|
Compact Linear Fresnel Reflector
A compact linear Fresnel reflector (CLFR) – also referred to as a concentrating linear Fresnel reflector – is a specific type of linear Fresnel reflector (LFR) technology. They are named for their similarity to a Fresnel lens, in which many small, thin lens fragments are combined to simulate a much thicker simple lens. These mirrors are capable of concentrating the sun's energy to approximately 30 times its normal intensity. Linear Fresnel reflectors use long, thin segments of mirrors to focus sunlight onto a fixed absorber located at a common focal point of the reflectors. This concentrated energy is transferred through the absorber into some thermal fluid (this is typically oil capable of maintaining a liquid state at very high temperatures). The fluid then goes through a heat exchanger to power a steam generator. As opposed to traditional LFR's, the CLFR utilizes multiple absorbers within the vicinity of the mirrors. History The first linear Fresnel reflector solar pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
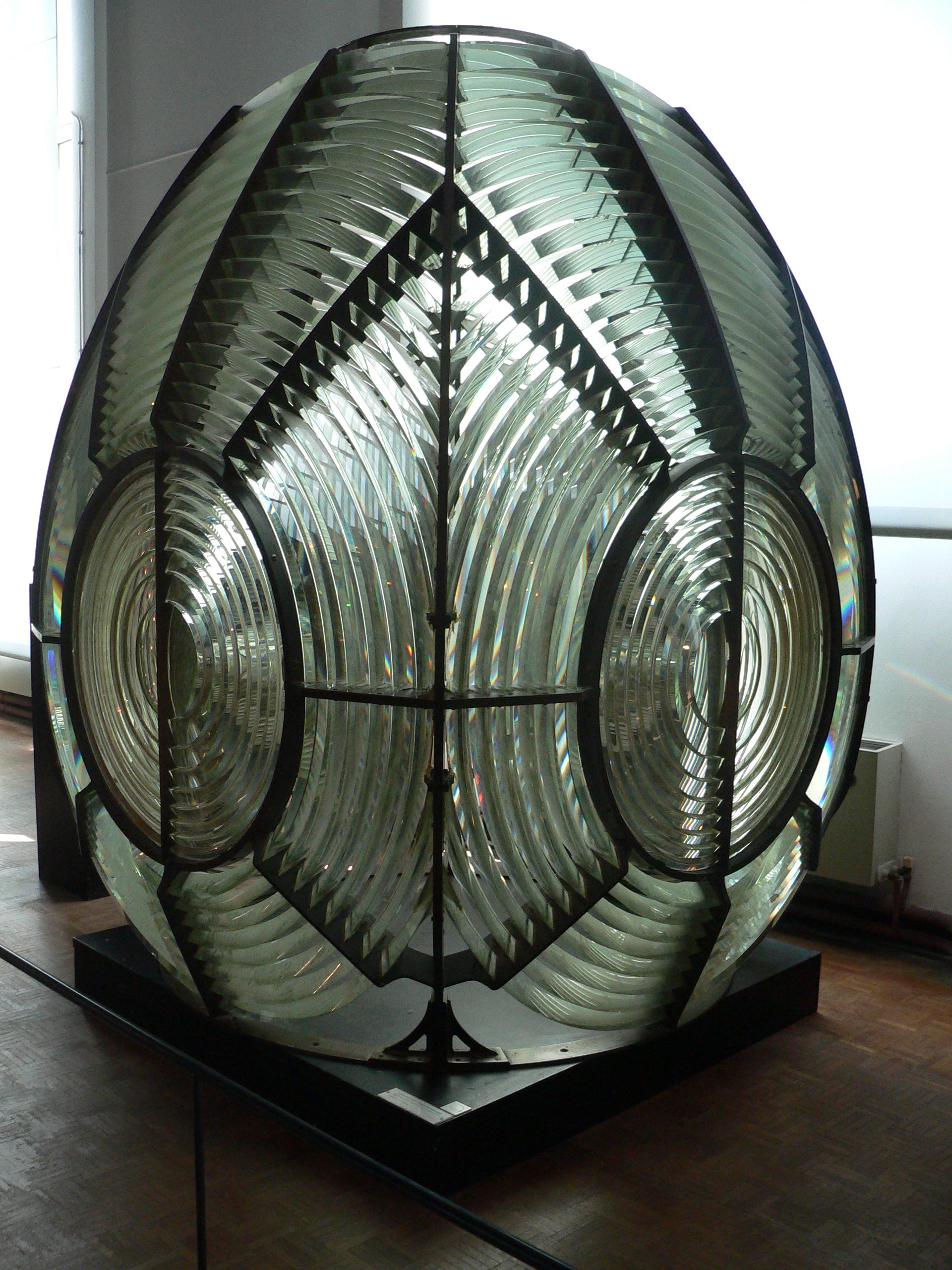 |
Fresnel Lens
A Fresnel lens ( ; ; or ) is a type of composite compact lens (optics), lens which reduces the amount of material required compared to a conventional lens by dividing the lens into a set of concentric annular sections. The simpler Dioptrics, dioptric (purely refraction, refractive) form of the lens was first proposed by Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon, and independently reinvented by the French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) for use in lighthouses. The Catadioptric system, catadioptric (combining refraction and reflection) form of the lens, entirely invented by Fresnel, has outer Prism (optics), prismatic elements that use total internal reflection as well as refraction to capture more oblique light from the light source and add it to the beam, making it visible at greater distances. The design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Enhanced Oil Recovery
Enhanced oil recovery (abbreviated EOR), also called tertiary recovery, is the extraction of crude oil from an oil field that cannot be extracted after primary and secondary recovery methods have been completely exhausted. Whereas primary and secondary recovery techniques rely on the pressure differential between the surface and the underground well, enhanced oil recovery functions by altering the physical or chemical properties of the oil itself in order to make it easier to extract. When EOR is used, 30% to 60% or more of a reservoir's oil can be extracted, compared to 20% to 40% using only Extraction of petroleum#Primary recovery, primary and Extraction of petroleum#Secondary recovery, secondary recovery. There are four main EOR techniques: carbon dioxide (CO2) injection, gas injection, thermal EOR, and chemical EOR. More advanced, speculative EOR techniques are sometimes called quaternary recovery. Carbon dioxide injection, known as CO2-EOR, is the most common method. In thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Electricity Generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For electric utility, utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its Electricity delivery, delivery (Electric power transmission, transmission, Electric power distribution, distribution, etc.) to end users or its Grid energy storage, storage, using for example, the Pumped-storage hydroelectricity, pumped-storage method. Consumable electricity is not freely available in nature, so it must be "produced", transforming other forms of energy to electricity. Production is carried out in power stations, also called "power plants". Electricity is most often generated at a power plant by electromechanical electric generator, generators, primarily driven by heat engines fueled by combustion or nuclear fission, but also by other means such as the kinetic energy of flowing water and wind. Other energy sources include solar photovoltaics and geothermal power. There are ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
BASF
BASF SE (), an initialism of its original name , is a European Multinational corporation, multinational company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters are located in Ludwigshafen, Germany. BASF comprises subsidiary, subsidiaries and joint ventures in more than 80 countries, operating six integrated production sites and 390 other production sites across Europe, Asia, Australia, the Americas and Africa. BASF has customers in over 190 countries and supplies products to a wide variety of industries. Despite its size and global presence, BASF has received relatively little public attention since it abandoned the manufacture and sale of BASF-branded consumer electronics products in the 1990s. The company began as a dye manufacturer in 1865. Fritz Haber worked with Carl Bosch, one of its employees, to invent the Haber-Bosch, Haber-Bosch process by 1912, after which the company grew rapidly. In 1925, the company merged with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Novatec Solar
Novatec Solar is a German provider of solar boilers using linear Fresnel collector technology based in Karlsruhe. Novatec Solar specialises in turnkey solutions, including the manufacture, supply, and assembly of solar fields. Timeline In March 2011, ABB acquired 35% of Novatec Solar. In April 2013, ABB sold its stake in Novatec Solar to existing shareholder Transfield Holdings. After the transaction, Transfield owned approximately 85% of Novatec Solar. In November 2014, Novatec announced to its bondholders that due to financial problems it was seeking a restructuring of its debt. Andreas Wittke (CEO) and Oliver Mundle (CFO) resigned their positions in the same month. Projects Novatec Solar has completed three projects with its linear Fresnel technology. Puerto Errado 1 Puerto Errado 1, located in southern Spain's Calasparra, was connected to the grid in 2009. With a capacity of 1.4 MW of electrical output, it was the first commercial Fresnel power plant in the world. It h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Kimberlina Solar Thermal Energy Plant
The 5 megawatt (MW) Kimberlina Solar Thermal Energy Plant in Bakersfield, California is the first commercial solar thermal power plant to be built by Areva Solar. Completed in 2008, the Kimberlina renewable energy solar boiler uses Compact Linear Fresnel Reflector (CLFR) technology to generate superheated steam. Each solar boiler has a group of 13 narrow, flat mirrors, that individually track and focus the sun's heat onto overhead pipes carrying water. The water boils directly into steam. The steam can then spin a turbine to generate electricity or be used as industrial steam for food, oil and desalination processes. The Kimberlina solar boiler currently achieves 750-degree F superheated steam. The next generation solar boiler under construction is designed to achieve 900-degree F superheated steam. AREVA Solar's boiler is the first and only solar boiler certified with an S-Stamp by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). The Kimberlina Solar Thermal Energy Plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Areva Solar
Areva Solar was part of the renewable energies portfolio of the French nuclear group Areva, headquartered in Mountain View, California, with offices in the United States and Australia. It designed, manufactured and installed solar steam generators for electric power production and industrial steam uses. Before 2010, the company existed as Ausra Inc. In August 2014, AREVA announced it was shuttering AREVA Solar. History Ausra was formed as Solar Heat and Power Pty Ltd in 2002 in Sydney, Australia. The company was co-founded by Dr. David Mills, Professor Graham Morrison and Peter Le Lievre. Solar Heat and Power Pty Ltd constructed a 1MW pilot solar plant at Liddell Power Station in 2005 and then began work on a 5MW extension to that project in 2006. The project was renamed the "John Marcheff Solar Project" by its owner, Macquarie Generation. Solar Heat and Power relocated to the United States in 2007 and was renamed as Ausra. The company began operation of its solar thermal power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
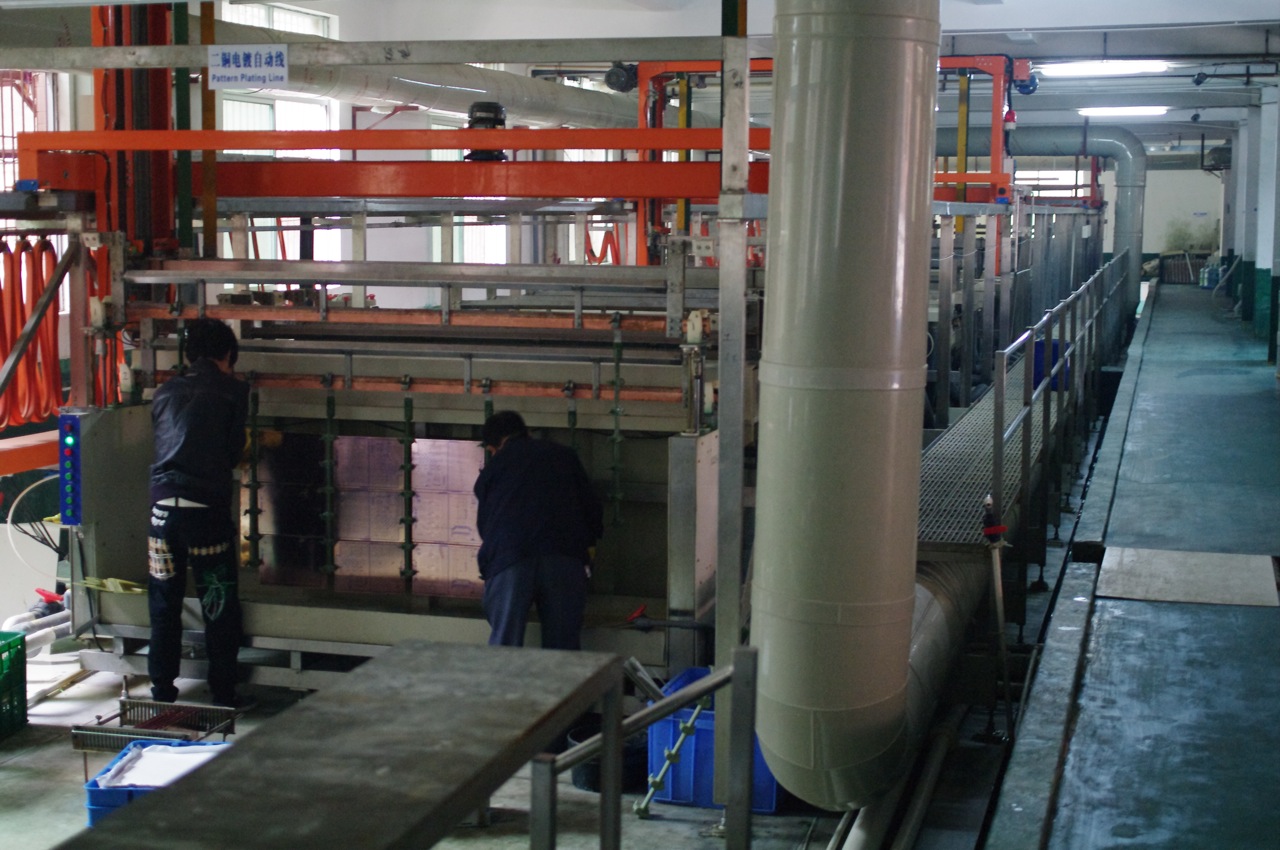 |
Electrochemical Deposition
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct electric current. The part to be coated acts as the cathode (negative electrode) of an electrolytic cell; the electrolyte is a solution of a salt whose cation is the metal to be coated, and the anode (positive electrode) is usually either a block of that metal, or of some inert conductive material. The current is provided by an external power supply. Electroplating is widely used in industry and decorative arts to improve the surface qualities of objects—such as resistance to abrasion (mechanical), abrasion and corrosion, lubricity, reflectivity, electrical conductivity, or appearance. It is used to build up thickness on undersized or worn-out parts and to manufacture metal plates with complex shape, a process called electroforming. It is used to deposit copper and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Selective Surface
In solar thermal collectors, a selective surface or selective absorber is a means of increasing its operation temperature and/or efficiency. The selectivity is defined as the ratio of solar radiation absorption (αsol) to thermal infrared radiation emission (εtherm). Selective surfaces take advantage of the differing wavelengths of incident solar radiation and the emissive radiation from the absorbing surface: * Solar radiation covers approximately the wavelengths 350 nm to 4000 nm; UV-A, visible and near infrared ( NIR, or IR-A plus IR-B). * Thermal infrared radiation, from materials with temperatures approximately in the interval -40 to 100 °C, covers approximately the wavelengths 4000 nm to 40,000 nm = 4 um to 40 um; The thermal infrared radiation interval being named or covered by: MIR, LWIR or IR-C. Materials Normally, a combination of materials is used. One of the first selective surfaces investigated was a semiconduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
CLFR Alternating Inclination
A compact linear Fresnel reflector (CLFR) – also referred to as a concentrating linear Fresnel reflector – is a specific type of linear Fresnel reflector (LFR) technology. They are named for their similarity to a Fresnel lens, in which many small, thin lens fragments are combined to simulate a much thicker simple lens. These mirrors are capable of concentrating the sun's energy to approximately 30 times its normal intensity. Linear Fresnel reflectors use long, thin segments of mirrors to focus sunlight onto a fixed absorber located at a common focal point of the reflectors. This concentrated energy is transferred through the absorber into some thermal fluid (this is typically oil capable of maintaining a liquid state at very high temperatures). The fluid then goes through a heat exchanger to power a steam generator. As opposed to traditional LFR's, the CLFR utilizes multiple absorbers within the vicinity of the mirrors. History The first linear Fresnel reflector solar pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Compact Linear Fresnel Reflector Absorber
Compact as used in politics may refer broadly to a pact or treaty; in more specific cases it may refer to: * Interstate compact, a type of agreement used by U.S. states * Blood compact, an ancient ritual of the Philippines * Compact government, a type of colonial rule utilized in British North America * Compact of Free Association whereby the sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia, the Republic of the Marshall Islands and the Republic of Palau have entered into as associated states with the United States. * Mayflower Compact, the first governing document of Plymouth Colony * United Nations Global Compact * Global Compact for Migration, a UN non-binding intergovernmental agreement Mathematics * Compact element, those elements of a partially ordered set that cannot be subsumed by a supremum of any directed set that does not already contain them * Compact operator, a linear operator that takes bounded subsets to relatively compact subsets, in functional analysis * Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |