|
Clear Lens Extraction
Clear lens extraction, also known as refractive lensectomy, custom lens replacement or refractive lens exchange is a surgical procedure in which clear lens of the human eye is removed. Unlike cataract surgery, where the cloudy lens is removed to treat a cataract, clear lens extraction is done to surgically correct refractive errors such as high myopia. It can also be done in hyperopic or presbyopic patients who wish to have a multifocal IOL implanted to avoid wearing glasses. It is also used as a treatment for diseases such as angle closure glaucoma. Overview As opposed to procedures that use lasers to make corrections to the corneal surface, such as LASIK, the clear lens extraction procedure uses the same procedures as cataract surgery. Indications Clear lens extraction can be done in patients with severe refractive error and/or presbyopia who wish to avoid spectacles. It is often necessary in patients with severe refractive error who cannot undergo other refractive proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Surgery
Refractive surgery is an optional eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This can include various methods of surgical remodeling of the cornea ( keratomileusis), lens implantation or lens replacement. The most common methods today use excimer lasers to reshape the curvature of the cornea. Refractive eye surgeries are used to treat common vision disorders such as myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia and astigmatism. History The first theoretical work on the potential of refractive surgery was published in 1885 by Hjalmar August Schiøtz, an ophthalmologist from Norway. In 1930, the Japanese ophthalmologist Tsutomu Sato made the first attempts at performing this kind of surgery, hoping to correct the vision of military pilots. His approach was to make radial cuts in the cornea, correcting effects by up to 6 diopters. The procedure unfortunately produced a high rate of corneal degeneration, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. In the United States, following graduation from medical school, one must complete a four-year residency in ophthalmology to become an ophthalmologist. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat ailments, such as eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care—medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
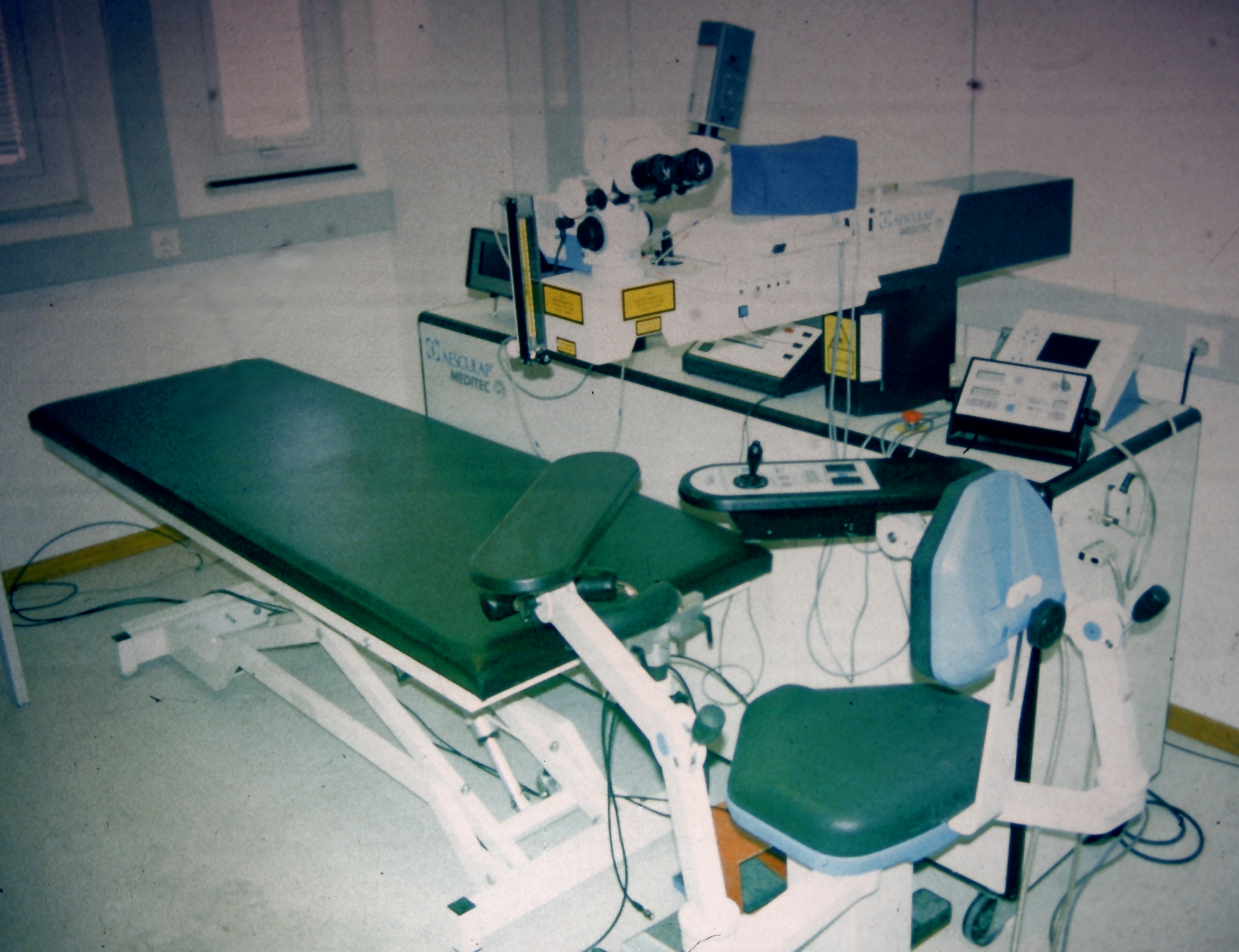
Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance (cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissue (biology), tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, operating theater, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vincenz Fukala
Vincenz Fukala (January 2, 1847 – October 27, 1911) was a Polish ophthalmologist and ophthalmology historian better known for early works on Clear lens extraction, the surgical removal of natural lens of the eye, as a treatment of high myopia. He also developed successful techniques for the treatment of ectropion. Biography Vincenz Fukala aka Wincenty Fukała was born into a Polish family in present-day Zhovkva in Ukraine on January 2, 1847. Fukala died on October 27, 1911, at Vienna. Career Studying medicine in University of Vienna, Fukala specialized in ophthalmology under Austrian ophthalmologist Carl Ferdinand von Arlt. After working as an ophthalmologist in Plzeň and Karlovy Vary in Bohemia for five years from 1889, he returned to Vienna in 1895. Fukala traveled to Egypt in 1872 to study trachoma, and to the United States in 1891 and 1892 to study scrofulous eye disease. Contributions Fukala is better known for early works on Clear lens extraction, the surgical removal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment is a condition where the retina pulls away from the tissue underneath it. It may start in a small area, but without quick treatment, it can spread across the entire retina, leading to serious vision loss and possibly blindness. Retinal detachment is a medical emergency that requires surgery. The retina is a thin layer at the back of the eye that processes visual information and sends it to the brain. When the retina detaches, common symptoms include seeing floaters, flashing lights, a dark shadow in vision, and sudden blurry vision. The most common type of retinal detachment is rhegmatogenous, which occurs when a tear or hole in the retina lets fluid from the center of the eye get behind it, causing the retina to pull away. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is most commonly caused by posterior vitreous detachment, a condition where the gel inside the eye breaks down and pulls on the retina. Risk factors include older age, nearsightedness ( myopia), eye injury, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitreous Detachment
A posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) is a condition of the eye in which the vitreous membrane separates from the retina. It refers to the separation of the posterior hyaloid membrane from the retina anywhere posterior to the vitreous base (a 3–4 mm wide attachment to the ora serrata). The condition is common for older adults; over 75% of those over the age of 65 develop it. Although less common among people in their 40s or 50s, the condition is not rare for those individuals. Some research has found that the condition is more common among women. Symptoms When this occurs there is a characteristic pattern of symptoms: * Flashes of light (photopsia) * A sudden dramatic increase in the number of floaters * A ring of floaters or hairs just to the temporal side of the central vision As a posterior vitreous detachment proceeds, adherent vitreous membrane may pull on the retina. While there are no pain fibers in the retina, vitreous traction may stimulate the retina, with r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphakia
Aphakia is the absence of the lens of the eye, due to surgical removal, such as in cataract surgery, a perforating wound or ulcer, or congenital anomaly. It causes a loss of ability to maintain focus ( accommodation), high degree of farsightedness ( hyperopia), and a deep anterior chamber. Complications include detachment of the vitreous or retina, and glaucoma. Babies are rarely born with aphakia. Occurrence most often results from surgery to remove a congenital cataract. Congenital cataracts usually develop as a result of infection of the fetus or genetic reasons. It is often difficult to identify the exact cause of these cataracts, especially if only one eye is affected. People with aphakia have relatively small pupils and their pupils dilate to a lesser degree. Causes Surgical removal of a lens, mainly in cataract surgery, is the most common cause of aphakia. Spontaneous traumatic absorption or congenital absence of lens matter is rare. Traumatic subluxation or disloca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroma Of Cornea
The stroma of the cornea (or substantia propria) is a fibrous, tough, unyielding, perfectly transparent and the thickest layer of the cornea of the eye. It is between Bowman's layer anteriorly, and Descemet's membrane posteriorly. At its centre, a human corneal stroma is composed of about 200 flattened ''lamellae'' (layers of collagen fibrils), superimposed one on another. They are each about 1.5-2.5 μm in thickness. The anterior lamellae interweave more than posterior lamellae. The fibrils of each lamella are parallel with one another, but at different angles to those of adjacent lamellae. The lamellae are produced by keratocytes (corneal connective tissue cells), which occupy about 10% of the substantia propria. Apart from the cells, the major non-aqueous constituents of the stroma are collagen fibrils and proteoglycans. The collagen fibrils are made of a mixture of type I and type V collagens. These molecules are tilted by about 15 degrees to the fibril axis, and because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Chamber Of Eyeball
The anterior chamber (Optometric Abbreviations#AC, AC) is the aqueous humor-filled space inside the eye between the iris (anatomy), iris and the cornea's innermost surface, the Corneal endothelium, endothelium. Hyphema, Uveitis, anterior uveitis and glaucoma are three main pathologies in this area. In hyphema, blood fills the anterior chamber as a result of a hemorrhage, most commonly after a blunt eye injury. Anterior uveitis is an inflammatory process affecting the iris (anatomy), iris and ciliary body, with resulting inflammatory signs in the anterior chamber. In glaucoma, blockage of the trabecular meshwork prevents the normal outflow of aqueous humour, resulting in increased intraocular pressure, progressive damage to the optic nerve head, and eventually blindness. The depth of the anterior chamber of the eye varies between 1.5 and 4.0 mm, averaging 3.0 mm. It tends to become shallower at older age and in eyes with Far-sightedness, hypermetropia (far sightedness) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phacoemulsification
Phacoemulsification is a cataract surgery method in which the internal lens of the eye which has developed a cataract is emulsified with the tip of an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from the eye. Aspirated fluids are replaced with irrigation of balanced salt solution to maintain the volume of the anterior chamber during the procedure. This procedure minimises the incision size and reduces the recovery time and risk of surgery-induced astigmatism. It is best suited to relatively soft cataracts, where the ultrasonic energy required is moderate, and insertion of foldable intraocular prosthetic lenses, which take advantage of the small incision possible. It is the most common procedure for cataract removal in the developed world, with an excellent prognosis in uncomplicated cases. Etymology The term originated from phaco- (Greek ''phako-'', comb. form of ''phakós'', lentil; see lens) + emulsification. Contraindications The same general contraindications for cataract surgery a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens Nucleus
The lens, or crystalline lens, is a transparent biconvex structure in most land vertebrate eyes. Relatively long, thin fiber cells make up the majority of the lens. These cells vary in architecture and are arranged in concentric layers. New layers of cells are recruited from a thin epithelium at the front of the lens, just below the basement membrane surrounding the lens. As a result the vertebrate lens grows throughout life. The surrounding lens membrane referred to as the lens capsule also grows in a systematic way, ensuring the lens maintains an optically suitable shape in concert with the underlying fiber cells. Thousands of suspensory ligaments are embedded into the capsule at its largest diameter which suspend the lens within the eye. Most of these lens structures are derived from the epithelium of the embryo before birth. Along with the cornea, aqueous, and vitreous humours, the lens refracts light, focusing it onto the retina. In many land animals the shape of the lens c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea Refraction, refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres. The cornea can be reshaped by surgical procedures such as LASIK. While the cornea contributes most of the eye's focusing power, its Focus (optics), focus is fixed. Accommodation (eye), Accommodation (the refocusing of light to better view near objects) is accomplished by changing the geometry of the lens. Medical terms related to the cornea often start with the prefix "''wikt:kerat-, kerat-''" from the Ancient Greek, Greek word κέρας, ''horn''. Structure The cornea has myelinated, unmyelinated nerve endings sensitive to touch, temperature and chemicals; a to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |