|
Clinodactyly
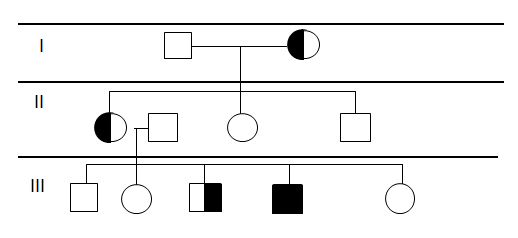
Clinodactyly is a medical term describing the curvature of a digit (a finger or toe) in the plane of the palm, most commonly the fifth finger (the "little finger") towards the adjacent fourth finger (the "ring finger"). It is a fairly common isolated anomaly which often goes unnoticed, but also occurs in combination with other abnormalities in certain genetic syndromes. The term comes . Genetics Clinodactyly is an autosomal dominant trait that has variable expressiveness and incomplete penetrance. Clinodactyly can be passed through inheritance and presents as either an isolated anomaly or a component manifestation of a genetic syndrome. Many syndromes are associated with clinodactyly, including those listed below. But the phenotype, by itself, is not a sensitive or specific diagnostic test for these syndromes (it is present in up to 18% of the normal population). * Down syndrome * Turner syndrome Turner syndrome (TS), commonly known as 45,X, or 45,X0,Also written as 45, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camptodactyly
Camptodactyly is a medical condition that causes one or more Digit (anatomy), digits (fingers or toes) to be permanently bent. It involves fixed Human anatomical terms#Types of movement, flexion deformity of the proximal interphalangeal articulations of hand, interphalangeal joints. Camptodactyly can be caused by a genetic disorder. In that case, it is an autosomal dominant trait that is known for its incomplete genetic expressivity (genetics), expressivity. This means that when a person has the genes for it, the condition may appear in both hands, one, or neither. A linkage scan proposed that the chromosomal locus of camptodactyly was 3q11.2-q13.12. Causes The specific cause of camptodactyly remains unknown, but there are a few deficiencies that lead to the condition. A deficient Lumbricals of the hand, lumbrical muscle controlling the flexion of the fingers, and abnormalities of the flexor and extensor tendons. A number of congenital syndromes may also cause camptodactyly: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OSLAM Syndrome
OSLAM syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant hereditary disorder. Its name is an initialism of " osteosarcoma, limb anomalies, and erythroid macrocytosis with megaloblastic marrow syndrome". OSLAM syndrome was recognised and described by Mulvilhill ' as a syndrome that increases susceptibility to tumours and is characterised by an impaired regulation of bone and marrow development.Weber G.F. (2007.) ''Molecular Mechanisms of Cancer'', Springer, pg. 558. Individuals with OSLAM syndrome have an elevated risk of bone cancer, limb abnormalities, and enlarged red blood cells. Signs and symptoms Clinical presentation is consistent with: * Bone cancer * Curved fifth fingers (clinodactyly) with brachymesophalangy (shortened phalanges of the toes and/or fingers (digits)) * Absence of one digital ray of the foot (a digit and corresponding metacarpal or metatarsal bone) * Bilateral radioulnar synostosis Radioulnar synostosis is a rare condition where there is an abnormal connection ( synos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver–Russell Syndrome
Silver–Russell syndrome, also called Silver–Russell dwarfism, is a rare congenital growth disorder. In the United States it is usually referred to as Russell–Silver syndrome, and Silver–Russell syndrome elsewhere. It is one of 200 types of dwarfism and one of five types of primordial dwarfism. Silver–Russell syndrome occurs in approximately one out of every 50,000 to 100,000 births. Males and females seem to be affected with equal frequency. Signs and symptoms Although confirmation of a specific genetic marker is in a significant number of individuals, there are no tests to clearly determine if this is what a person has. As a syndrome, a diagnosis is typically given for children upon confirmation of the presence of several symptoms listed below. Symptoms are intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) combined with some of the following: * Often small for gestational age (SGA) at birth (birth weight less than 2.8 kg) * Feeding problems: the baby is uninterested in feed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XXYY Syndrome
XXYY syndrome is a sex chromosome anomaly in which males have two extra chromosomes, one X and one Y chromosome. Human cells usually contain two sex chromosomes, one from the mother and one from the father. Usually, females have two X chromosomes (XX) and males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). The appearance of at least one Y chromosome with a properly functioning SRY gene makes a male. Therefore, humans with XXYY are genotypically male. Males with XXYY syndrome have 48 chromosomes instead of the typical 46. This is why XXYY syndrome is sometimes written as 48, XXYY syndrome or 48, XXYY. It affects an estimated one in every 18,000–40,000 male births. Signs and symptoms Very frequent signs and symptoms of this condition include the following: Cause 48,XXYY syndrome is a condition related to the X and Y chromosomes (the sex chromosomes). People normally have 46 chromosomes in each cell. Two of the 46 chromosomes, known as X and Y, are called sex chromosomes because they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Genetics
Medical genetics is the branch of medicine that involves the diagnosis and management of hereditary disorders. Medical genetics differs from human genetics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics. In contrast, the study of typically non-medical phenotypes such as the genetics of eye color would be considered part of human genetics, but not necessarily relevant to medical genetics (except in situations such as albinism). ''Genetic medicine'' is a newer term for medical genetics and incorporates areas such as gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the rapidly emerging new medical specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orofaciodigital Syndrome 1
Orofaciodigital syndrome 1 (OFD1), also called Papillon-Léage and Psaume syndrome, is an X-linked congenital disorder characterized by malformations of the face, oral cavity, and digits with polycystic kidney disease and variable involvement of the central nervous system. Presentation Cause Orofaciodigital syndrome type 1 is caused by mutations in the OFD1 gene. OFD1 localizes to both centrosomes and basal bodies within the human genetic cellular structure. This suggests that this syndrome may fall into a broad category of ciliary diseases. The ciliary organelles are present in many cellular types throughout the human body. Cilia defects adversely affect numerous critical developmental signaling pathways essential to cellular development. Other types include: * * * * Relation to other rare genetic disorders Recent findings in genetic research have suggested that a large number of genetic disorders, both genetic syndromes and genetic diseases, that were not pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetric Ultrasonography
Obstetric ultrasonography, or prenatal ultrasound, is the use of medical ultrasonography in pregnancy, in which sound waves are used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the uterus (womb). The procedure is a standard part of Pregnancy, prenatal care in many countries, as it can provide a variety of information about the health of the mother, the timing and progress of the pregnancy, and the health and development of the embryo or fetus. The International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology (ISUOG) recommends that pregnant women have routine Obstetrics, obstetric ultrasounds between 18 weeks' and 22 weeks' Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age (the anatomy scan) in order to confirm pregnancy dating, to measure the fetus so that growth abnormalities can be recognized quickly later in pregnancy, and to assess for congenital malformations and Multiple birth, multiple pregnancies (twins, etc). Additionally, the ISUOG recommends th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Complications may include aortic dissection, joint dislocations, scoliosis, chronic pain, or early osteoarthritis. The existing classification was last updated in 2017, when a number of rarer forms of EDS were added. EDS occurs due to mutations in one or more particular genes—there are 19 genes that can contribute to the condition. The specific gene affected determines the type of EDS, though the genetic causes of hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome are still unknown. Some cases result from a new variation occurring during early development, while others are inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner. Typically, these variations result in defects in the structure or processing of the protein collagen or tenascin. Diagnos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noonan Syndrome
Noonan syndrome (NS) is a genetic disorder that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored eyes, low-set ears, a short neck, and a small lower jaw. Heart problems may include pulmonary valve stenosis. The breast bone may either protrude or be sunken, while the spine may be abnormally curved. Intelligence is often normal. Complications of NS can include leukemia. Some of NS' symptoms are shared with Watson syndrome, a related genetic condition. A number of genetic mutations can result in Noonan syndrome. The condition may be inherited as an autosomal dominant condition or occur as a new mutation. Noonan syndrome is a type of RASopathy, the underlying mechanism for which involves sustained activation of the RAS/MAPK cell signaling pathway. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, medical imaging, and blood test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13q Deletion Syndrome
13q deletion syndrome is a rare genetic disease caused by the deletion of some or all of the large arm of human chromosome 13. Depending upon the size and location of the deletion on chromosome 13, the physical and mental manifestations will vary. It has the potential to cause intellectual disability and congenital malformations that affect a variety of organ systems. Because of the rarity of the disease in addition to the variations in the disease, the specific genes that cause this disease are unknown. This disease is also known as: * 13q- Syndrome, Partial, * Deletion 13q Syndrome, Partial * Monosomy 13q, Partial * Partial Monosomy of the Long Arm of Chromosome 13 Signs and symptoms Variations of the signs and symptoms occur depending upon the area of chromosome 13 that is deleted. Deletions from the centromere to 13q32 or any deletions including the 13q32 band are associated with slow growth, intellectual disability, and congenital malformations. Deletions from 13q33 to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |