|
Composite Aircraft
A composite aircraft is made up of multiple ''component'' craft. It takes off and flies initially as a single aircraft, with the components able to separate in flight and continue as an independent aircraft.Harper (1937) Typically the larger aircraft acts as a ''carrier aircraft'' or ''mother ship'', with the smaller sometimes called a ''parasite aircraft, parasite'' or ''jockey'' craft. The first composite aircraft flew in 1916, during World War I, when the United Kingdom, British launched a Bristol Scout from a Felixstowe Porte Baby flying boat. Between the World Wars, American experiments with airship/biplane composites led to the construction of two airborne aircraft carriers, while the British Short Mayo Composite, Short Mayo seaplane composite demonstrated successful transatlantic mail delivery. During the Second World War some composites saw operational use including the Mistel ("mistletoe"), the larger unmanned component of a composite aircraft configuration developed in G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Material
A composite or composite material (also composition material) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Composite materials with more than one distinct layer are called ''composite laminates''. Typical engineered composite materials are made up of a binding agent forming the ''matrix'' and a Filler (materials), filler material (particulates or fibres) giving ''substance'', e.g.: * Concrete, reinforced concrete and masonry with cement, lime or Mortar (masonry), mortar (which is itself a composite material) as a binder * Composite wood such as glulam and plywood with wood glue as a binder * Reinforced plastics, such as fiberglass and fibre-rein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XF9C 1 Aircraft Hooking Onto USS Akron, May 1932
The Curtiss F9C Sparrowhawk is a light 1930s biplane fighter aircraft that was carried by the United States Navy airships and . It is an example of a parasite fighter, a small airplane designed to be deployed from a larger aircraft such as an airship or bomber. Design and development The concept of fixed-wing aircraft being carried and launched from airships was initially developed during the First World War - initially, this proposal originated in the United Kingdom, to allow British interceptors to conserve fuel by being carried to an altitude whereby they could then engage German zeppelins.H. J. C Harpe"Composite History" ''Flight'' 1 November 1937 The increasing use of airships in the armed forces of various countries led to variations on the idea of using aircraft with them, with major uses being for reconnaissance, extending the reach of the airship beyond the horizon, and to provide the airship with a degree of self-defence. In the late 1920s, the US Navy began experime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Los Angeles (ZR-3)
USS ''Los Angeles'' was a rigid airship, designated ZR-3, which was built in 1923–1924 by the Luftschiffbau Zeppelin, Zeppelin company in Friedrichshafen, Germany, as war reparations. She was delivered to the United States Navy in October 1924 and after being used mainly for experimental work, particularly in the development of the American parasite fighter program, was decommissioned in 1932. Design The second of USS Los Angeles, four vessels to carry the name USS ''Los Angeles'', the airship was built for the United States Navy as a replacement for the Zeppelins that had been assigned to the United States as war reparations following World War I, and had been sabotaged by their crews in 1919. Under the terms of the Treaty of Versailles Luftschiffbau Zeppelin were not permitted to build military airships. In consequence ''Los Angeles'', which had the Zeppelin works number LZ 126, was built as a passenger airship, although the treaty limitation on the permissible volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 million tons in 2021. It has the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with List of aircraft carriers in service, eleven in service, one undergoing trials, two new carriers under construction, and six other carriers planned as of 2024. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the U.S. Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 299 deployable combat vessels and about 4,012 operational aircraft as of 18 July 2023. The U.S. Navy is one of six United States Armed Forces, armed forces of the United States and one of eight uniformed services of the United States. The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TC-3
The TC-3 and the TC-7 were the two United States Army Air Corps The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1926 and 1941. After World War I, as early aviation became an increasingly important part of modern warfare, a philosophical ri ... non-rigid blimps used for parasite fighter trials conducted in 1923–24. A single Sperry Messenger biplane was equipped with a skyhook to engage the temporary trapeze mounted to the control carriage of the blimp itself. The first successful docking was achieved on December 15, 1924. Despite the completely successful results of the program, the Army chose not to develop the concept further. It was the Navy which began the better-known project in 1925 using rigid airships, the USS ''Los Angeles'' (ZR-3), the USS ''Macon'' (ZRS-5) and the USS ''Akron'' (ZRS-4). Scott Field in St. Clair County, Illinois, had a US Army Lighter-than-Air Base from 1921–1937 for trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LZ 129 Hindenburg
LZ 129 ''Hindenburg'' (; Aircraft registration, Registration: D-LZ 129) was a German commercial passenger-carrying rigid airship, the lead ship of Hindenburg class airship, its class, the longest class of flying machine and the largest airship by envelope volume. It was designed and built by the Zeppelin Company (Luftschiffbau Zeppelin, ''Luftschiffbau Zeppelin GmbH'') on the shores of Lake Constance in Friedrichshafen, Germany, and was operated by the German Zeppelin Airline Company (''Deutsche Zeppelin-Reederei''). It was named after Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg, who was President of Germany (1919–1945), President of Germany from 1925 until his death in 1934. The airship first flew from March 1936 as a #Die_Deutschlandfahrt, Nazi propaganda vessel until it Hindenburg disaster, burst into flames 14 months later on May 6, 1937, while attempting to land at Naval Air Engineering Station Lakehurst, Lakehurst Naval Air Station in Manchester Township, New Jersey, at the end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Zeppelins
This is a complete list of Zeppelins constructed by the German Zeppelin companies from 1900 until 1938. Other rigid airships that are also sometimes referred to as zeppelins but not built by Zeppelin are not included. The Zeppelin company based in Friedrichshafen, Germany, numbered their aircraft ''LZ 1/2/ ...'', with ''LZ'' standing for "Luftschiff [airship] Zeppelin". Additionally, craft used for civilian purposes were named, whereas military airships were usually given "tactical numbers": * The Imperial German Army, ''Deutsches Heer'' called its first Zeppelins ''Z I/II/ ... /XI/XII''. During World War I they switched to using ''LZ'' numbers, later adding 30 to obscure the total production. * The Imperial German Navy, ''Kaiserliche Marine'''s Zeppelins were labelled ''L 1/2/ ...''. Since 1997, airships of the new type Zeppelin NT have been flying. They are not included here. They are Semi-rigid airship, not rigid airships and do not represent a continuity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albatros D
An albatross is one of a family of large winged seabirds. Albatross or Albatros may also refer to: Animals * Albatross (butterfly) or ''Appias'', a genus of butterfly * Albatross (horse) (1968–1998), a Standardbred horse Literature * Albatross Books, a German publishing house that produced the first modern mass market paperback books * Albatros Literaturpreis, a literary award * "L'albatros" (poem) ("The Albatross"), 1859 poem by Charles Baudelaire * ''The Albatross'' (novella), a 1971 novella by Susan Hill * ''The Albatross'', the fictional propeller-sustained airship in Jules Verne's novel '' Robur the Conqueror'' * ''Albatross'' (novel), a 2019 novel by Terry Fallis * ''Albatross'' (magazine), 1970s lesbian satirical magazine Film and television * Films Albatros, a French film production company which operated between 1922 and 1939 * ''Albatross'' (2011 film), a British film * ''Albatross'' (2015 film), an Icelandic film * ''Albatross'' (2022 film), an Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
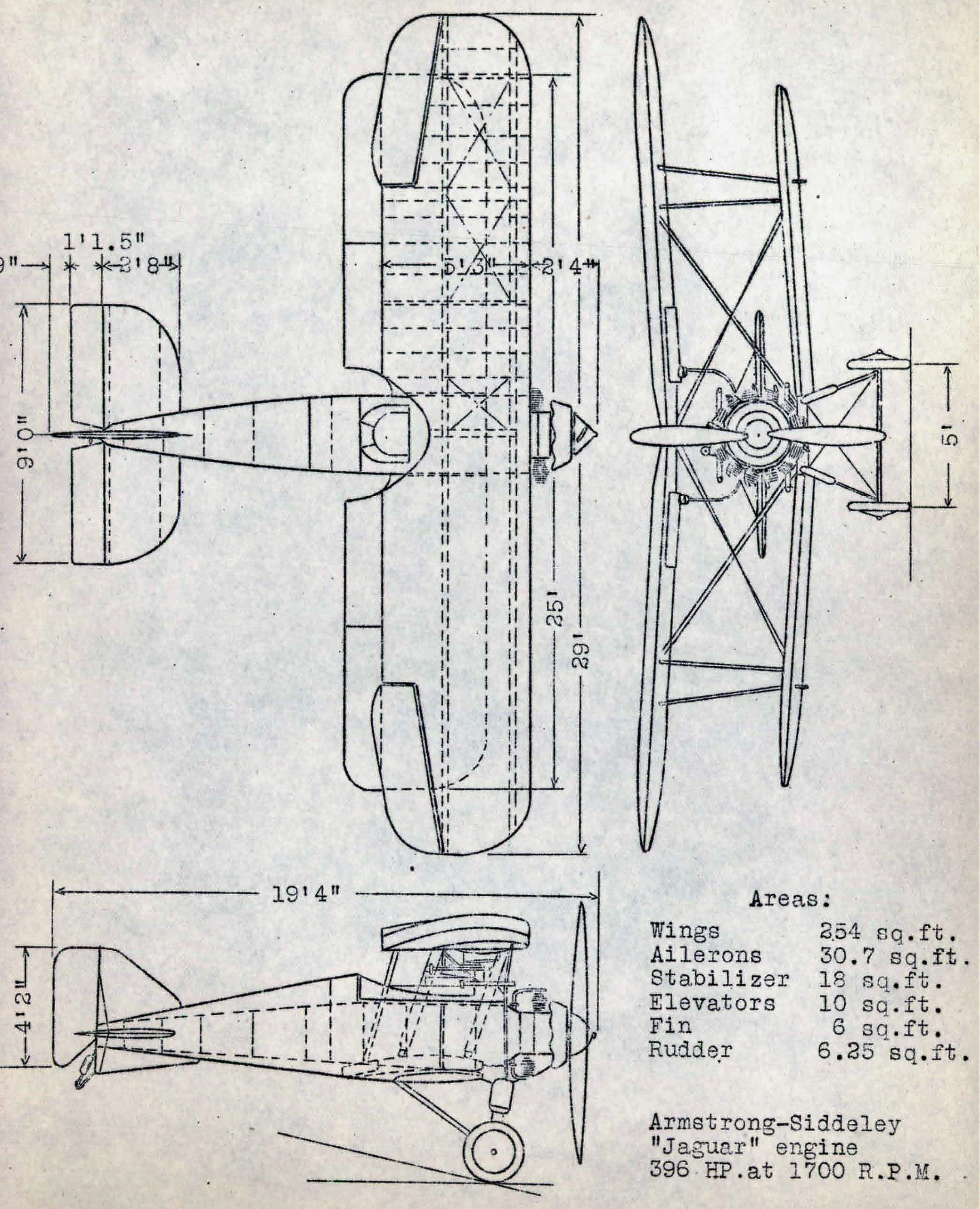
Gloster Grebe
The Gloster Grebe was developed by the Gloster Aircraft Company from the Gloster Grouse (an experimental aircraft later developed as a trainer), and was the Royal Air Force's first post-First World War fighter aircraft, entering service in 1923. Design In 1923, Gloster modified a Gloster Sparrowhawk fighter trainer with new wings to test a layout proposed by chief designer Henry Folland, combining a thick, high-lift section upper wing and a thinner, medium-lift lower wing, with the intention of combining high lift for takeoff with low drag. After the Grouse demonstrated that the new layout was a success, the British Air Ministry placed an order for three prototype fighters based on the Grouse (and therefore derived ultimately from Folland's Nieuport Nighthawk fighter of 1919), but powered by a Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar III radial engine, as the "Nighthawk (thick-winged)". The first of the prototypes (Gloster built a fourth machine as a company-owned demonstrator), by now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Havilland Humming Bird
The de Havilland DH.53 Humming Bird is a British single-seat, single-engine, low-wing monoplane light aircraft first flown in the 1920s. Design and development In response to the ''Daily Mail'' Light Aeroplane Competition of 1923, de Havilland built two DH.53s which were named ''Humming Bird'' and ''Sylvia II''. The DH.53 was a low-wing single-seat monoplane powered by a Douglas motorcycle engine. At Lympne, in October 1923, the DH.53s did not win any prizes but gave an impressive performance.Jackson 1987, p. 203. After the trial, ''Humming Bird'' was reengined with a Blackburne Tomtit two-cylinder engine, and fitted with a revised undercarriage. The Air Ministry became interested in the design and ordered eight Tomtit-powered aircraft in 1924 as communications and training aircraft for the Royal Air Force.Jackson 1987, p. 204. Early in 1924 twelve aircraft were built at Stag Lane Aerodrome and were named Humming Bird after the first prototype. Eight aircraft were for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R33 Class Airship
The R.33 class of British rigid airships were built for the Royal Naval Air Service during the First World War, but were not completed until after the end of hostilities, by which time the RNAS had become part of the Royal Air Force. The lead ship, R.33, served successfully for ten years and survived one of the most alarming and heroic incidents in airship history when she was torn from her mooring mast in a gale. She was called a "Pulham Pig" by the locals, as the blimps based there had been, and is immortalised in the village sign for Pulham St Mary. The only other airship in the class, R.34, became the first aircraft to make an east to west transatlantic flight in July 1919 and, with the return flight, made the first two-way crossing. It was decommissioned two years later, after being damaged during a storm. The crew nicknamed her "Tiny". Design and development Substantially larger than the preceding R31 class, the R.33 class was in the design stage in 1916 when the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMA 23
The 23 class were rigid airships produced in the United Kingdom during the First World War. Development of the 23 class began in August 1915 when Vickers was asked to improve the 9r design by increasing its gas capacity by adding a bay and increasing the capacity of the bow and stern gas cells. The 23-class was designed by H.B. Pratt and Barnes Wallis of Vickers. Vickers built the first and last of the four ships. The other two were built by William Beardmore and Company and Armstrong-Whitworth. While the 23 class airships were never used in combat, the four ships provided many hours of valuable training and experimental data for British airship crews and designers. Although a total of 17 of these ships were contemplated at one time, only four were ever built.Higham 1961, pp. 135 The 23 class was found to be significantly overweight, leading to its cancellation in favour of the more-refined R23X class. Design and development Following proposals in July 1915 to order more ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |