Camptodactyly on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Camptodactyly is a medical condition that causes one or more Digit (anatomy), digits (fingers or toes) to be permanently bent. It involves fixed Human anatomical terms#Types of movement, flexion deformity of the proximal interphalangeal articulations of hand, interphalangeal joints.
Camptodactyly can be caused by a genetic disorder. In that case, it is an autosomal dominant trait that is known for its incomplete genetic expressivity (genetics), expressivity. This means that when a person has the genes for it, the condition may appear in both hands, one, or neither. A linkage scan proposed that the chromosomal locus of camptodactyly was 3q11.2-q13.12.
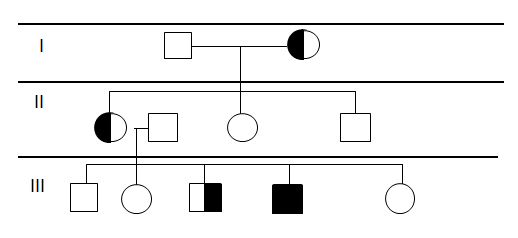 The pattern of inheritance is determined by the phenotypic expression of a gene—which is called ''expressivity (genetics), expressivity''. Camptodactyly can be passed on through generations in various levels of phenotypic expression, which include both or only one hand. This means that the genetic expressivity is incomplete. It can be inherited from either parent.
In most of its cases, camptodactyly occurs sporadically, but it has been found in several studies that it is inherited as an autosomal dominant condition.
The pattern of inheritance is determined by the phenotypic expression of a gene—which is called ''expressivity (genetics), expressivity''. Camptodactyly can be passed on through generations in various levels of phenotypic expression, which include both or only one hand. This means that the genetic expressivity is incomplete. It can be inherited from either parent.
In most of its cases, camptodactyly occurs sporadically, but it has been found in several studies that it is inherited as an autosomal dominant condition.
 If a contracture is less than 30 degrees, it may not interfere with normal functioning. The common treatment is splinting and occupational therapy. Surgery is the last option for most cases as the result may not be satisfactory.
If a contracture is less than 30 degrees, it may not interfere with normal functioning. The common treatment is splinting and occupational therapy. Surgery is the last option for most cases as the result may not be satisfactory.
Causes
The specific cause of camptodactyly remains unknown, but there are a few deficiencies that lead to the condition. A deficient Lumbricals of the hand, lumbrical muscle controlling the flexion of the fingers, and abnormalities of the flexor and extensor tendons. A number of congenital syndromes may also cause camptodactyly: * Jacobsen syndrome * Beals syndrome * Blau syndrome * Freeman–Sheldon syndrome * Cerebrohepatorenal syndrome * Weaver syndrome * Christianson syndrome * Gordon syndrome * Jaccoud arthropathy * Lenz microphthalmia syndrome * Marshall–Smith–Weaver syndrome * Oculo-dento-digital syndrome * Tel Hashomer camptodactyly syndrome * Toriello–Carey syndrome * Trisomy 13 * Stuve–Wiedemann syndrome * Loeys–Dietz syndrome * Fetal alcohol syndrome * Fryns syndrome * Marfan syndrome * Carnio-carpo-tarsal dystrophyGenetics
 The pattern of inheritance is determined by the phenotypic expression of a gene—which is called ''expressivity (genetics), expressivity''. Camptodactyly can be passed on through generations in various levels of phenotypic expression, which include both or only one hand. This means that the genetic expressivity is incomplete. It can be inherited from either parent.
In most of its cases, camptodactyly occurs sporadically, but it has been found in several studies that it is inherited as an autosomal dominant condition.
The pattern of inheritance is determined by the phenotypic expression of a gene—which is called ''expressivity (genetics), expressivity''. Camptodactyly can be passed on through generations in various levels of phenotypic expression, which include both or only one hand. This means that the genetic expressivity is incomplete. It can be inherited from either parent.
In most of its cases, camptodactyly occurs sporadically, but it has been found in several studies that it is inherited as an autosomal dominant condition.
Treatment
 If a contracture is less than 30 degrees, it may not interfere with normal functioning. The common treatment is splinting and occupational therapy. Surgery is the last option for most cases as the result may not be satisfactory.
If a contracture is less than 30 degrees, it may not interfere with normal functioning. The common treatment is splinting and occupational therapy. Surgery is the last option for most cases as the result may not be satisfactory.
Etymology
The name is derived from the ancient Greek words καμπτός, ''kamptos'' (''bent'') and δάκτυλος, ''daktylos'' (''finger'').See also
* ClinodactylyReferences
External links
* * {{Medical resources , DiseasesDB = 30760 , ICD10 = {{ICD10, Q, 68, 1, q, 68 , ICD9 = {{ICD9, 755.59 , ICDO = , OMIM = 114200 , MedlinePlus = , eMedicineSubj = , eMedicineTopic = , MeshID = Congenital disorders Fingers