|
Comma (rhetoric)
In Ancient Greek rhetoric, a comma (κόμμα ''komma'', plural κόμματα ''kommata'') is a short clause, something less than a colon. The plural of ‘’’comma’’’ in English is ‘’�commata��’’. In the system of Aristophanes of Byzantium, commata were separated by middle interpunct An interpunct , also known as an interpoint, middle dot, middot, centered dot or centred dot, is a punctuation mark consisting of a vertically centered dot used for interword separation in Classical Latin. ( Word-separating spaces did not appe ...s. In antiquity, a comma was defined as a combination of words that has no more than eight syllables. There is a short text which arguably could have been inserted in the first epistle of John called the Johannine Comma. References * http://rhetoric.byu.edu/Figures/C/comma.htm Part of glossary of classical rhetorical terms Bibliography * Bruce M. Metzger, Bart D. Ehrman, ''The Text of the New Testament. Its Transmission, Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
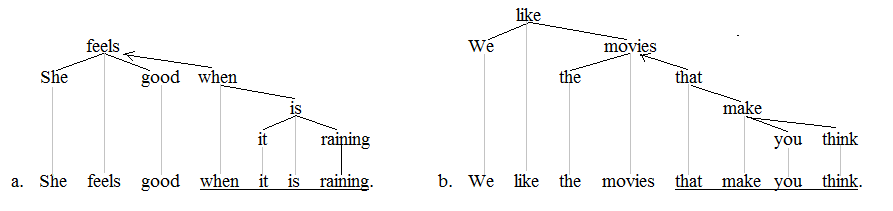
Clause
In language, a clause is a Constituent (linguistics), constituent or Phrase (grammar), phrase that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic Predicate (grammar), predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject (grammar), subject and a syntactic Predicate (grammar), predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with or without any object (grammar), objects and other Grammatical modifier, modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unexpressed if it is easily deducible from the context, especially in null-subject languages but also in other languages, including instances of the imperative mood in English grammar, English. A complete simple sentence contains a single clause with a finite verb. Complex sentences contain at least one clause subordinated (dependent clause, ''dependent'') to an ''independent clause'' (one that could stand alone as a simple sentence), which may be co-ordinated with other independents with or without dependents. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colon (rhetoric)
A colon (from Greek: , ''pl.'' , ''cola''.) can be defined as a single unit of poetry. In textual criticism, a colon is a line consisting of a single clause. The term is most often used in the study of Hebrew poetry to refer to the fundamental unit of Hebrew poetry. A colon usually does not occur alone, but instead with one or two others to form a bicolon or a tricolon. Older terminology for the same concepts (cola = stich or hemistich, bicolon = distich, tricolon = tristich) are no longer used as often, but some newer synonyms have also appeared (colon = line or verset, bicolon = dyadic line, tricolon = triadic line). In writing, these cola are often separated by colons. An isocolon is a sentence composed of cola of equal syllabic length. When Jerome translated the books of the Prophets, he arranged the text colometrically. The colometric system was used in bilingual codices of New Testament, such as Codex Bezae and Codex Claromontanus. Some Greek and Latin manuscripts also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristophanes Of Byzantium
__NOTOC__ Aristophanes of Byzantium ( ; Byzantium – Alexandria BC) was a Hellenistic Greek scholar, critic and grammarian, particularly renowned for his work in Homeric scholarship, but also for work on other classical authors such as Pindar and Hesiod. He soon moved to Alexandria and studied under Zenodotus, Callimachus, and Dionysius Iambus. He succeeded Eratosthenes as head librarian of the Library of Alexandria at the age of sixty. His students included Callistratus, Aristarchus of Samothrace, and perhaps Agallis. He was succeeded by Apollonius "The Classifier" (not to be confused with Apollonius of Rhodes, a previous head librarian of Alexandria). Aristophanes' pupil, Aristarchus of Samothrace, would be the sixth head librarian at the Library of Alexandria. Work Aristophanes was the first to deny that the " Precepts of Chiron" was the work of Hesiod. Inventions Accent system Aristophanes is credited with reducing the accents used in Greek to desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpunct
An interpunct , also known as an interpoint, middle dot, middot, centered dot or centred dot, is a punctuation mark consisting of a vertically centered dot used for interword separation in Classical Latin. ( Word-separating spaces did not appear until some time between 600 and 800 CE.) It appears in a variety of uses in some modern languages. The multiplication dot or "dot operator" is frequently used in mathematical and scientific notation, and it may differ in appearance from the interpunct. In written language Various dictionaries use the interpunct (in this context, sometimes called a hyphenation point) to indicate where to split a word and insert a hyphen if the word doesn't fit on the line. There is also a separate Unicode character, . English In British typography, the space dot was once used as the formal decimal point. Its use was advocated by laws and can still be found in some UK-based academic journals such as ''The Lancet''. When the pound sterling was de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannine Comma
The Johannine Comma () is an interpolated phrase (comma) in verses of the First Epistle of John. The text (with the comma in italics and enclosed by brackets) in the King James Version of the Bible reads: In the Greek Textus Receptus (TR), the verse reads thus:ὅτι τρεῖς εἰσιν οἱ μαρτυροῦντες εν τῷ οὐρανῷ, ὁ πατήρ, ὁ λόγος, καὶ τὸ Ἅγιον Πνεῦμα· καὶ οὗτοι οἱ τρεῖς ἕν εἰσι.It became a touchpoint for the Christian theological debate over the doctrine of the Trinity from the early church councils to the Catholic and Protestant disputes in the early modern period. It may first be noted that the words "in heaven, the Father, the Word, and the Holy Ghost: and these three are one" (KJV) found in older translations at 1 John 5:7 are thought by some to be spurious additions to the original text. A footnote in the Jerusalem Bible, a Catholic translation, says that these word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |