 A tree structure, tree diagram, or tree model is a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a
A tree structure, tree diagram, or tree model is a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
in a graphical form. It is named a "tree structure" because the classic representation resembles a tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
, although the chart is generally upside down compared to a biological tree, with the "stem" at the top and the "leaves" at the bottom.
A tree structure is conceptual, and appears in several forms. For a discussion of tree structures in specific fields, see Tree (data structure)
In computer science, a tree is a widely used abstract data type that represents a hierarchical tree structure with a set of connected nodes. Each node in the tree can be connected to many children (depending on the type of tree), but must be co ...
for computer science; insofar as it relates to graph theory, see tree (graph theory) or tree (set theory). Other related articles are listed below.
Terminology and properties
The tree elements are called "node
In general, a node is a localized swelling (a "knot") or a point of intersection (a vertex).
Node may refer to:
In mathematics
* Vertex (graph theory), a vertex in a mathematical graph
*Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, lines ...
s".
The lines connecting elements are called "branches".
Nodes without children are called leaf nodes, "end-nodes", or "leaves".
Every finite tree structure has a member that has no superior. This member is called the "root" or root node. The root is the starting node. But the converse is not true: infinite tree structures may or may not have a root node.
The names of relationships between nodes model the kinship terminology
Kinship terminology is the system used in languages to refer to the persons to whom an individual is related through kinship. Different societies classify kinship relations differently and therefore use different systems of kinship terminology; ...
of family relations. The gender-neutral names "parent" and "child" have largely displaced the older "father" and "son" terminology. The term "uncle" is still widely used for other nodes at the same level as the parent, although it is sometimes replaced with gender-neutral terms like "ommer".
* A node's "parent" is a node one step higher in the hierarchy (i.e. closer to the root node) and lying on the same branch.
* "Sibling" ("brother" or "sister") nodes share the same parent node.
* A node's "uncles" (sometimes "ommers") are siblings of that node's parent.
* A node that is connected to all lower-level nodes is called an "ancestor". The connected lower-level nodes are "descendants" of the ancestor node.
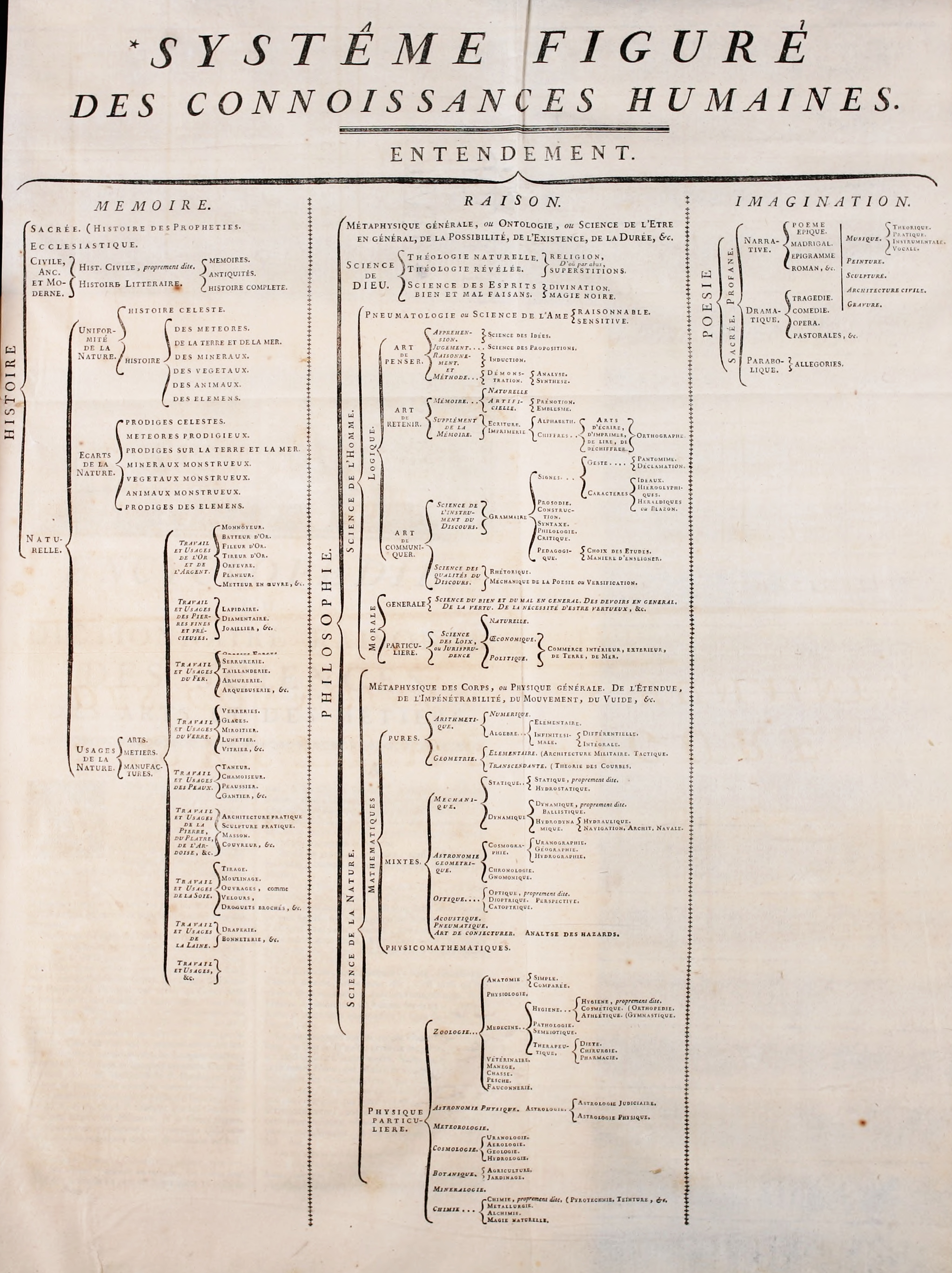
In the example, "encyclopedia" is the parent of "science" and "culture", its children. "Art" and "craft" are siblings, and children of "culture", which is their parent and thus one of their ancestors. Also, "encyclopedia", as the root of the tree, is the ancestor of "science", "culture", "art" and "craft". Finally, "science", "art" and "craft", as leaves, are ancestors of no other node.
Tree structures can depict all kinds of taxonomic knowledge, such as family tree
A family tree, also called a genealogy or a pedigree chart, is a chart representing family relationships in a conventional tree structure. More detailed family trees, used in medicine and social work, are known as genograms.
Representations of ...
s, the biological evolutionary tree, the evolutionary tree of a language family, the grammatical structure of a language (a key example being S → NP VP, meaning a sentence is a noun phrase and a verb phrase, with each in turn having other components which have other components), the way web pages are logically ordered in a web site, mathematical trees of integer sets, et cetera.
The Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first editio ...
records use of both the terms "tree structure" and "tree-diagram" from 1965 in Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American professor and public intellectual known for his work in linguistics, political activism, and social criticism. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is also a ...
's '' Aspects of the Theory of Syntax''.
In a tree structure there is one and only one path from any point to any other point.
Computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
uses tree structures extensively (''see'' Tree (data structure)
In computer science, a tree is a widely used abstract data type that represents a hierarchical tree structure with a set of connected nodes. Each node in the tree can be connected to many children (depending on the type of tree), but must be co ...
and telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
.)
For a formal definition see set theory
Set theory is the branch of mathematical logic that studies Set (mathematics), sets, which can be informally described as collections of objects. Although objects of any kind can be collected into a set, set theory – as a branch of mathema ...
, and for a generalization in which children are not necessarily successors, see prefix order.
Examples of tree structures
 * Internet:
** usenet hierarchy
** Document Object Model's logical structure,
* Internet:
** usenet hierarchy
** Document Object Model's logical structure, Yahoo!
Yahoo (, styled yahoo''!'' in its logo) is an American web portal that provides the search engine Yahoo Search and related services including My Yahoo, Yahoo Mail, Yahoo News, Yahoo Finance, Yahoo Sports, y!entertainment, yahoo!life, and its a ...
subject index, Curlie
* Operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
: directory structure
* Information management: Dewey Decimal System, PSH, this hierarchical bulleted list
* Management: hierarchical organization
An organization or organisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences) is an legal entity, entity—such as ...
al structures
* Computer science:
** binary search tree
** red–black tree
** AVL tree
** R-tree
** doubly logarithmic tree
* Biology: evolutionary tree
* Business: pyramid selling scheme
* Project management: work breakdown structure
* Linguistics:
** (Syntax) Phrase structure trees
** (Historical Linguistics) Tree model of language change
* Sports: business chess, playoffs brackets
* Mathematics: Von Neumann universe
* Group theory: descendant trees
Representing trees
There are many ways of visually representing tree structures. Almost always, these boil down to variations, or combinations, of a few basic styles:Classical node-link diagrams
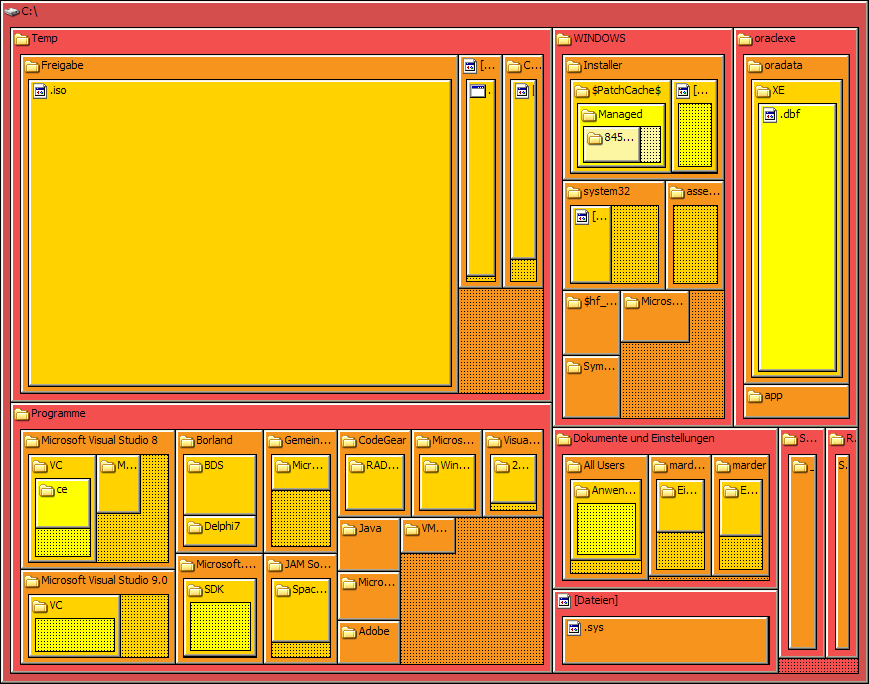
Classical node-link diagrams, that connect nodes together with line segments:Nested sets
Nested sets that use enclosure or containment to show parenthood; examples include TreeMaps, fractal maps, and Euler diagrams:Layered "icicle" diagrams
Layered "icicle" diagrams that use alignment/adjacency.Outlines and tree views
Lists or diagrams that use indentation, sometimes called " outlines" or " tree views". An outline:
:encyclopedia
::culture
:::art
:::craft
::science
A tree view:
*encyclopedia
**culture
***art
***craft
**science
Nested parentheses
A correspondence to nested parentheses was first noticed by Sir Arthur Cayley:
((art,craft)culture,science)encyclopedia
or
encyclopedia(culture(art,craft),science)
or
encyclopedia(culture(art,craft),science)
Radial trees
Trees can also be represented radially:See also
;Kinds of trees: * B-tree * Dancing tree *Decision tree
A decision tree is a decision support system, decision support recursive partitioning structure that uses a Tree (graph theory), tree-like Causal model, model of decisions and their possible consequences, including probability, chance event ou ...
* Left-child right-sibling binary tree
* Porphyrian tree
* Tree (data structure)
In computer science, a tree is a widely used abstract data type that represents a hierarchical tree structure with a set of connected nodes. Each node in the tree can be connected to many children (depending on the type of tree), but must be co ...
* Tree (graph theory)
* Tree (set theory)
;Related articles:
* Data drilling
* Hierarchical model: clustering and query
* Tree testing
References
Further reading
Identification of some of the basic styles of tree structures can be found in: * Jacques Bertin, ''Semiology of Graphics'', 1983, University of Wisconsin Press (2nd edition 1973, ; * *Brian Johnson and Ben Shneiderman,Tree-maps: A space-filling approach to the visualization of hierarchical information structures
, in ''Proceedings of IEEE Visualization (VIS)'', 1991, pp. 284–291, ; * Peter Eades, Tao Lin, and Xuemin Lin, "Two Tree Drawing Conventions", ''International Journal of Computational Geometry and Applications'', 1993, volume 3, number 2, pp. 133–153. *
External links
Visualization of phylogenetic trees on the T-REX server
Using a tree structure to design a business process
– from the Society for Technical Communication {{DEFAULTSORT:Tree Structure Trees (data structures) Conceptual models de:Baum (Datenstruktur) pl:Struktura drzewiasta