|
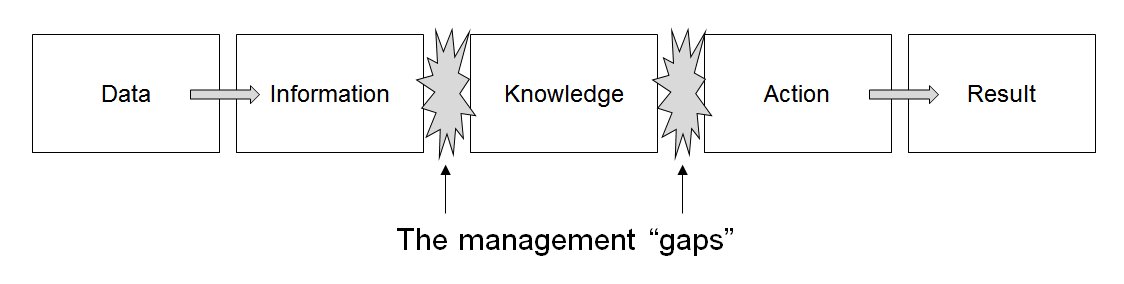
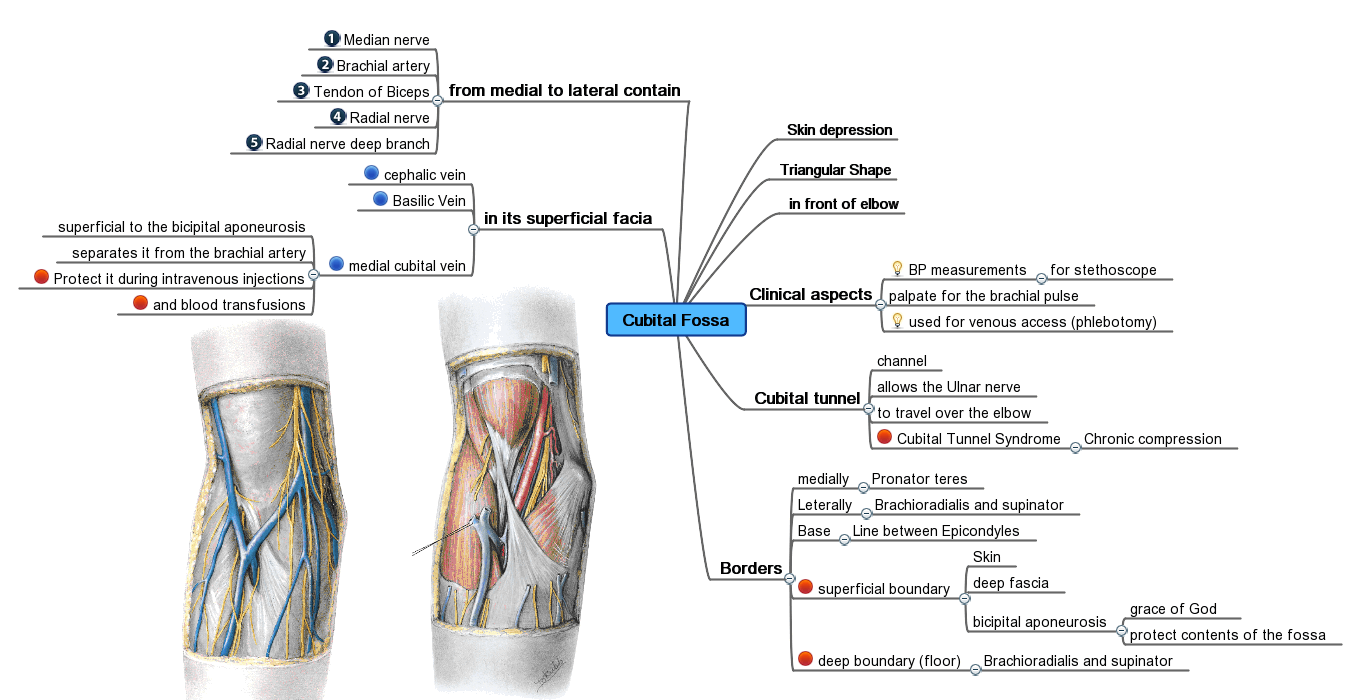
Concept Mapping
A concept map or conceptual diagram is a diagram that depicts suggested relationships between concepts. Concept maps may be used by instructional designers, engineers, technical writers, and others to organize and structure knowledge. A concept map typically represents ideas and information as boxes or circles, which it connects with labeled arrows, often in a downward-branching hierarchical structure but also in free-form maps. The relationship between concepts can be articulated in '' linking phrases'' such as "causes", "requires", "such as" or "contributes to". The technique for visualizing these relationships among different concepts is called ''concept mapping''. Concept maps have been used to define the ontology of computer systems, for example with the object-role modeling or Unified Modeling Language formalism. Differences from other visualizations * '' Topic maps'': Both concept maps and topic maps are kinds of knowledge graph, but topic maps were developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generic Programming
Generic programming is a style of computer programming in which algorithms are written in terms of data types ''to-be-specified-later'' that are then ''instantiated'' when needed for specific types provided as parameters. This approach, pioneered in the programming language ML in 1973, permits writing common functions or data types that differ only in the set of types on which they operate when used, thus reducing duplicate code. Generic programming was introduced to the mainstream with Ada in 1977. With templates in C++, generic programming became part of the repertoire of professional library design. The techniques were further improved and ''parameterized types'' were introduced in the influential 1994 book '' Design Patterns''. New techniques were introduced by Andrei Alexandrescu in his 2001 book '' Modern C++ Design: Generic Programming and Design Patterns Applied''. Subsequently, D implemented the same ideas. Such software entities are known as ''generics'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Management
Information management (IM) is the appropriate and optimized capture, storage, retrieval, and use of information. It may be personal information management or organizational. Information management for organizations concerns a cycle of organizational activity: the acquisition of information from one or more sources, the custodianship and the distribution of that information to those who need it, and its ultimate disposal through archiving or deletion and extraction. This cycle of information organisation involves a variety of stakeholder (corporate), stakeholders, including those who are responsible for assuring the quality (business), quality, accessibility and utility of acquired information; those who are responsible for its safe Data storage device, storage and :wikt:disposal, disposal; and those who need it for decision making. Stakeholders might have rights to originate, change, distribute or delete information according to organisational information management policies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain-storming
Brainstorming is a creativity technique in which a group of people interact to suggest ideas spontaneously in response to a prompt. Stress is typically placed on the volume and variety of ideas, including ideas that may seem outlandish or "off-the-wall". Ideas are noted down during the activity, but not assessed or critiqued until later. The absence of criticism and assessment is intended to avoid inhibiting participants in their idea production. The term was popularized by advertising executive Alex Faickney Osborn in the classic work '' Applied Imagination'' (1953). History In 1939, advertising executive Alex F. Osborn began developing methods for creative problem-solving. He was frustrated by employees' inability to develop creative ideas individually for ad campaigns. In response, he began hosting group-thinking sessions and discovered a significant improvement in the quality and quantity of ideas produced by employees. He first termed the process as ''organized ideation' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creativity
Creativity is the ability to form novel and valuable Idea, ideas or works using one's imagination. Products of creativity may be intangible (e.g. an idea, scientific theory, Literature, literary work, musical composition, or joke), or a physical object (e.g. an invention, dish or meal, piece of Jewellery, jewelry, costume, a painting). Creativity may also describe the ability to find Creative problem-solving, new solutions to problems, or new methods to accomplish a goal. Therefore, creativity enables people to Solves problem, solve problems in new ways. Most ancient cultures (including Ancient Greece, History of China#Ancient China, Ancient China, and Outline of ancient India, Ancient India) lacked the concept of creativity, seeing art as a form of discovery rather than a form of creation. In the Judeo-Christian-Islamic tradition, creativity was seen as the sole province of God, and human creativity was considered an expression of God's work; the modern conception of creativi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knowledge Arena
A knowledge arena is a virtual space where individuals can manipulate concepts and relationships to form a concept map. Individuals using a computer with appropriate software can represent concepts and the relationships between concepts in a node-relationship-node formalism. The process of thinking about the concepts and making associations between them has been called "off-loading" by Ray McAleese. See also: {{cite journal , last=McAleese , first=Ray , date=2000 , url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228951375 , title=Skill acquisition: the curious case of information searching , journal=Interactive Learning Environments , volume=8 , issue=1 , pages=23–49 , doi=10.1076/1049-4820(200004)8:1;1-G;FT023, s2cid=6490674 The concept map is a form of a semantic network or semantic graph. It is formally based on graph theory. In the concept map, concepts are represented by nodes. The relationship between nodes are represented by typed links ( edges). In creating a map or graphic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Ausubel
David Paul Ausubel (October 25, 1918 – July 9, 2008) was an American psychologist. His most significant contribution to the fields of educational psychology, cognitive science, and science education learning was on the development and research on "''advance organizers''" (see below) since 1960. Biography Family He was born on October 25, 1918, and grew up in Brooklyn, New York.Ausubel, D.P. David Ausubel. Retrieved June 9, 2010, from http://www.davidausubel.org/ He was nephew of the Jewish historian Nathan Ausubel. Ausubel and his wife Pearl had two children. Education and academic career Ausubel studied at the University of Pennsylvania where he graduated with honors in 1939, receiving a bachelor's degree majoring in psychology. Ausubel later graduated from medical school in 1943 at Middlesex University (Massachusetts), Middlesex University where he went on to complete a rotating internship at Gouverneur Hospital, located on the Lower East Side of Manhattan, New York. Ausub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constructivism (learning Theory)
Constructivism in education is a theory that suggests that learners do not passively acquire knowledge through direct instruction. Instead, they ''construct'' their understanding through experiences and social interaction, integrating new information with their existing knowledge. This theory originates from Swiss developmental psychologist Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development. Background Constructivism in education is rooted in epistemology, a theory of knowledge concerned with the logical categories of knowledge and its justification. It acknowledges that learners bring prior knowledge and experiences shaped by their social and cultural environment and that learning is a process of students "constructing" knowledge based on their experiences. While behaviorism focuses on understanding what students are doing, constructivism emphasizes the importance of understanding what students are thinking and how to enrich their thinking.Seifert, Kelvin & Sutton, Rosemary. Educ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornell University
Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson White in 1865. Since its founding, Cornell University has been a Mixed-sex education, co-educational and nonsectarian institution. As of fall 2024, the student body included 16,128 undergraduate and 10,665 graduate students from all 50 U.S. states and 130 countries. The university is organized into eight Undergraduate education, undergraduate colleges and seven Postgraduate education, graduate divisions on its main Ithaca campus. Each college and academic division has near autonomy in defining its respective admission standards and academic curriculum. In addition to its primary campus in Ithaca, Cornell University administers three satellite campuses, including two in New York City, the Weill Cornell Medicine, medical school and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
College Teaching
''College Teaching'' (formerly ''Improving College & University Teaching'') is a quarterly cross-disciplinary academic journal focused on the subject of teaching in higher education and the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, with special focus on improving student learning. The journal website states that it "provides an interdisciplinary academic forum on issues in teaching and learning at the undergraduate or graduate level." The journal employs double-blind peer review. The first issue was published in 1953 under the title ''Improving College and University Teaching'', and the current title was adopted in 1985. According to Scopus, the CiteScore 2017 was .45. Scimago lists the journal as Q3, SJR .27 for 2017. Publication information * Quarterly * Publisher: currently Taylor & Francis, formerly published by Heldref Publications Taylor & Francis Group is an international company originating in the United Kingdom that publishes books and academic journals. Its parts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Structure
A tree structure, tree diagram, or tree model is a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a structure in a graphical form. It is named a "tree structure" because the classic representation resembles a tree, although the chart is generally upside down compared to a biological tree, with the "stem" at the top and the "leaves" at the bottom. A tree structure is conceptual, and appears in several forms. For a discussion of tree structures in specific fields, see Tree (data structure) for computer science; insofar as it relates to graph theory, see tree (graph theory) or tree (set theory). Other related articles are listed below. Terminology and properties The tree elements are called "nodes". The lines connecting elements are called "branches". Nodes without children are called leaf nodes, "end-nodes", or "leaves". Every finite tree structure has a member that has no superior. This member is called the "root" or root node. The root is the starting node. But the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mind Maps
A mind map is a diagram used to visually organize information into a hierarchy, showing relationships among pieces of the whole. It is often based on a single concept, drawn as an image in the center of a blank page, to which associated representations of ideas such as images, words and parts of words are added. Major ideas are connected directly to the central concept, and other ideas branch out from those major ideas. Mind maps can also be drawn by hand, either as "notes" during a lecture, meeting or planning session, for example, or as higher quality pictures when more time is available. Mind maps are considered to be a type of spider diagram. Origin Although the term "mind map" was first popularized by British popular psychology author and television personality Tony Buzan, the use of diagrams that visually "map" information using branching and radial maps traces back centuries. These pictorial methods record knowledge and model systems, and have a long history in le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |