects the fact that molecules of weakly self-associate. Most metal chlorides are polymers, wherein the chloride atoms bridge between the metals. Its melting point is similar to that of . has a "closed" electronic shell, with the same number of electrons as the nobl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium(III) Chloride
Titanium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl3. At least four distinct species have this formula; additionally hydrated derivatives are known. TiCl3 is one of the most common halides of titanium and is an important catalyst for the manufacture of polyolefins. Structure and bonding In TiCl3, each titanium atom has one ''d'' electron, rendering its derivatives paramagnetic, that is, the substance is attracted into a magnetic field. Solutions of titanium(III) chloride are violet, which arises from excitations of its ''d''-electron. The colour is not very intense since the transition is forbidden by the Laporte selection rule. Four solid forms or polymorphs of TiCl3 are known. All feature titanium in an octahedral coordination sphere. These forms can be distinguished by crystallography as well as by their magnetic properties, which probes exchange interactions. β-TiCl3 crystallizes as brown needles. Its structure consists of chains of TiCl6 octahedra th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium(II) Chloride
Titanium(II) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula TiCl2. The black solid has been studied only moderately, probably because of its high reactivity. Ti(II) is a strong reducing agent: it has a high affinity for oxygen and reacts irreversibly with water to produce H2. The usual preparation is the thermal disproportionation of TiCl3 at 500 °C. The reaction is driven by the loss of volatile TiCl4: ::2 TiCl3 → TiCl2 + TiCl4 The method is similar to that for the conversion of VCl3 into VCl2 and VCl4. TiCl2 crystallizes as the layered CdI2 structure. Thus, the Ti(II) centers are octahedrally coordinated to six chloride ligands. Derivatives Molecular complexes are known such as TiCl2(chel)2, where chel is DMPE (CH3)2PCH2CH2P(CH3)2 and TMEDA ((CH3)2NCH2CH2N(CH3)2). Such species are prepared by reduction of related Ti(III) and Ti(IV) complexes. Unusual electronic effects have been observed in these species: TiCl2 CH3)2PCH2CH2P(CH3)2sub>2 is paramagnetic wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoelectronicity
Isoelectronicity is a phenomenon observed when two or more molecules have the same structure (positions and connectivities among atoms) and the same electronic configurations, but differ by what specific elements are at certain locations in the structure. For example, , , and are isoelectronic, while and = are not. This definition is sometimes termed valence isoelectronicity. Definitions can sometimes be not as strict, sometimes requiring identity of the total electron count and with it the entire electronic configuration. More usually, definitions are broader, and may extend to allowing different numbers of atoms in the species being compared.A. A. Aradi & T. P. Fehlner, "Isoelectronic Organometallic Molecules", in F. G. A. Stone & Robert West (eds.) ''Advances in Organometallic Chemistry Vol. 30'' (1990), Chapter 5 (at p. 190google books link/ref> The importance of the concept lies in identifying significantly related species, as pairs or series. Isoelectronic specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Disulfide
Hydrogen disulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This hydrogen chalcogenide is a pale yellow volatile liquid with a camphor-like odor. It decomposes readily to hydrogen sulfide () and elemental sulfur. Structure The connection of atoms in the hydrogen disulfide molecule is . The structure of hydrogen disulfide is similar to that of hydrogen peroxide, with C2 point group symmetry. Both molecules are distinctly nonplanar. The dihedral angle between the and planes is 90.6°, compared with 111.5° in . The bond angle is 92°, close to 90° for unhybridized divalent sulfur. Synthesis Hydrogen disulfide can be synthesised by cracking polysulfanes () according to this idealized equation: : The main impurity is trisulfane (). The precursor polysulfane is produced by the reaction of hydrochloric acid with aqueous sodium polysulfide. The polysulfane precipitates as an oil. Reactions Upon contact with water or alcohols, hydrogen disulfide readily decomposes under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Thioperoxide
Hydrogen thioperoxide, also called oxadisulfane or sulfanol, is the chemical with the structure H–S–O–H. It can be considered as the simple sulfur-substituted analog of the common hydrogen peroxide (H–O–O–H) chemical, and as the simplest hydrogen chalcogenide containing more than one type of chalcogen. The chemical has been described as the "missing link" between hydrogen peroxide and hydrogen disulfide (H–S–S–H), though it is substantially less stable than either of the other two. It is the inorganic parent structure of the sulfenic acid class of organic compounds (R–S–O–H) and also the oxadisulfide linkage (R1–S–O–R2), where "R" is any organic structure. Sulfur is present in oxidation state 0. Formation Hydrogen thioperoxide has been synthesized in labs by photolysis of a mixture of ozone and hydrogen sulfide frozen in argon at 8 K and by pyrolysis of di-''tert''-butyl sulfoxide. Yet another synthesis is by an electric discharge through wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or "high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as both a monopropellant and an oxidizer in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly into water and elemental oxygen when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a Stabilizer (chemistry), stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in an opaque bottle. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |